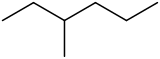
3-Methylhexane
3-Methylhexane is a branched hydrocarbon with two enantiomers.[2] It is one of the isomers of heptane.
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
3-Methylhexane[1] | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| 1718739 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.008.768 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 1206 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C7H16 | |
| Molar mass | 100.205 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colorless liquid |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Density | 686 mg mL−1 |
| Melting point | −119.40 °C; −182.92 °F; 153.75 K |
| Boiling point | 91.6 to 92.2 °C; 196.8 to 197.9 °F; 364.7 to 365.3 K |
| log P | 4.118 |
| Vapor pressure | 14.7 kPa (at 37.7 °C) |
Henry's law constant (kH) |
3.2 nmol Pa−1 kg−1 |
Refractive index (nD) |
1.388–1.389 |
| Thermochemistry | |
Heat capacity (C) |
216.7 J K−1 mol−1 (at −9.0 °C) |
Std molar entropy (S |
309.6 J K−1 mol−1 |
Std enthalpy of formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
−228.7–−226.1 kJ mol−1 |
Std enthalpy of combustion (ΔcH⦵298) |
−4.8151–−4.8127 MJ mol−1 |
| Hazards | |
EU classification (DSD) (outdated) |
|
| R-phrases (outdated) | R11, R38, R50/53, R65, R67 |
| S-phrases (outdated) | (S2), S16, S29, S33 |
| Flash point | −1.0 °C (30.2 °F; 272.1 K) |
| 280 °C (536 °F; 553 K) | |
| Explosive limits | 1–7% |
| Related compounds | |
Related alkanes |
|
Related compounds |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
The molecule is chiral, and is one of the two isomers of heptane to have this property. The enantiomers are (R)-3-methylhexane[3] and (S)-3-methylhexane.[4]
References
- "3-METHYLHEXANE – Compound Summary". PubChem Compound. USA: Nation Center for Biotechnology Information. 26 March 2005. Identification and Related Records. Retrieved 6 March 2012.
- Tro, Nivaldo J. Chemistry A Molecular Approach. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson Prentice Hall, 2008
- https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/13800357
- https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/638046
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.
