1987 Eastern Province massacres
The 1987 Eastern Province massacres were a series of massacres of the Sinhalese population in the Eastern Province of Sri Lanka during the Sri Lankan Civil War. Though they began spontaneously, they became more organized, with the LTTE leading the violence. Over 200 Sinhalese were killed by mob and militant violence, and over 20,000 fled the Eastern Province.[1]
| 1987 Eastern Province massacres | |
|---|---|
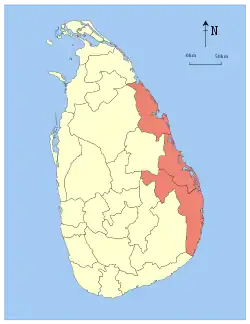 | |
| Location | Eastern Province, Sri Lanka, Sri Lanka |
| Coordinates | 8°35′N 81°13′E |
| Date | 29 September 1987– 8 October 1987 |
| Target | Primarily Sinhalese civilians |
| Deaths | 200+ |
| Perpetrators | Tamil mobs, Liberation Tigers of Tamil Eelam, Indian Peacekeeping Force, other Tamil nationalist militant groups |
Background
The Eastern province was a highly contested zone between the Sinhalese and Tamils. Since the 1930s, the majority Sinhalese government settled Sinhalese in the Eastern province, with the explicit intention to restore what they saw as lost ancient Sinhala settlements,[2] as well as to reduce the Tamils' claim to local autonomy.[3] Tamil nationalists viewed this as an attempt to alter the demographics of their 'traditional Tamil homeland', thus weakening the Tamils' stake in it.[2]
During the 1983 riots, Trincomalee was the site of anti-Tamil violence at the hands of Sinhalese sailors. In 1985, every Tamil village in Trincomalee District was systematically destroyed by the Sri Lankan Army with the help of Sinhalese settlers in an unprovoked, well-orchestrated campaign to drive out the local Tamil population.[4][5] During this campaign, hundreds of Tamil civilians were killed and several women were raped.[5] In September 1985, the entire Tamil population of Trincomalee town was displaced to forests and refugee camps in an attack that wiped out the town, including the destruction of 12 temples and a mosque.[6]
The year 1987 saw notorious violent incidents against Sinhalese civilians by the LTTE in or near the Eastern Province. On April 17, an LTTE unit had waylaid a bus carrying southbound Sinhalese from Trincomalee at Aluth Oya and massacred them. The week after, the village of Jayantipura near Kantale was attacked and over 15 Sinhalese were killed.[7] On June 2, an LTTE unit massacred novice Buddhist monks and other Sinhalese civilians in Aranthalawa.[8]
In late September 1987, Thileepan began a hunger strike. On the 21st of September, a scuffle broke out between a Tamil group of 'satyagrahis' who gathered in support of Thileepan and a Sinhalese group at the Anuradhapura Junction in Trincomalee. Ethnic violence had begun where the Sinhalese and Tamils were both perpetrators and victims. On September 24, Sinhalese from Mihindupura had left in bullock carts; the next morning, the carts returned without them and 9 charred bodies were found with a burnt cart. The LTTE was suspected to have perpetrated the killings.[9] Thileepan eventually died from his hunger strike, inviting grief from the Tamil community. Around the same time, the IPKF had nominated members for the Interim Council of the North and East, a majority of them being LTTE representatives.
