Diethynylbenzene dianion
In organic chemistry, a diethynylbenzene dianion is a structure consisting of two ethynyl anions as substituents on a benzene ring. With the chemical formula C
6H
4C2−
4, three positional isomers are possible, differing in the relative positions of the two substituents around the ring:
- ortho-diethynylbenzene dianion
- meta-diethynylbenzene dianion
- para-diethynylbenzene dianion
The gaseous state of anions are of theoretical interest. They have been generated by decarboxylation of benzene dipropynoic acids, using the technique of mass spectrometry.[1][2]
Observation
These dianions were generated in a linear quadrupole ion-trap mass spectrometer. Electrospray ionization (ESI) of the diacid precursor results in the dicarboxylate dianion ([C6H4(C3O2)2]2−) by loss of two hydrogen atoms, identified spectrometrically by its mass-to-charge ratio (m/z) of 106. This dianion was mass-selected and then subjected to collision-induced dissociation (CID), resulting in the consecutive loss of two carbon dioxide molecules to form the diethynyl dianion ([C6H4(C2)2]2−) at 62 m/z. For the ortho isomer, the reaction process is as follows, with the other isomers following an analogous process depending on the isomer of the original diacid:
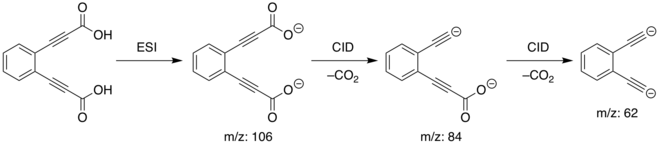
Reactions
Reactions of the gas-phase dianions were studied by reacting with a small quantity of various reagents added to the helium carrier gas in the spectrometer. For example, reaction with deuterium oxide (heavy water) produced the singly-deuterated monanion C6H4(C22H)(C–
2) identified as 126 m/z. Reaction with benzene produced the phenyl anion (77 m/z) highlighting the extreme basicity of the dianion. Attempted reaction with deuterium gas and deuterated methane was not successful despite the favourable thermodynamics; the authors attribute this to the high activation barrier for proton abstraction from those substrates.[1]
Isomers
| Diethynylbenzene dianion isomers | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Names | |||
| Common name | ortho-Diethynylbenzene dianion | meta-Diethynylbenzene dianion | para-Diethynylbenzene dianion |
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol) |
Interactive image | Interactive image | Interactive image |
| InChI |
| ||
| SMILES |
|
|
|
| Properties | |||
| Molecular formula | C10H42– | ||
| Molar mass | 124.142 g·mol−1 | ||
See also
References
- Poad, Berwyck L. J.; Reed, Nicholas D.; Hansen, Christopher S.; Trevitt, Adam J.; Blanksby, Stephen J.; Mackay, Emily G.; Sherburn, Michael S.; Chan, Bun; Radom, Leo (12 January 2018). "Preparation of an ion with the highest calculated proton affinity: ortho-diethynylbenzene dianion". Chemical Science. 7 (9): 6245–6250. doi:10.1039/C6SC01726F. PMC 6024202. PMID 30034765.
- Bergius, Will (19 July 2016). "Basically record breaking". Chemistry World.