200th Separate Motor Rifle Brigade
The 200th Separate Motor Rifle Brigade is a military formation of the Northern Fleet based at Pechenga in Murmansk Oblast.[1] The brigade was formed from the 131st Motor Rifle Division in 1997 and is one of the two Russian Arctic warfare brigades.
| 200th Separate Motor Rifle Brigade | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Active | 1 December 1997–present |
| Country | Russia |
| Branch | Coastal Troops of the Russian Navy |
| Type | Motorized Infantry |
| Part of | Northern Fleet Coastal Troops |
| Garrison/HQ | Pechenga |
| Engagements | War in Donbass |
| Decorations | |
| Battle honours | Pechenga |
| Insignia | |
| Shoulder Sleeve Insignia |  |
In 2014 brigade's units participated in the War in Donbass according to Bellingcat contributor.[2]
History
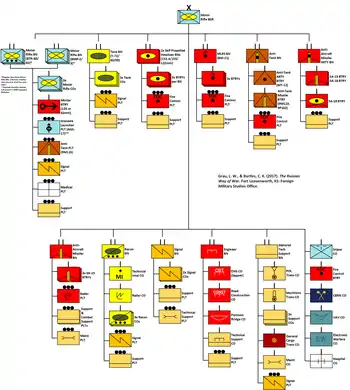
The 200th Brigade was formed from the former 131st Motor Rifle Division in 1997. It inherited the honorifics "Pechenga Order of Kutuzov" from the division.
Transition to professional contract status was planned to finish at the end of 2006. At the beginning of April 2006 the brigade had about 700 professional personnel, practically all sergeant positions having been filled by kontraktniks (Russian: контрактник contracted professional soldiers). More than 180 military men and women have signed contracts for service in communications, medical, and rear services subunits. The brigade has about 10 professional soldiers from other Commonwealth of Independent States members. At the beginning of 2006, during a trip to the Leningrad Military District, the 200th Brigade was visited by the Minister of Defence, Sergei Ivanov. The brigade has association links with the Norwegian 6th Division (Norway) and the Swedish Norrbottens Regiment.
It formed part of the 6th Army in the Western Military District.[3] As of November 2011 it became the first of two new Arctic brigades of the Russian Ground Forces.[4][5][6] The unit has had some disciplinary problems.[7] In November 2012 it became part of the Coastal Troops of the Northern Fleet.[8]
In 2014, according to Bellingcat contributor, the brigade was involved in the War in Donbass.[2][9] Brigade's units participated in the battle of Luhansk Airport and were spotted in the Khryashchevatoe village, a Luhansk suburb.[2] In October 2014, Senior Lieutenant Yevgeny Trundayev, commander of the anti-tank platoon of the 1st Motorized Infantry Battalion, was killed in the clashes for 32nd checkpoint, a battle in Luhansk region. He was later awarded the title of Hero of the Russian Federation.[10]
Equipment
The 200th Separate Motor Rifle Brigade has the following equipment:
- 41 × T-80BVM Main Battle Tanks
- 36 × 2S19 Msta self-propelled howitzers
- 18 × BM-21 Grad Multiple Rocket Launchers
- MT-LB based 9P149 tank destroyers with 9K114 Shturm Anti-tank missile
- SA-13 Gopher
- Rapira 100-MM AT gun
- SA-8 Gecko
- SA-19 Grison
Commanders
- Colonel Vitaly Leonidovich Razgonov (September 2009–April 2011)[7]
References
- "131st Motorised Rifle Division". www.ww2.dk. Retrieved 2017-01-25.
- "Russia's 200th Motorized Infantry Brigade in the Donbass – bellingcat". bellingcat. 2016-01-16. Retrieved 2017-01-25.
- 200TH DET MOT BDE, PECHENGA, WEST, 2011-11-17,
- "Russia plans Arctic army brigades". BBC News. 1 July 2011. Retrieved 13 August 2016.
- Development of Russia’s Arctic Brigade, 2011-11-17,
- Pettersen, Trude (11 August 2011). "Russia's Arctic force may include paratroopers". Barents Observer. Archived from the original on 6 April 2012. Retrieved 13 August 2016.
- Another Trouble Brigade, 2011-11-17,
- Pettersen, Trude (26 November 2012). "Motorized infantry brigade to Northern Fleet". Barents Observer. Archived from the original on 13 January 2017. Retrieved 13 August 2016.
- Aksai707 (2016-07-04). "Russia's 200th Motorized Infantry Brigade in the Donbass: The Tell-Tale Tanks – bellingcat". Retrieved 2016-09-03.
- "Russia's 200th Motorized Infantry Brigade in the Donbass: The Hero of Russia – bellingcat". bellingcat. 2016-06-21. Retrieved 2017-01-25.