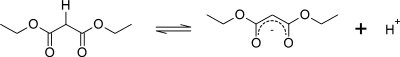Diethyl malonate
Diethyl malonate, also known as DEM, is the diethyl ester of malonic acid. It occurs naturally in grapes and strawberries as a colourless liquid with an apple-like odour, and is used in perfumes. It is also used to synthesize other compounds such as barbiturates, artificial flavourings, vitamin B1, and vitamin B6.
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Diethyl malonate[1] | |
| Preferred IUPAC name
Diethyl propanedioate | |
| Other names
Diethyl malonate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| Abbreviations | DEM |
| 774687 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.006 |
| EC Number |
|
| MeSH | Diethyl+malonate |
PubChem CID |
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C7H12O4 | |
| Molar mass | 160.17 g/mol |
| Appearance | colourless liquid |
| Density | 1.05 g/cm3, liquid |
| Melting point | −50 °C (−58 °F; 223 K) |
| Boiling point | 199 °C (390 °F; 472 K) |
| negligible | |
| Acidity (pKa) | 14 |
| -92.6·10−6 cm3/mol | |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | Harmful (X), Flammable (F) |
| Safety data sheet | Oxford University MSDS |
| Flash point | 200 °C (392 °F; 473 K) |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds |
Dimethyl malonate Malonic acid |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Structure and properties
Malonic acid is a rather simple dicarboxylic acid, with two the carboxyl groups close together. In forming diethyl malonate from malonic acid, the hydroxyl group (-OH) on both of the carboxyl groups is replaced by an ethoxy group (-OEt; -OCH2CH3). The methylene group (-CH2-) in the middle of the malonic part of the diethyl malonate molecule is neighboured by two carbonyl groups (-C(=O)-).[2]
The hydrogen atoms on the carbon adjacent to the carbonyl group in a molecule is significantly more acidic than hydrogen atoms on a carbon adjacent to alkyl groups (up to 30 orders of magnitude). (This is known as the α position with respect to the carbonyl.) The hydrogen atoms on a carbon adjacent to two carbonyl groups are even more acidic because the carbonyl groups help stabilize the carbanion resulting from the removal of a proton from the methylene group between them.
The extent of resonance stabilization of this compound's conjugate base is depicted by the three resonance forms below:
Preparation
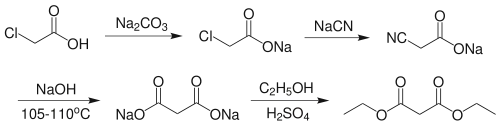
Diethyl malonate may be prepared by reacting the sodium salt of chloroacetic acid with sodium cyanide, followed by base hydrolysis of the resultant nitrile to give the sodium salt of the malonic acid. Fischer esterification gives diethyl malonate:
Reactions
Malonic ester synthesis
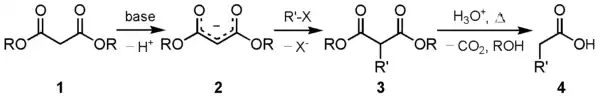
One of the principal uses of this compound is in the malonic ester synthesis. The carbanion (2) formed by reacting diethyl malonate (1) with a suitable base can be alkylated with a suitable electrophile. This alkylated 1,3-dicarbonyl compound (3) readily undergoes decarboxylation with loss of carbon dioxide, to give a substituted acetic acid (4):
In general, salts of the alkoxide anion whose alkyl part corresponds to the one used in the above alkylation are preferred as the base. The use of a conventional base may give base hydrolysis products- for example, sodium hydroxide would simply produce sodium malonate and the alcohol- while other alkoxide salts will cause scrambling by transesterification. Only the "same" alkoxide anion as the one that one used to alkylate the deprotonated active methylenic site will prevent both base hydrolysis and transesterification.
Other reactions
Like many other esters, this compound undergoes the Claisen ester condensations. The advantage of using this compound is that unwanted self-condensation reactions are avoided. Like other esters, this compound undergoes bromination at the alpha position.[3]
Diethyl malonate can be nitrosated with excess sodium nitrite in acetic acid to afford diethyl oximinomalonate, catalytic hydrogenolysis of which in ethanol over Pd/C affords diethyl aminomalonate (DEAM). DEAM can be acetylated to produce diethyl acetamidomalonate (useful in amino-acid synthesis), or can be added with 3-substituted 2,4-diketones to boiling acetic acid to afford in maximal yield variously substituted ethyl pyrrole-2-carboxylates of interest for porphyrin synthesis. (Ref. J.B. Paine III, D. Dolphin, J. Org. Chem. 1985, 50, 5598-5604.)
References
- 'malonic acid' is recognised as a valid, expert-verified name for what would systematically be called 'propanedioic acid' according to ChemSpider.
- "IR spectrum of Malonic acid". Archived from the original on 2010-06-26. Retrieved 2010-02-14.
- C. S. Palmer and P. W. McWherter. "Ethyl Bromomalonate". Organic Syntheses.; Collective Volume, 1, p. 245