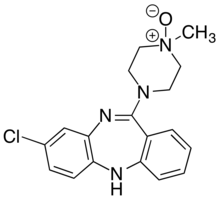
Clozapine N-oxide
Clozapine N-oxide (CNO) is a synthetic drug used mainly in biomedical research as a ligand to activate DREADD receptors.[1] Although CNO was initially believed to be biologically inert, it has been shown to reverse metabolise into clozapine which has a series of effects on serotonin and dopamine receptors.[2]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
3-chloro-6-(4-methyl-4-oxidopiperazin-4-ium-1-yl)-11H-benzo[b][1,4]benzodiazepine | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.164.243 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C18H19ClN4O | |
| Molar mass | 342.83 g·mol−1 |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |   |
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
| H301, H315, H319, H335 | |
| P261, P264, P270, P271, P280, P301+310, P302+352, P304+340, P305+351+338, P312, P321, P330, P332+313, P337+313, P362, P403+233, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Alternatives to CNO with more inert character and faster kinetics include Compound 21 (C21)[3] and deschloroclozapine (DCZ).[4]
References
- Armbruster, B. N.; Li, X.; Pausch, M. H.; Herlitze, S.; Roth, B. L. (2007-03-02). "Evolving the lock to fit the key to create a family of G protein-coupled receptors potently activated by an inert ligand". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 104 (12): 5163–5168. doi:10.1073/pnas.0700293104. ISSN 0027-8424.
- Manvich, Daniel F.; Webster, Kevin A.; Foster, Stephanie L.; Farrell, Martilias S.; Ritchie, James C.; Porter, Joseph H.; Weinshenker, David (2018-03-01). "The DREADD agonist clozapine N-oxide (CNO) is reverse-metabolized to clozapine and produces clozapine-like interoceptive stimulus effects in rats and mice". Scientific Reports. 8 (1): 1–10. doi:10.1038/s41598-018-22116-z. ISSN 2045-2322.
- Bonaventura, Jordi; Eldridge, Mark A. G.; Hu, Feng; Gomez, Juan L.; Sanchez-Soto, Marta; Abramyan, Ara M.; Lam, Sherry; Boehm, Matthew A.; Ruiz, Christina; Farrell, Mitchell R.; Moreno, Andrea (2019-10-11). "High-potency ligands for DREADD imaging and activation in rodents and monkeys". Nature Communications. 10 (1): 4627. doi:10.1038/s41467-019-12236-z. ISSN 2041-1723.
- Nagai, Yuji; Miyakawa, Naohisa; Takuwa, Hiroyuki; Hori, Yukiko; Oyama, Kei; Ji, Bin; Takahashi, Manami; Huang, Xi-Ping; Slocum, Samuel T.; DiBerto, Jeffrey F.; Xiong, Yan (September 2020). "Deschloroclozapine, a potent and selective chemogenetic actuator enables rapid neuronal and behavioral modulations in mice and monkeys". Nature Neuroscience. 23 (9): 1157–1167. doi:10.1038/s41593-020-0661-3. ISSN 1546-1726.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.