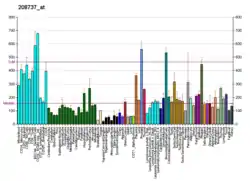
ATP6V1G1
V-type proton ATPase subunit G 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ATP6V1G1 gene.[5][6]
This gene encodes a component of vacuolar ATPase (V-ATPase), a multisubunit enzyme that mediates acidification of eukaryotic intracellular organelles. V-ATPase dependent organelle acidification is necessary for such intracellular processes as protein sorting, zymogen activation, receptor-mediated endocytosis, and synaptic vesicle proton gradient generation. V-ATPase is composed of a cytosolic V1 domain and a transmembrane V0 domain. The V1 domain consists of three A, three B, and two G subunits, as well as a C, D, E, F, and H subunit. The V1 domain contains the ATP catalytic site. The protein encoded by this gene is one of three V1 domain G subunit proteins. Pseudogenes of this gene have been characterized.[6]
References
- GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000136888 - Ensembl, May 2017
- GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000039105 - Ensembl, May 2017
- "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- Mao M, Fu G, Wu JS, Zhang QH, Zhou J, Kan LX, Huang QH, He KL, Gu BW, Han ZG, Shen Y, Gu J, Yu YP, Xu SH, Wang YX, Chen SJ, Chen Z (Aug 1998). "Identification of genes expressed in human CD34+ hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells by expressed sequence tags and efficient full-length cDNA cloning". Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 95 (14): 8175–80. doi:10.1073/pnas.95.14.8175. PMC 20949. PMID 9653160.
- "Entrez Gene: ATP6V1G1 ATPase, H+ transporting, lysosomal 13kDa, V1 subunit G1".
External links
- Human ATP6V1G1 genome location and ATP6V1G1 gene details page in the UCSC Genome Browser.
Further reading
- Finbow ME, Harrison MA (1997). "The vacuolar H+-ATPase: a universal proton pump of eukaryotes". Biochem. J. 324 (Pt 3): 697–712. doi:10.1042/bj3240697. PMC 1218484. PMID 9210392.
- Stevens TH, Forgac M (1998). "Structure, function and regulation of the vacuolar (H+)-ATPase". Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 13: 779–808. doi:10.1146/annurev.cellbio.13.1.779. PMID 9442887.
- Nelson N, Harvey WR (1999). "Vacuolar and plasma membrane proton-adenosinetriphosphatases". Physiol. Rev. 79 (2): 361–85. doi:10.1152/physrev.1999.79.2.361. PMID 10221984.
- Forgac M (1999). "Structure and properties of the vacuolar (H+)-ATPases". J. Biol. Chem. 274 (19): 12951–4. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.19.12951. PMID 10224039.
- Kane PM (1999). "Introduction: V-ATPases 1992-1998". J. Bioenerg. Biomembr. 31 (1): 3–5. doi:10.1023/A:1001884227654. PMID 10340843.
- Wieczorek H, Brown D, Grinstein S, et al. (1999). "Animal plasma membrane energization by proton-motive V-ATPases". BioEssays. 21 (8): 637–48. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1521-1878(199908)21:8<637::AID-BIES3>3.0.CO;2-W. PMID 10440860.
- Nishi T, Forgac M (2002). "The vacuolar (H+)-ATPases--nature's most versatile proton pumps". Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 3 (2): 94–103. doi:10.1038/nrm729. PMID 11836511. S2CID 21122465.
- Kawasaki-Nishi S, Nishi T, Forgac M (2003). "Proton translocation driven by ATP hydrolysis in V-ATPases". FEBS Lett. 545 (1): 76–85. doi:10.1016/S0014-5793(03)00396-X. PMID 12788495. S2CID 10507213.
- Morel N (2004). "Neurotransmitter release: the dark side of the vacuolar-H+ATPase". Biol. Cell. 95 (7): 453–7. doi:10.1016/S0248-4900(03)00075-3. PMID 14597263. S2CID 17519696.
- Zhang QH, Ye M, Wu XY, et al. (2001). "Cloning and Functional Analysis of cDNAs with Open Reading Frames for 300 Previously Undefined Genes Expressed in CD34+ Hematopoietic Stem/Progenitor Cells". Genome Res. 10 (10): 1546–60. doi:10.1101/gr.140200. PMC 310934. PMID 11042152.
- Smith AN, Borthwick KJ, Karet FE (2003). "Molecular cloning and characterization of novel tissue-specific isoforms of the human vacuolar H(+)-ATPase C, G and d subunits, and their evaluation in autosomal recessive distal renal tubular acidosis". Gene. 297 (1–2): 169–77. doi:10.1016/S0378-1119(02)00884-3. PMID 12384298.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.