Ballymahon
Ballymahon (Irish: Baile Uí Mhatháin, meaning "Mahon's town")[2] on the River Inny is a town in the southern part of County Longford, Ireland. It is located at the junction of the N55 National secondary road and the R392 regional road.[3]
Ballymahon
Baile Uí Mhatháin | |
|---|---|
Town | |
 Ballymahon | |
 Ballymahon Location in Ireland | |
| Coordinates: 53°34′00″N 7°46′00″W | |
| Country | Ireland |
| Province | Leinster |
| County | County Longford |
| Elevation | 82 m (269 ft) |
| Population (2016)[1] | 1,877 |
| Time zone | UTC+0 (WET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC-1 (IST (WEST)) |
| Eircode routing key | N39 |
| Telephone area code | +353(0)90 |
| Website | www |
History
Ballymahon derives its name from the Irish language term Baile Uí Mhatháin or Baile Mathuna, meaning "Town of Mahon". This may refer to Mahon (Mathgamain mac Cennétig), a southern chieftain and the elder brother of Brian Boru, who is believed by some to have fought a battle in 960 in the vicinity of Ballymahon at Shrule (in Irish Sruaith Fhuil, River of Blood) where he defeated O'Rourke of Cavan and laid claim to lands in the area. This is disputed by others who claim Mahon may relate to a sub chieftain of the O'Farrells who ruled over this part of County Longford in the 14th century.[4]
The earliest documentary evidence of Ballymahon is from the year 1578, when lands in the area were granted to the Dillon family, later Earls of Roscommon.[5] By 1654, the maps of William Petty's Down Survey shows Ballymahon as a group of houses situated at the southern end of the present town, on the right bank of the River Inny.
Two main families, the Shuldham family of Moigh House and the King-Harman family of Newcastle House, developed the town in the mid-nineteenth century.[6] The buildings in the town are of late Georgian architecture, with two and three-storey gabled houses, colour-washed and in rows of three and four. From 1788 to 1853, the Roman Catholic bishops of Ardagh and Clonmacnoise resided in the town,[5] and the parish church served as a Pro-Cathedral until St Mel's Cathedral was built in Longford.
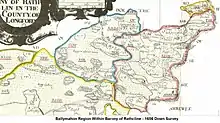
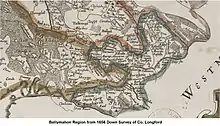
Geography
The River Inny, a tributary of the River Shannon, flows westwards through Ballymahon in the direction of Lough Ree three miles from the town. A stretch of the Inny from Newcastle Bridge to Ballymahon town is used for beginner to intermediate kayaking, canoeing and time trials.
The Royal Canal also passes westwards through Ballymahon from Dublin to Clondra, County Longford.[7] Following extensive works the canal has been restored and is now fully navigable. Brannigan Harbour, c.1 km from Ballymahon town, is on the Royal Canal and is a common point for boats and barges to stop and pass.
Buildings of note
- Ballymahon Courthouse and Market House, originally built in the early 19th century, is a community library. It is situated in the centre of the town (built 1819).[8]
- St Catherine's Church with its narrow spire is a prominent feature in the town (built 1800, rebuilt 1824)[9]
- Ballymahon Mill, now converted into apartments, is a six-storey building on the southern end of the town and adjacent to the town's bridge and River Inny (built 1839)
- St Matthew's Church is a Gothic-style Church which is located on the northwest side of Ballymahon (built 1906)[10]
- Other buildings of interest in the area include: Newcastle House (built between 1710 and 1860), Castlecore House (built between 1740–65), Ledwithstown House (built 1746), the Bank of Ireland Building (built 1869), and the Convent of Mercy (built 1882)
- Opposite St Catherine's Church is the old RIC police barracks built on the northern edge of what local tradition holds was a castle or fortress of the O'Farrell Clan, earthworks of which can still be seen off the Fairgreen/Thomand Lodge Road. It is said to have been originally built as a hospital. It became a Garda barracks after the establishment of the Irish Free State and remained in service until 1996 when a new, smaller, station was built on the southern bank of the river opposite the old mill. The barracks was attacked during the War of Independence in August 1920.[11] The attack was led by General Seán MacEoin, Seán Connolly (who fired the first shot in the Easter Rising, killing an unarmed sentry, Constable O'Brien, outside Dublin Castle, and was later killed himself in the Selton Hill ambush) and Frank Davis. A small party of local volunteers also took part in the raid which mainly aimed to seize firearms. MacEoin later visited the barracks to campaign during an election campaign in the 1950s. Ruairí Ó Brádaigh was held here in the 1950s during the IRA Border War which ended in 1962.
