Cholesteryl ester
Cholesteryl ester, a dietary lipid, is an ester of cholesterol. The ester bond is formed between the carboxylate group of a fatty acid and the hydroxyl group of cholesterol. Cholesteryl esters have a lower solubility in water due to their increased hydrophobicity. Esters are formed by replacing at least one –OH (hydroxyl) group with an –O–alkyl (alkoxy) group. They are hydrolyzed by pancreatic enzymes, cholesterol esterase, to produce cholesterol and free fatty acids.[1] They are associated with atherosclerosis.[2]
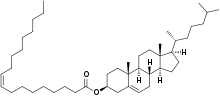
Cholesterol oleate, a member of the cholesteryl ester family
See also
References
- Ferrier, Richard A. Harvey, Denise R. (2011). Lippincott's illustrated reviews, biochemistry (5th ed.). Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer Health. p. 175. ISBN 9781608314126.
- Cholesterol+Esters at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.