Brüggen Glacier
Brüggen Glacier, also known as Pío XI Glacier, is in southern Chile and is the largest western outflow from the Southern Patagonian Ice Field. Now about 66 km (41 mi) in length, it is the longest glacier in the southern hemisphere outside Antarctica.[2] Unlike most glaciers worldwide, it advanced significantly from 1945 to 1976, Brüggen surged 5 km (3.1 mi) across the Eyre Fjord, reaching the western shore by 1962 and cutting off Lake Greve from the sea. The glacier continued advancing both northward and southward in the fjord to near its present position before stabilizing. The growth covers a distance of more than 10 km (6.2 mi) north to south, adding nearly 60 square kilometres (23 sq mi) of ice. The glacier is named after the German geologist Juan Brüggen Messtorff.
| Brüggen Glacier | |
|---|---|
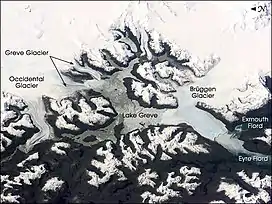 Brüggen Glacier and surrounding area, September 2001 | |
| Type | Tidewater glacier |
| Location | Chile |
| Coordinates | 49°13′S 74°00′W[1] |
| Area | 1,265 km2 (488 sq mi) [1] |
| Length | 66 km (41 mi) [1] |
| Terminus | Sealevel |
| Status | Advancing |
References
- http://www.glaciologia.cl/spi.html Archived March 24, 2012, at the Wayback Machine
- In the northern hemisphere, Tajikistan's Fedchenko Glacier is 77 km long. In the Karakoram Mountains, Siachen Glacier is 76 km long, Biafo Glacier is 67 km long, Baltoro is 63 km long, and Baltura is 57 km long. Kyrgyzstan's South Inylchek (Enylchek) Glacier is 60.5 km in length. None in the southern hemisphere outside of Antarctica and Bruggen Glacier approach this length. Measurements are from recent imagery, generally also with Russian 1:200,000 scale topographic mapping for reference as well as the 1990 Orographic Sketch Map: Karakoram: Sheets 1 and 2, Swiss Foundation for Alpine Research, Zurich.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Pio XI Glacier. |
- See Figure 55 in this USGS study for a map and discussion of the glacier's advances and retreats
- (in Spanish) http://www.glaciologia.cl/pioxi.htm
- Photos of Pío XI Glacier on Flickr
- Photo Gallery

