Dunlin
The dunlin (Calidris alpina) is a small wader, sometimes separated with the other "stints" in Erolia. The English name is a dialect form of "dunling", first recorded in 1531–2. It derives from dun, "dull brown", with the suffix -ling, meaning a person or thing with the given quality.[2] The genus name is from Ancient Greek kalidris or skalidris, a term used by Aristotle for some grey-coloured waterside birds. The specific alpina is from Latin and means "of high mountains", in this case referring to the Alps.[3]
| Dunlin | |
|---|---|
_juvenile.jpg.webp) | |
| Juvenile, Farmoor Reservoir, Oxfordshire | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Charadriiformes |
| Family: | Scolopacidae |
| Genus: | Calidris |
| Species: | C. alpina |
| Binomial name | |
| Calidris alpina | |
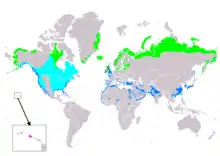 | |
| Range of C. alpina Breeding Resident Non-breeding Passage Vagrant (seasonality uncertain) | |
| Synonyms | |
| |
It is a circumpolar breeder in Arctic or subarctic regions. Birds that breed in northern Europe and Asia are long-distance migrants, wintering south to Africa, southeast Asia and the Middle East. Birds that breed in Alaska and the Canadian Arctic migrate short distances to the Pacific and Atlantic coasts of North America, although those nesting in northern Alaska overwinter in Asia. Many dunlins winter along the Iberian south coast.
Description


Measurements:[4]
- Length: 6.3-8.7 in (16-22 cm)
- Weight: 1.7-2.7 oz (48.7-75.9 g)
- Wingspan: 14.2-15.0 in (36-38 cm)
An adult dunlin in breeding plumage shows the distinctive black belly which no other similar-sized wader possesses. The winter dunlin is basically grey above and white below. Juveniles are brown above with two whitish "V" shapes on the back. They usually have black marks on the flanks or belly and show a strong white wingbar in flight.
The legs and slightly decurved bill are black. There are a number of subspecies differing mainly in the extent of rufous colouration in the breeding plumage and the bill length. Bill length varies between sexes, the females having longer bills than the males.
On the tip of the Dunlin's bill is a soft covering that fills with blood and with many nerve endings, forming a sensitive probe that is used to locate invertebrate prey in mud and sand. Although the bill can look sharp-pointed in dead specimens, in life it is blunt.[5]
Subspecies
- C. a. arctica, (Schiøler, 1922), breeds in northeast Greenland.
- C. a. schinzii, (Brehm & Schilling, 1822), breeds in southeast Greenland, Iceland, the British Isles, Scandinavia & the Baltic.
- C. a. alpina, (Linnaeus, 1758), breeds in northern Europe and northwest Siberia.
- C. a. centralis, (Buturlin, 1932), breeds in north-central and northeast Siberia.
- C. a. sakhalina, (Vieillot, 1816), breeds in eastern Russia to the Chukchi Peninsula.
- C. a. kistchinski, Tomkovich, 1986, breeds around the Sea of Okhotsk to Kuril Islands and Kamchatka.
- C. a. actites, Nechaev & Tomkovich, 1988, breeds on Sakhalin.
- C. a. arcticola, (Todd, 1953), breeds from northwest Alaska to northwest Canada.
- C. a. pacifica, (Coues, 1861), breeds in western and southern Alaska.
- C. a. hudsonia, (Todd, 1953), breeds in central Canada.
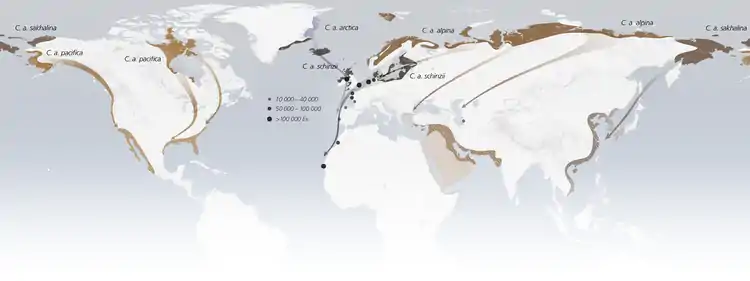 Distribution of subspecies, migration routes, and major European wintering sites |
Nesting


