Anne Louise Gregory Ritter
Anne Louise Gregory Ritter (July 11, 1868 – November 15, 1929) was an American artist and art teacher. Her early works were in oils and watercolor, but when she met Artus Van Briggle, she began working with him on pottery design and glazing. The couple established the Van Briggle Pottery in Colorado Springs, Colorado, in 1901. After her husband's death in 1904, Anne continued to run the pottery and built a new factory in her husband's honor. In 1912 she leased the pottery to Edmund deForest Curtis, returned to teaching and sold the firm in 1922. She moved to Denver in 1923 and returned to painting.
Anne Louise Gregory Ritter | |
|---|---|
%252C_1900.JPG.webp) Anne Gregory, 1900 | |
| Born | Anne Louise Gregory July 11, 1868 Plattsburgh, New York |
| Died | November 15, 1929 (aged 61) Denver, Colorado |
| Nationality | USA |
| Occupation | Artist, teacher |
| Years active | 1896-1929 |
| Known for | Van Briggle Pottery |
Biography
Anne Louise Gregory (sometimes given as Anna Lawrence Gregory) was born July 11, 1868, in Plattsburgh, New York. She studied landscape painting with Charles Melville Dewey in New York and then studied oil painting, water colors and clay modeling at the Victoria-Lyzeum of Berlin. In 1894, she was studying in Paris at the Académie Colarossi, when she met fellow artist Artus Van Briggle, who was researching oriental pottery matte glazes.[1] Gregory's works had earned a solid reputation and she had been accepted to participate in the Paris Salon in several shows.[2] The couple became engaged and in 1896 returned to the United States, where he went to Ohio and she went to Pennsylvania. Gregory took up a teaching post at a local high school, teaching art, French and German.[3]
In 1900, Gregory moved to Colorado Springs, where Van Briggle was then residing. She took up a post as Art Supervisor at Colorado Springs High School and worked with Van Briggle in launching the business, pottery design and experimentation.[4] Over the next two years, Artus and Anne continued experimenting with products, incorporated the company and prepared for their public opening. Anne was not on the Board of Directors and Artus held all of the company shares.[5] On June 18, 1902, on Cheyenne Mountain in a place known as Helen Hunt Jackson's Garden, near Colorado Springs, Colorado, Gregory and Van Briggle married.[6]
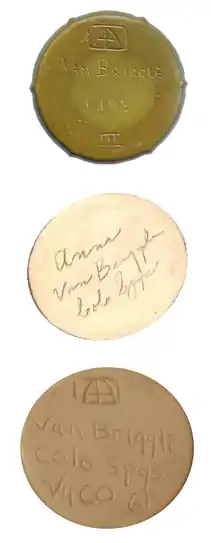
Due to her husband's increasingly poor health from tuberculosis, Anne took over most of the daily functions of the business and design work for the company.[7] Throughout the remainder of 1902 and 1903, pottery was shipped to larger cities, tours of the plant were given and entries were sent to the Paris salon.[7] For the 1903 Salon, it was noted that all 24 pieces sent were accepted, which was a rarity as art for commercial purposes was usually rejected, even if produced by well-known firms such as Tiffany's. The couple's entries, which were marked with both of their names[2] won "2 gold, 1 silver, and 12 bronze medals" at the 1903 and 1904 Salon.[8] Pieces produced by Artus were incised with the Roman numeral "iii", pieces which Anne worked on carried the double mark "AA" for the couple's initials. Pottery carrying the signature "Anna Van Briggle" date from between 1955 and 1968, long after her death[9] and were neither her works nor inspired by her. Works marked "Anna Van Briggle" are actually marked in that manner to distinguish a different type of clay and glaze in use in the late 1950s to the 1960s and have nothing to do with the artist.[10]
The couple also sent entries to the 1904 Louisiana Purchase Exposition as the St. Louis World’s Fair was known, where they won two gold, one silver, and two bronze medals. Though they wintered in Tucson hoping for an improvement in Artus' health, his condition worsened and he died on July 4, 1904.[11] After her husband's death, Anne erected a pottery plant on Uintah Street in his memory. The building was completed in 1907[12] and opened in 1908 with a larger factory and a showroom allowing for business expansion.[13]
Anne continued to run the company, even after her remarriage in July 1908 to a Swiss mining engineer, Etienne Ritter, until 1912[13] when she leased it to Edmund deForest Curtis, who ran the operation until 1916.[14] Anne returned to teaching, giving art classes at Colorado College.[13] In 1922, she sold the company to J.F. and I.H. Lewis[12] and the following year moved to Denver with her husband, returning to painting.[13]
Anne died on November 15, 1929, in Denver, Colorado.[15]
External links
References
- Simmons, R. Laurie; Simmons, Thomas H. (2009). "Artus and Anne Van Briggle and Colorado College" (PDF). A Colorado College Reader: 115. Retrieved July 26, 2015.
- "Paris Salon Accords Place to Van Briggle Ware". The Weekly Gazette. Colorado Springs, Colorado. May 14, 1903. p. 6. Retrieved July 26, 2015 – via Newspapers.com.

- "Simmons (2009)", p. 117.
- "Simmons (2009)", p 121"
- "Simmons (2009)", p. 123.
- "With Nature and a Few Friends". The Weekly Gazette. Colorado Springs, Colorado. June 19, 1902. p. 11. Retrieved July 26, 2015 – via Newspapers.com.

- "Simmons (2009)", p. 124.
- "Van Briggle Made Profound Impact in World Art Circles". Colorado Springs Gazette Telegraph. Colorado Springs, Colorado. May 23, 1976. p. 101. Retrieved July 26, 2015 – via Newspapers.com.

- "Question". The Daily Journal. Fergus Falls, Minnesota. September 6, 1972. p. 5. Retrieved July 26, 2015.
- "Anna Van - The True Story". Clem Hull. Clement Marot Hull. 2005. Retrieved July 26, 2015.
- "Simmons (2009)", p. 127.
- "Colorado College Buys Van Briggle Landmark". Colorado Springs Gazette Telegraph. Colorado Springs, Colorado. December 8, 1968. p. 55. Retrieved July 26, 2015 – via Newspapers.com.

- "Simmons (2009)", p. 128.
- McCutchan, Ann (April 30, 1993). "Matte finish characterizes Van Briggle ware". News Record. North Hills, Pennsylvania. p. 18. Retrieved July 26, 2015 – via Newspapers.com.

- "Anne Louise Gregory Ritter". Find a Grave. Find a Grave. Retrieved July 26, 2015.