Butomus umbellatus
Butomus umbellatus is the Old World Palearctic and Asian plant species in the family Butomaceae. Common names include flowering rush[3] or grass rush.
| Flowering rush | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Monocots |
| Order: | Alismatales |
| Family: | Butomaceae |
| Genus: | Butomus |
| Species: | B. umbellatus |
| Binomial name | |
| Butomus umbellatus L. | |
| Synonyms[1] | |
| |
Description
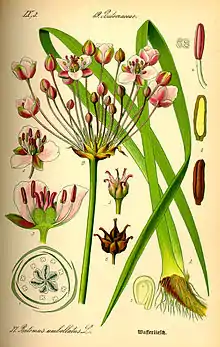
The plant is a rhizomatous, hairless, perennial aquatic plant. Its name is derived from Greek bous, meaning "cow", "ox" etc. and tome, a cut (the verb 'temnein' meaning "to cut"), which refers to the plant's swordlike leaves.[4]
Other than suggested by its English common name, it is not a true rush. It is native to Old World continents and grows on the margins of still and slowly moving water down to a depth of about 3 m. It has pink flowers. Introduced into North America as an ornamental plant it has now become a serious invasive weed[5] in the Great Lakes area and in parts of the Pacific Northwest.[6] In Israel, one of its native countries, it is an endangered species due to the dwindling of its habitat. It can also be found in Great Britain locally, for example Butomus umbellatus at Gwent Levels SSSI on the Caldicot and Wentloog Levels[4][7]
The plant has linear, pointed leaves up to 1 metre long, or more. The leaves are triangular in cross-section and arise in two rows along the rhizome/base. They are untoothed, parallel veined and twisted.[4][8]
The inflorescence is umbel-like consisting of a single terminal flower surrounded by three cymes. The flowers are regular and bisexual, 2 to 3 cm across. There are three petal-like sepals which are pink with darker veins. They persist in the fruit. The three petals are like the sepals but somewhat larger. 6 - 9 stamens. Carpels superior, 6 - 9 and slightly united at the base. When ripe they are obovoid and crowned with a persistent style. Ovules are numerous and found scattered over the inner surface of the carpel wall, except on the midrib and edges. Fruit is a follicle. The seeds have no endosperm and a straight embryo. It flowers from July until August.[4]
Uses
Butomus umbellatus is cultivated as an ornamental waterside plant.[9]
In parts of Russia the rhizomes are used as food.
References
- The Plant List, Butomus umbellatus L.
- 1885 illustration from Prof. Dr. Otto Wilhelm Thomé Flora von Deutschland, Österreich und der Schweiz 1885, Gera, Germany
- "Butomus umbellatus". Natural Resources Conservation Service PLANTS Database. USDA. Retrieved 10 January 2016.
- "Butomus umbellatus in Flora of North America @ efloras.org". www.efloras.org. Retrieved 2017-01-31.
- "Flowering Rush (Butomus umbellatus) Ecological Risk Screening Summary" (PDF). U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service. 2018. Retrieved 16 March 2020.
- Biota of North America Program 2014 county distribution map Image
- Natural World Magazine, Spring 2009, The Wildlife Trust, published by Think publishing
- Rose, Francis (2006). The Wild Flower Key. Frederick Warne & Co. pp. 480–481. ISBN 978-0-7232-5175-0.
- "RHS Plant Selector - Butomus umbellatus". Retrieved 23 February 2020.