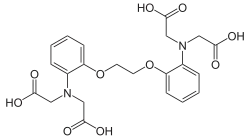
BAPTA
BAPTA (1,2-bis(o-aminophenoxy)ethane-N,N,N′,N′-tetraacetic acid) is a calcium-specific aminopolycarboxylic acid. The presence of four carboxylic acid functional groups makes possible the binding of two calcium ions. The extensive flexibility of the carboxylate ligands is critical to the coordination of calcium and other metal ions. Due to its properties, it is used in research to chelate Ca2+, similarly to EGTA and EDTA.
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
1,2-bis(o-aminophenoxy)ethane-N,N,N′,N′-tetraacetic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.157.377 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C22H24N2O10 | |
| Molar mass | 476.433 |
| Density | 1.494 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 177 to 179 °C (351 to 354 °F; 450 to 452 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
There is a range of reported values for the dissociation constant of BAPTA, though 0.2 μM appears consistently.[1] The rate constant for calcium binding is 500 μM−1 s−1.[1]
References
- Ricci AJ, Wu YC, Fettiplace R (15 October 1998). "The endogenous calcium buffer and the time course of transducer adaptation in auditory hair cells". The Journal of Neuroscience. 18 (20): 8261–77. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.18-20-08261.1998. PMC 6792854. PMID 9763471.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.
