Bismabenzene
Bismabenzene (C5H5Bi) is the parent representative of a group of organobismuth compounds that are related to benzene with a carbon atom replaced by a bismuth atom. Bismabenzene itself has been synthesised but not isolated because it is too reactive.[1][2]
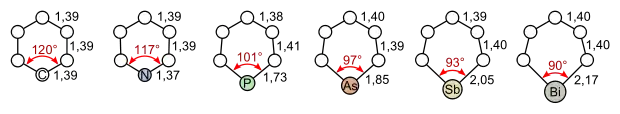
Bond lengths and angles of benzene, pyridine, phosphorine, arsabenzene, stibabenzene, and bismabenzene
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Bismine, Bismin | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C5H5Bi | |
| Molar mass | 274.075 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
An unstable derivative with 4-alkyl substituents was reported in 1982.[3] A stable derivative was reported in 2016.[1][4] This derivative has two tri(isopropyl)silyl substituents in the ortho positions and was synthesised from aluminacyclohexadiene, bismuth trichloride and DBU.
References
- Chemists create stable bismuth benzene derivative Fernando Gomollon-Bel 29 September 2016 https://www.chemistryworld.com/news/chemists-create-stable-bismuth-benzene-derivative/1017447.article
- Bismabenzene. Reaction of Group V heteroaromatic compounds with hexafluorobutyne Arthur J. Ashe III and Michael D. Gordon Journal of the American Chemical Society 1972 94 (21), 7596-7597 doi: 10.1021/ja00776a063
- Stabilization of stibabenzene and bismabenzene by 4-alkyl substituents Arthur J. Ashe III, Timothy R. Diephouse, and Maher Y. El-Sheikh Journal of the American Chemical Society 1982 104 (21), 5693-5699 doi: 10.1021/ja00385a024
- An Isolable Bismabenzene: Synthesis, Structure, and Reactivity Takuya Ishii, Katsunori Suzuki, Taichi Nakamura, and Makoto Yamashita Journal of the American Chemical Society Article 2016 138 (39) 12787−12790 doi: 10.1021/jacs.6b08714
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.