The nest is a shallow scrape on the ground lined with vegetation, into which typically four eggs are laid and incubated by the male and female parents. Chicks are precocial, however are brooded during early development. They start to fly at approximately three weeks of age. The majority of brood care is provided by the male, as the female deserts the brood and often leaves the breeding area.
The call is a typical sandpiper "peep", and the display song a harsh trill.
The dunlin is one of the species to which the Agreement on the Conservation of African-Eurasian Migratory Waterbirds (AEWA) applies.
Apparent hybrids between this species and the white-rumped sandpiper as well as with the purple sandpiper have been reported from the Atlantic coasts of North America[6][7] and Europe,[8] respectively.
Behaviour
The dunlin is highly gregarious in winter, sometimes forming large flocks on coastal mudflats or sandy beaches. Large numbers can often be seen swirling in synchronized flight on stop-overs during migration or on their winter habitat.
This bird is one of the most common waders throughout its breeding and wintering ranges, and it is the species with which other waders tend to be compared. At 17–21 cm (6.7–8.3 in) length and with a 32–36 cm (13–14 in) wingspan, it is similar in size to a common starling, but stouter, with a thicker bill.
The dunlin moves along the coastal mudflat beaches it prefers with a characteristic "sewing machine" feeding action, methodically picking small food items. Insects form the main part of the dunlin's diet on the nesting grounds; it eats molluscs, worms and crustaceans in coastal areas.

Dunlin are small migratory waders, however they show strong philopatry with individuals of the Southern Dunlin (Calidris alpina schinzii) in Sweden and Finland returning to, or very close to, their natal patches. Habitat fragmentation has reduced the availability of habitat patches to these birds through reducing patch size and increasing patch isolation. This reduced connectivity between patches has reduced the movements of Dunlin leaving them more susceptible to inbreeding in these locations. Future management for the conservation of Southern Dunlin should include increasing the connectivity between habitat patches.[9]
References
- BirdLife International (2012). "Calidris alpina". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2012. Retrieved 26 November 2013.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- "Dunlin". Oxford English Dictionary (Online ed.). Oxford University Press. (Subscription or participating institution membership required.)
- Jobling, James A (2010). The Helm Dictionary of Scientific Bird Names. London: Christopher Helm. pp. 42, 84. ISBN 978-1-4081-2501-4.
- "Dunlin Identification, All About Birds, Cornell Lab of Ornithology". www.allaboutbirds.org. Retrieved 2020-09-27.
- Kaiser, Gary W. (2007). The Inner Bird: Anatomy and Evolution. UBC Press. p. 24. ISBN 978-0-7748-1344-0.
- McLaughlin, K.A.; Wormington, A. (2000). "An apparent Dunlin × White-rumped Sandpiper hybrid". Ontario Birds. 18 (1): 8–12.
- Wilson, Angus. "A putative hybrid white-rumped sandpiper × dunlin from the east coast of the USA". Ocean Wanderers. Retrieved 11 October 2006.
- Millington, Richard (1994). "A mystery Calidris at Cley". Birding World. 7 (2): 61–63. Archived from the original on 17 June 2004.
- Pakanen, V.-M.; Koivula, K.; Flodin, L.-Å.; Grissot, A.; Hagstedt, R.; Larsson, M.; Pauliny, A.; Rönkä, N.; Blomqvist, D. (2017). "Between-patch natal dispersal declines with increasing natal patch size and distance to other patches in the endangered Southern Dunlin Calidris alpina schinzii". Ibis. 159 (3): 611–622. doi:10.1111/ibi.12463.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Calidris alpina. |
| Wikispecies has information related to Calidris alpina. |
- BirdLife species factsheet for Calidris alpina
- "Calidris alpina". Avibase.

- "Dunlin media". Internet Bird Collection.
- Dunlin Species Account - Cornell Lab of Ornithology
- Dunlin - Calidris alpina - USGS Patuxent Bird Identification InfoCenter
- Ageing and sexing (PDF; 1.6 MB) by Javier Blasco-Zumeta & Gerd-Michael Heinze
- Dunlin photo gallery at VIREO (Drexel University)
- Interactive range map of Calidris alpina at IUCN Red List maps
- Audio recordings of Dunlin on Xeno-canto.
- Calidris alpina in Field Guide: Birds of the World on Flickr
- Dunlin media from ARKive


.jpg.webp)