Transport and communications

Ballymahon is on the N55 road,[12] a National Secondary route leading from Athlone, about 22 kilometres to the south, towards Belfast and Northern Ireland. The county town of Longford lies about 22 kilometres to the north-west. The R392 road links Ballymahon to Mullingar in the East and to Roscommon in the West, via Lanesborough–Ballyleague.[12] This route was a portion of an ancient ceremonial way from Rathcroghan to the Hill of Tara. Intact portions of the ancient roadway can be seen at the nearby Corlea Trackway and the ceremonial route attests to the straightness of the R392.
The Royal Canal links Ballymahon to Dublin, via several towns such as Mullingar and Maynooth, and to the River Shannon at Clondra.
Education
Ballymahon has a primary school, St. Matthew's National School, which opened in 2014 (for ages 4–12) as well as two mixed secondary schools (for ages 12–19), Mercy Secondary School (1980 and Ballymahon Vocational School. The nearest third-level college is AIT in Athlone, some 22 km away.
Culture and sport
Ballymahon is home to the Bog Lane Theatre. It also hosts the Oliver Goldsmith Summer School, a festival of literature which is held on the June Bank Holiday Weekend, with poetry readings held at Goldsmith's birthplace in Pallas. Ballymahon also plays host to the Still Voices International Film Festival every August.[13]
The town's Gaelic football (GAA) club is Ballymahon GAA,[14] and its association football (soccer) soccer club is Ballymahon AFC.
Twin towns
Ballymahon is twinned with two adjacent towns in the Morbihan region of Brittany, North-west France. These towns are:
Twinning events and cross-cultural tours are held annually.
People
.jpg.webp)

- Sir Thomas Molyneux (1661–1733) and William Molyneux (1656–1698), natural philosopher and writer, were descendants of the Dowdall-Molyneux family who had large estates in Ballymulvey, near Ballymahon.
- Thomas Marlay (c.1680–1756), Lord Chief Justice of Ireland, was born at Creevagh Beg, Ballymahon.
- Oliver Goldsmith (1728–1774), author, was born in the nearby townland of Pallas and raised in nearby Lissoy (The Pigeons). His mother was resident in the town in her latter years in a building adjacent to Diffley's hardware shop which was demolished during the widening of the N55 junction in the early 1990s. Ballymahon has a monument on the main street commemorating the poet as well as a commemorative monument and park at his birthplace in Pallas.
- John Keegan Casey (1846–1870), known as "the Poet of the Fenians" was born in 1846 in County Westmeath before his family moved to Gurteen outside Ballymahon where his father was schoolmaster. Casey later taught in the area and became involved in the Fenian movement in the area. He died on St Patrick's Day 1870.
- John Henry Patterson (1867–1947), soldier and author, was born in Forgney. He was best known for his book The Man-Eaters of Tsavo (1907), which details his experiences while building a railway bridge in Kenya in the late 1890s.
- Dr Kathleen Lynn, political and women's rights activist and medical doctor, lived in Ballymahon for four years in her youth from 1882 to 1886, while her father served as a Church of Ireland clergyman to the Ballymahon Parish.
- James Dooley (1877-1950), Australian politician, Premier of New South Wales.
References
- "Sapmap Area - Settlements - Ballymahon". Census 2016. Central Statistics Office. April 2016. Retrieved 31 January 2020.
- "Baile Uí Mhatháin / Ballymahon". logainm.ie. Irish Placenames Commission. Retrieved 31 January 2020.
- https://www.longfordleader.ie/section/654/ballymahon
- O'Hanlon, Ciaran (2015). "Origin of the name Ballymahon". Teathbha - County Longford Historical Society. IV (2): 161–63.
- "A Concise History of Ballymahon". ballymahontown.com. Retrieved 1 February 2020.
- "Towns & Villages - Ballymahon". longford.ie. Longford County Council. Retrieved 1 February 2020.
- "Royal Canal Group". ballymahontown.com. Retrieved 31 January 2020.
- "Ballymahon Market House, Ballymahon, County Longford". buildingsofireland.ie. National Inventory of Architectural Heritage. Retrieved 31 January 2020.
- "St. Catherine's Church of Ireland Church, Ballymahon, County Longford". buildingsofireland.ie. National Inventory of Architectural Heritage. Retrieved 31 January 2020.
- "St. Matthew's Roman Catholic Church, Ballymahon, County Longford". buildingsofireland.ie. National Inventory of Architectural Heritage. Retrieved 31 January 2020.
- "Ballymahon Royal Irish Constabularly Barracks, Ballymahon, County Longford". buildingsofireland.ie. National Inventory of Architectural Heritage. Retrieved 31 January 2020.
- Appendix 1D: Local Service Towns Ballymahon & Lanesborough (PDF). Longford County Development Plan 2015–2021 (Report). Longford County Council. 2015. p. 44.
- "Still Voices Short Film Festival". stillvoicesfilmfestival.com. Retrieved 31 January 2020.
- "Ballymahon GAA Club - Home". Ballymahongaa.com. Retrieved 31 January 2020.