Bioluminescence imaging
Bioluminescence imaging (BLI) is a technology developed over the past decade that allows for the noninvasive study of ongoing biological processes. Recently, bioluminescence tomography (BLT) has become possible and several systems have become commercially available. In 2011, PerkinElmer acquired one of the most popular lines of optical imaging systems with bioluminescence from Caliper Life Sciences.[1]
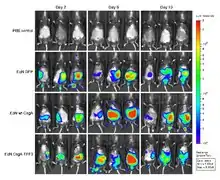
Background
Bioluminescence is the process of light emission in living organisms. Bioluminescence imaging utilizes native light emission from one of several organisms which bioluminesce. The three main sources are the North American firefly, the sea pansy (and related marine organisms), and bacteria like Photorhabdus luminescens and Vibrio fischeri. The DNA encoding the luminescent protein is incorporated into the laboratory animal either via a viral vector or by creating a transgenic animal. Rodent models of cancer spread can be studied through bioluminescence imaging.for e.g.Mouse models of breast cancer metastasis.
Systems derived from the three groups above differ in key ways:
- Firefly luciferase requires D-luciferin to be injected into the subject prior to imaging. The peak emission wavelength is about 560 nm. Due to the attenuation of blue-green light in tissues, the red-shift (compared to the other systems) of this emission makes detection of firefly luciferase much more sensitive in vivo.
- Renilla luciferase (from the Sea pansy) requires its substrate, coelenterazine, to be injected as well. As opposed to luciferin, coelenterazine has a lower bioavailability (likely due to MDR1 transporting it out of mammalian cells). Additionally, the peak emission wavelength is about 480 nm.
- Bacterial luciferase has an advantage in that the lux operon used to express it also encodes the enzymes required for substrate biosynthesis. Although originally believed to be functional only in prokaryotic organisms, where it is widely used for developing bioluminescent pathogens, it has been genetically engineered to work in mammalian expression systems as well.[2][3] This luciferase reaction has a peak wavelength of about 490 nm.
While the total amount of light emitted from bioluminescence is typically small and not detected by the human eye, an ultra-sensitive CCD camera can image bioluminescence from an external vantage point.
Applications
Common applications of BLI include in vivo studies of infection[4] (with bioluminescent pathogens), cancer progression (using a bioluminescent cancer cell line), and reconstitution kinetics (using bioluminescent stem cells).[5]
Researchers at UT Southwestern Medical Center have shown that bioluminescence imaging can be used to determine the effectiveness of cancer drugs that choke off a tumor's blood supply. The technique requires luciferin to be added to the bloodstream, which carries it to cells throughout the body. When luciferin reaches cells that have been altered to carry the firefly gene, those cells emit light.[6]
The BLT inverse problem of 3D reconstruction of the distribution of bioluminescent molecules from data measured on the animal surface is inherently ill-posed. The first small animal study using BLT was conducted by researchers at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles, USA in 2005. Following this development, many research groups in USA and China have built systems that enable BLT.
Mustard plants have had the gene that makes fireflies' tails glow added to them so that the plants glow when touched. The effect lasts for an hour, but an utra-sensitive camera is needed to see the glow.[7]
Autoluminograph
An autoluminograph is a photograph produced by placing a light emitting object directly on a piece of film. A famous example is an autoluminograph published in Science magazine in 1986[8] of a glowing transgenic tobacco plant bearing the luciferase gene of fireflies placed on Kodak Ektachrome 200 film.
Induced metabolic bioluminescence imaging
Induced metabolic bioluminescence imaging (imBI) is used to obtain a metabolic snapshot of biological tissues.[9] Metabolites that may be quantified through imBI include glucose, lactate, pyruvate, ATP, glucose-6-phophate, or D2-hydroxygluturate.[10] imBI can be used to determine the lactate concentration of tumors or to measure the metabolism of the brain.[10][9]
References
- "PerkinElmer to Acquire Caliper Life Sciences for $600M in Cash | GEN News Highlights | GEN". GEN. Retrieved 2016-06-10.
- Close, Dan M.; Patterson, Stacey S.; Ripp, Steven; Baek, Seung J.; Sanseverino, John; Sayler, Gary S. (2010). Pan, Xiaoping (ed.). "Autonomous Bioluminescent Expression of the Bacterial Luciferase Gene Cassette (lux) in a Mammalian Cell Line". PLOS ONE. 5 (8): e12441. Bibcode:2010PLoSO...512441C. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0012441. PMC 2929204. PMID 20805991.
