Archaeosine
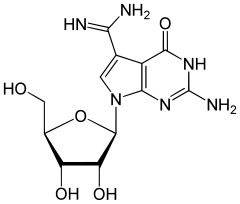
Archaeosine (/kjuːiːn/) (G*) is a modified nucleobase found in the dihydrouracil loop at position 15 of tRNAs found in Archaea,[1] and is thought to be important for the heat resistance of thermophilic archaea such as Thermococcus kodakarensis.[2][3][4]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2-amino-7-[(2R,3R,4S,5R)-3,4-dihydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)oxolan-2-yl]-4-oxo-3H-pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine-5-carboximidamide | |
| Other names
7-formamidino-7-deazaguanosine | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C12H16N6O5 | |
| Molar mass | 324.297 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
See also
References
- Kilpatrick MW, Walker RT (September 1981). "The nucleotide sequence of the tRNAMMet from the archaebacterium Thermoplasma acidophilum". Nucleic Acids Research. 9 (17): 4387–90. doi:10.1093/nar/9.17.4387. PMC 327441. PMID 6913864.
- McCarty RM, Bandarian V (August 2012). "Biosynthesis of pyrrolopyrimidines". Bioorganic Chemistry. 43: 15–25. doi:10.1016/j.bioorg.2012.01.001. PMC 4022189. PMID 22382038.
- Lorenz C, Lünse CE, Mörl M (April 2017). "tRNA Modifications: Impact on Structure and Thermal Adaptation". Biomolecules. 7 (2). doi:10.3390/biom7020035. PMID 28375166.
- Turner B, Burkhart BW, Weidenbach K, Ross R, Limbach PA, Schmitz RA, et al. (March 2020). "Archaeosine Modification of Archaeal tRNA: Role in Structural Stabilization". Journal of Bacteriology. 202 (8). doi:10.1128/JB.00748-19. PMID 32041795.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.