Cocamide DEA
Cocamide DEA, or cocamide diethanolamine, is a diethanolamide made by reacting the mixture of fatty acids from coconut oils with diethanolamine.[2] It is a viscous liquid and is used as a foaming agent in bath products like shampoos and hand soaps, and in cosmetics as an emulsifying agent. See cocamide for the discussion of the lengths of carbon chains in the molecules in the mixture. The chemical formula of individual components is CH3(CH2)nC(=O)N(CH2CH2OH)2, where n typically ranges from 8 to 18.
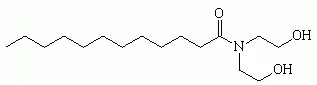 Lauramide DEA, the major component of cocamide DEA | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| ChemSpider |
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.065.123 |
| EC Number |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| Properties | |
| CH3(CH2)nC(=O)N(CH2CH2OH)2, n ~ 8-18 | |
| Appearance | Yellowish to yellow viscous liquid[1] |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms | 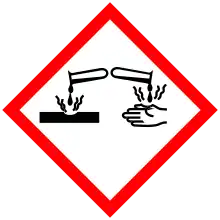  |
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
| H315, H318, H319 | |
| P264, P280, P302+352, P305+351+338, P310, P321, P332+313, P337+313, P362 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Safety
The International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) lists coconut oil diethanolamine condensate (cocamide DEA) as an IARC Group 2B carcinogen, which identifies this chemical as possibly carcinogenic to humans.[3] The listing is based on a dermal animal bioassay.[4]
In June 2012, the California Office of Environmental Health Hazard Assessment added cocamide DEA to the California Proposition 65 (1986) list of chemicals known to cause cancer.[5]
Cocamide DEA has a high irritation potential.[6]
References
- Cocamide DEA
- Therapeutic Goods Administration. "Chemical Substances" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 15 June 2009. Retrieved 20 June 2009.
- "International Agency for Research on Cancer: Agents Classified by the IARC Monographs, Volumes 1–105".
- "IARC Monograph 101" (PDF). IARC. Retrieved 29 September 2018.
- "Chemicals Listed Effective June 22, 2012 As Known To The State Of California To Cause Cancer: benzophenone (CAS No. 119-61-9), coconut oil diethanolamine condensate (cocamide diethanolamine) (CAS No. 68603-42-9), diethanolamine (CAS No. 111-42-2), and 2-methylimidazole (CAS No. 693-98-1)". Retrieved 2012-06-22.
- Turkoglu M, Sakr A (December 1999). "Evaluation of irritation potential of surfactant mixtures". Int J Cosmet Sci. 21 (6): 371–82. doi:10.1046/j.1467-2494.1999.211920.x. PMID 18503452.