- Close, Dan M.; Hahn, Ruth E.; Patterson, Stacey S.; Baek, Seung J.; Ripp, Steven A.; Sayler, Gary S. (2011). "Comparison of human optimized bacterial luciferase, firefly luciferase, and green fluorescent protein for continuous imaging of cell culture and animal models". Journal of Biomedical Optics. 16 (4): 047003–047003–10. Bibcode:2011JBO....16d7003C. doi:10.1117/1.3564910. PMC 3094131. PMID 21529093.
- Xiong, Yan Q.; Willard, Julie; Kadurugamuwa, Jagath L.; Yu, Jun; Francis, Kevin P.; Bayer, Arnold S. (2004). "Real-Time in Vivo Bioluminescent Imaging for Evaluating the Efficacy of Antibiotics in a Rat Staphylococcus aureus Endocarditis Model". Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy. 49 (1): 380–7. doi:10.1128/AAC.49.1.380-387.2005. PMC 538900. PMID 15616318.
- Di Rocco, Giuliana; Gentile, Antonietta; Antonini, Annalisa; Truffa, Silvia; Piaggio, Giulia; Capogrossi, Maurizio C.; Toietta, Gabriele (1 September 2012). "Analysis of biodistribution and engraftment into the liver of genetically modified mesenchymal stromal cells derived from adipose tissue" (PDF). Cell Transplantation. 21 (9): 1997–2008. doi:10.3727/096368911X637452. PMID 22469297. S2CID 21603693.
- Zhao, Dawen; Richer, Edmond; Antich, Peter P.; Mason, Ralph P. (2008). "Antivascular effects of combretastatin A4 phosphate in breast cancer xenograft assessed using dynamic bioluminescence imaging and confirmed by MRI". The FASEB Journal. 22 (7): 2445–51. doi:10.1096/fj.07-103713. PMC 4426986. PMID 18263704. Lay summary – Newswise (May 29, 2008).
- Dr. Chris Riley, “Glowing plants reveal touch sensitivity”, BBC 17 May 2000.
- Ow, D.W.; Wood, K.V.; DeLuca, M.; de Wet, J.R.; Helinski, D.R. & Howell, S.H. (1986). "Transient and stable expression of the firefly luciferase gene in plant cells and transgenic plants". Science. 234 (4778). American Association for the Advancement of Science. p. 856. ISSN 0036-8075.
- Walenta, Stefan; Voelxen, Nadine F.; Sattler, Ulrike G. A.; Mueller-Klieser, Wolfgang (2014). "Localizing and Quantifying Metabolites in Situ with Luminometry: Induced Metabolic Bioluminescence Imaging (ImBI)". Brain Energy Metabolism. Neuromethods. 90. pp. 195–216. doi:10.1007/978-1-4939-1059-5_9. ISBN 978-1-4939-1058-8.
- Parks, Scott K.; Mueller-Klieser, Wolfgang; Pouysségur, Jacques (2020). "Lactate and Acidity in the Cancer Microenvironment". Annual Review of Cancer Biology. 4: 141–158. doi:10.1146/annurev-cancerbio-030419-033556.
Further reading
- Hutchens, Martha; Luker, Gary D. (2007). "Applications of bioluminescence imaging to the study of infectious diseases" (PDF). Cellular Microbiology. 9 (10): 2315–22. doi:10.1111/j.1462-5822.2007.00995.x. hdl:2027.42/73608. PMID 17587328.
- Chaudhari, Abhijit J; Darvas, Felix; Bading, James R; Moats, Rex A; Conti, Peter S; Smith, Desmond J; Cherry, Simon R; Leahy, Richard M (2005). "Hyperspectral and multispectral bioluminescence optical tomography for small animal imaging". Physics in Medicine and Biology. 50 (23): 5421–41. Bibcode:2005PMB....50.5421C. doi:10.1088/0031-9155/50/23/001. PMID 16306643.
- Wang, Ge; Li, Yi; Jiang, Ming (2004). "Uniqueness theorems in bioluminescence tomography" (PDF). Medical Physics. 31 (8): 2289–99. Bibcode:2004MedPh..31.2289W. doi:10.1118/1.1766420. hdl:10211.3/198368. PMID 15377096.
