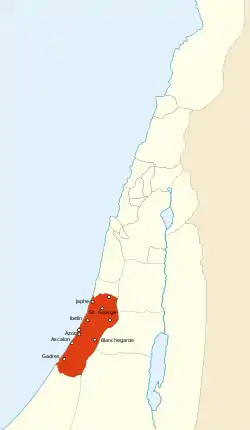
County of Jaffa and Ascalon
The double County of Jaffa and Ascalon was one of the four major seigneuries comprising the major Crusader state of the Kingdom of Jerusalem, according to 13th-century commentator John of Ibelin.
County of Jaffa and Ascalon | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1100–1268 | |||||||||
 | |||||||||
| Status | Vassal of Kingdom of Jerusalem | ||||||||
| Capital | Jaffa | ||||||||
| Common languages | Latin, Old French, Italian (also Arabic and Greek) | ||||||||
| Religion | Roman Catholicism, Eastern Catholicism, Greek Orthodoxy, Syriac Orthodoxy, Islam, Judaism | ||||||||
| Government | Feudal monarchy | ||||||||
| Count | |||||||||
• c.1100 | Roger and Gerard | ||||||||
• 1266–1268 | James of Ibelin | ||||||||
| Historical era | High Middle Ages | ||||||||
• First Crusade | 1100 | ||||||||
• Conquered by Baibars | 1268 | ||||||||
| |||||||||
History
Jaffa was fortified by Godfrey of Bouillon after the First Crusade in 1100, and was unsuccessfully claimed by Daimbert of Pisa, the first Latin Patriarch. It remained part of the royal domain until it was given to Hugh of Le Puiset in 1110. When Hugh II rebelled against King Fulk in 1134 the county was divided into a number of smaller holdings, and Jaffa itself became a royal domain. Soon it was designated as the apanage of Fulk's second son, Amalric. After the siege of Ascalon in 1153, Fulk's first son King Baldwin III conquered Ascalon, and it was added to the territory of his brother Amalric.[1]
It passed in and out of direct royal control when its holders were husbands or close relatives of the then-reigning Monarch or royal heir, or its usufruct went to a member of the royal family. In that period, it usually produced income for one or several members of Amalric's first family. In 1221 it was given to Walter IV of Brienne by his uncle John of Brienne, Walter being married to a granddaughter of King Amalric II, who had held the county as successor of his brother King Guy. Around 1250 it was given to a branch of the Ibelin family. With the capture of Jaffa by Baibars in 1268, the county became titular. It was bestowed anew upon John Perez Fabrice by James II of Cyprus and Jerusalem.
Vassals
The County of Jaffa and Ascalon had a number of vassals of its own:
- Lordship of Ramla
- Lordship of Ibelin
- Lordship of Mirabel (technically separate from the above, but held by the Ibelins)
Counts of Jaffa and Ascalon
(italicized names are titular counts only)
- Roger and Gerard (c. 1100)
- Baldwin I of Jerusalem (1100–1110)
- Hugh I of Jaffa (1110–1118), first cousin of king Baldwin II of Jerusalem
- Albert of Namur (1118–1122), stepfather and regent to Hugh II
- Hugh II of Jaffa (1122–1134), confiscated
- Melisende (1134–1151) with her husband Fulk (1131–1143) and her son Baldwin III (1143–1151)
- Amalric I of Jerusalem (1151–1174)
- Baldwin IV of Jerusalem (1174–1176)
- Sibylla of Jerusalem (1176–1190), with her husbands William of Montferrat (1176–1177) and Guy of Lusignan (1180–1191)
- Geoffrey of Lusignan (1191–1193), brother of Guy of Lusignan
- Amalric II of Jerusalem (1193–1205), with his wife Isabella I (1197–1205)
- Maria of Montferrat (1205–1212), with her husband John of Brienne (1210–1212)
- Isabella II of Jerusalem (1212–1221), under regency of her father John of Brienne
- Walter IV of Brienne (1221–1244), nephew of John of Brienne and husband of Amalric II's granddaughter
- John of Ibelin (1244–1266), Isabella I's half-brother's son
- James of Ibelin, son of John (1266–1268)
Titular counts
- James of Ibelin (1268–1276)
- Guy of Ibelin (1276–1304)
- Hugh of Ibelin (1304–1349)
- Balian II of Ibelin (1349 – c. 1352)
- Guy of Ibelin (c. 1352 – c. 1353)
- Balian of Ibelin (c. 1353 – c. 1365)
- John of Ibelin (c. 1365 – c. 1367)
- Mary of Ibelin (with Regnier le Petit) (c. 1367)
- Florin (c. 1450) perh. the same as
- Jacques de Flory (d. 1463)
- John Perez Fabrice
- Louis Perez Fabrice
- Georges Contaren
- N. Contaren
- Georges Contaren II (c. 1579)
See also
References
- Runciman, A History of the Crusades, Vol. II: The Kingdom of Jerusalem and the Frankish East, 1100-1187, pp. 339-340
Sources
- John L. La Monte, Feudal Monarchy in the Latin Kingdom of Jerusalem, 1100-1291. The Medieval Academy of America, 1932.
- Jonathan Riley-Smith, The Feudal Nobility and the Kingdom of Jerusalem, 1174-1277. The Macmillan Press, 1973.
- Steven Runciman, A History of the Crusades, Vol. II: The Kingdom of Jerusalem and the Frankish East, 1100-1187. Cambridge University Press, 1952.
- Steven Tibble, Monarchy and Lordships in the Latin Kingdom of Jerusalem, 1099-1291. Clarendon Press, 1989.
