AANAT (gene)
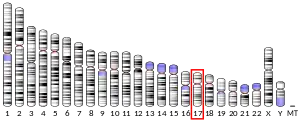
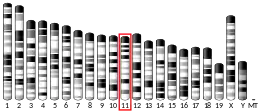
AANAT is a gene that encodes an enzyme aralkylamine N-acetyltransferase.[5] It is the key regulator of day-night cycle (circadian rhythm). It is found in all animals. In humans it is present on chromosome 17, in chimpanzees chromosome 17, in mouse and sheep chromosome 11, in rat chromosome 10, and in chicken chromosome 18.[6]
Function
The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the acetyltransferase superfamily. It is the penultimate enzyme in melatonin synthesis and controls the night/day rhythm in melatonin production in the vertebrate pineal gland. Melatonin is essential for the function of the circadian clock that influences activity and sleep. This enzyme is regulated by cAMP-dependent phosphorylation that promotes its interaction with 14-3-3 proteins and thus protects the enzyme against proteasomal degradation.[5]
Clinical significance
This gene may contribute to numerous genetic diseases such as delayed sleep phase syndrome.[5]
References
- GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000129673 - Ensembl, May 2017
- GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000020804 - Ensembl, May 2017
- "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Entrez Gene: Aralkylamine N-acetyltransferase".
- "AANAT". NCBI. Retrieved 2 November 2014.
This article incorporates text from the United States National Library of Medicine, which is in the public domain.
External links
- Human AANAT genome location and AANAT gene details page in the UCSC Genome Browser.