Aerial Service Mercury Senior
The Aerial Service Mercury Senior, Aerial Mercury Senior or just Mercury Senior was a US biplane mailplane designed to operate at night between New York City and Chicago. A different, smaller, lower wing improved its performance for daytime flights. One was built and used by the United States Post Office Department.
| Senior | |
|---|---|
| Role | Mailplane |
| National origin | US |
| Manufacturer | Aerial Service |
| Designer | Harvey C. Mummert |
| First flight | 1925 |
| Retired | 1928 |
| Primary user | United States Post Office Department |
| Number built | 1 |
Design and development
The Mercury Senior was a single bay biplane without stagger and with dihedral only on the lower wing. Both wings were rectangular in plan out to blunted tips and had constant, thick sections; they were built around twin spruce and plywood spars and fabric covered. The upper wing was held over the fuselage by a pair of N-form cabane struts. The interplane struts were in parallel pairs, assisted by the usual wire cross-bracing. There were externally interconnected ailerons on both upper and lower wings.[1]
The novel feature of the Senior was the choice of lower wing: two were available, one with a shorter span than the upper wing and one with a longer span. The latter increased the total wing area by about 27% and decreased the wing loading by 19%. Lower wing loadings decrease aircraft speeds, so the longer span set provided lower night landing speeds at the price of reduced cruising speed.[1]
The fuselage of the Senior was a welded steel tube frame, its forward part covered with light metal and the rear with plywood. Externally it was flat-sided with rounded upper decking. A 400 hp (300 kW) Liberty L-12 water-cooled V12 engine in the nose drove a two-bladed, steel Curtiss propeller. Its honeycomb radiator was ahead of the engine, which had long exhaust pipes on both sides of the fuselage to take the emissions past the pilot. His open cockpit was well behind the trailing edge of the wing.[1] Up to 1,000 lb (450 kg)[2] of mail was stored in the space between engine and cockpit.[1]
The rear surfaces of the Senior were large, with a rectangular, strut-braced tailplane mounted on top of the fuselage carrying elevators hinged at the end of it. Its wire-braced, tall, broad, rounded fin had a straight-edged unbalanced rudder which, like the elevators, overhung the extreme tail.[1]
The Senior's landing gear was fixed and conventional with wheels, well apart, on a single axle held on two V-struts; the forward struts of the Vs contained shock absorbers. An angled, flexible tailskid, with another small shock absorber between its ends, projected beyond the extreme tail. For night landings a pair of searchlights in streamlined housings were attached below the lower wings, under the feet of the interplane struts.[1]
Operational history
The sole Senior flew for the first time in 1925 and was used by the Post Office until 1928.[2]
Operators
- United States Post Office Department
Specifications (night flight configuration)
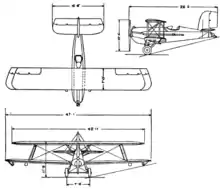
Data from Les Ailes, July 1925[1]
General characteristics
- Crew: one
- Length: 28 ft 7 in (8.70 m)
- Upper wingspan: 43 ft 0 in (13.10 m)
- Lower wingspan: 48 ft 0 in (14.64 m) (33 ft 4 in (10.17 m) in day configuration)
- Height: 11 ft 4 in (3.46 m)
- Wing area: 597.4 sq ft (55.50 m2) (467.2 sq ft (43.40 m2) in day configuration)
- Empty weight: 3,638 lb (1,650 kg) (3,494 lb (1,585 kg) in day configuration
- Gross weight: 5,512 lb (2,500 kg) (5,360 lb (2,430 kg) in day configuration)
- Powerplant: 1 × Liberty L-12 water-cooled V12, 400 hp (300 kW)
- Propellers: 2-bladed metal Curtiss
Performance
- Maximum speed: 126 mph (202 km/h, 109 kn) (135 mph; 118 kn (218 km/h) in day configuration)
- Cruise speed: 110 mph (177 km/h, 96 kn) (115 mph; 100 kn (185 km/h)) in day configuration)
- Range: 500 mi (800 km, 430 nmi) at cruising speed (560 mi (900 km) in day configuration)
- Service ceiling: 16,000 ft (5,000 m) (14,960 ft (4,560 m) in day configuration)
- Wing loading: 9.3 lb/sq ft (45.4 kg/m2) (11.5 lb/sqft (56 kg/m2)) in day configuration)
- Minimum speed: 52 mph; 45 kn (84 km/h) (57 mph; 50 kn (92 km/h) in day configuration)
References
- Serryer, J. (17 July 1925). "L'avion postal "Aérial Mercury"". Les Ailes (213): 2.
- "Aerofiles - Mercury". Retrieved 28 April 2017.