Incident
Trincomalee riots
After the Interim Council was announced to be mostly LTTE nominees, anti-Sinhalese violence flared in Trincomalee, an ethnically heterogeneous city, on September 29. On September 30, 2 Tamils were found hacked to death; in retaliation, a Tamil group killed 3 Sinhalese men in a truck.[9] The violence became more organized on October 1, with LTTE members leading rioters and warning Sinhalese to evacuate their homes lest they be killed. In Trincomalee and throughout the Eastern Province, properties were set on fire, and over 2,000 people, mostly Sinhalese, were rendered homeless.[1][9] In Trincomalee, Tamil rioters, with the help of militant leaders, brutally killed Sinhalese men and raped Sinhalese women. A Sinhalese truck driver was burnt to death along with his truck and an elderly Sinhalese man was beaten to death. Sinhalese had been burned in their homes, and Sinhalese patients had been thrown out of the hospital, killing some.[10] Around 50 Sinhalese who were well established in the community had been killed in the area of the main Sinhalese school. Corpses were thrown into wells that were covered up.[11] The IPKF prevented any intervention by the Sri Lankan Army. They fired at a crowd of Sinhalese gathered at the King's Hotel Junction, killing one. At J. R. Jayawardene's request, the IPKF had 11 platoons come into Trincomalee to restore order. On October 4, the IPKF shot a Sinhalese Buddhist monk who had demonstrated against them.[9]
Militant action
Following the suicide of the 11 Tamil Tigers in Sri Lankan police custody on October 5, Tamil militant violence spread throughout the Eastern Province. In Batticaloa, Sinhalese who had long coexisted amicably with Tamils had been attacked, even upsetting some LTTE leaders.[12] According to Batticaloa residents, the family of a Sinhalese taxi driver had been killed by an LTTE member called Niranjan Kingsley, and a Sinhalese goldsmith had been murdered by two brothers named Dayalan and Puruchotan.[13] Sinhalese and Muslims were massacred in buses, trains, and villages in various regions in the Eastern province.[14][15][16] One massacre in Kiran was masterminded by an LTTE leader named Devi.[13] By the end of the violence, over 200 Sinhalese civilians were estimated to be dead, and 20,000 were made refugees. The actual number of dead may be higher as some people disappeared and their fates were unknown.[1]
References
- Rubin, Barnett (1987). Cycles of Violence: Human Rights in Sri Lanka Since the Indo-Sri Lanka Agreement. Human Rights Watch. ISBN 9780938579434. Retrieved 8 December 2018.
- Peebles, Patrick (February 1990). "Colonization and Ethnic Conflict in the Dry Zone of Sri Lanka". The Journal of Asian Studies. 49 (1): 30–55. doi:10.2307/2058432. JSTOR 2058432.
- "Report No.7, The clash of ideologies and the continuing tragedy in the Batticaloa & Amparai Districts, Chapter 8, Colonisation - Issues and Non-Issues". uthr.org. University Teacher of Human Rights - Jaffna. Retrieved 3 January 2020.
- "Can the East be won through Human Culling?". uthr.org. University Teacher of Human Rights - Jaffna. Retrieved 11 December 2018.
- Gassbeek, Timmo (2010). Bridging troubled waters? Everyday inter-ethnic interaction in a context of violent conflict in Kottiyar Pattu, Trincomalee, Sri Lanka (PhD). Wageningen University. p. 144-157.
- The Hindu, 22 September 1985, 52 Tamil villages in Trincomalee District razed to the ground in two months
- When Tiger terrorists massacred 127 civilians in Habarana Archived 2015-09-24 at the Wayback Machine, Sunday Observer, K.M.H.C.B. Kulatunga
- Lawrence, Patricia (2000-10-02). "Violence, Suffering, Amman: The Work of Oracles in Sri Lanka's Eastern War Zone". In Das, Veena; Kleinman, Arthur (eds.). Violence and Subjectivity. University of California Press. p. 172. ISBN 0520216083. Retrieved 30 July 2019.
- Hoole, Rajan (July 2001). Sri Lanka: The Arrogance of Power: Myths, Decadence & Murder (1st ed.). University Teachers for Human Rights (Jaffna). p. 226. ISBN 9559447041.
- Barber, Ben (1987-10-13). "In Sri Lanka, the Killing Goes On". Newsday. Long Island, N.Y: Newsday LLC.
- "Trincomalee: State Ideology and the Politics of Fear". University Teachers for Human Rights (Jaffna). Retrieved 27 March 2019.
- "Human rights and The Issues of War and Peace". uthr.org. University Teacher for Human Rights Jaffna. Archived from the original on 6 May 2020. Retrieved 10 December 2018.
- Hamlyn, Michael (13 October 1987). "Gunmen lose grip of fear on Batticaloa". The Times.
- Cruez, Patrick (October 7, 1987). "Rebels Kill 140 Sinhalese in Six Attacks". AP News. Retrieved 11 May 2019.
- Weintraub, Richard (October 7, 1987). "Tamils Kill Dozens in Revenge". Washington Post. Retrieved 11 May 2019.
- Weisman, Steven (October 8, 1987). "160 Die in Sri Lanka; India Vows to Curb Attacks". The New York Times. Retrieved 11 May 2019.