Edenred
Edenred is a French company specialised in prepaid corporate services. The Group is independent since June 2010 following the split with Accor. Formerly known as Accor Services, Edenred is the inventor of Ticket Restaurant, created in 1962, and a leading distributor of meal vouchers. Today, Edenred offers solutions for employee benefits, loyalty programs, fleet and mobility and corporate payment. 44 million employees use Edenred services worldwide.[2]
.png.webp) Edenred logo | |
| Type | Public limited company |
|---|---|
| Euronext: EDEN CAC Next 20 Component | |
| Industry | Prepaid corporate services |
| Founded | June 29, 2010[note 1] |
| Headquarters | , |
Area served | Worldwide |
Key people | Bertrand Dumazy (Chairman and CEO) |
| Products | Ticket Restaurant® |
| Revenue | €1.339 billion (2017) |
Number of employees | Over 8,000 employees as of February 20, 2018 |
| Website | Edenred.com |
History
Inspired by the original Luncheon Voucher, a concept launched in the United Kingdom in 1954, Jacques Borel created Ticket Restaurant on the French market in 1962. A French government decree, passed in 1967, officially recognized the meal voucher as an employee benefit. The concept was launched outside France starting in 1976.
Employee benefits continued to grow worldwide, first in Europe and then in Latin America, thanks to two programs: Ticket Restaurant and Ticket Alimentación. The Ticket Restaurant® entity, which had been a subsidiary of the Accor Group since 1983, set itself a new course in 1998, when it became Accor Services.
From the 2000s, the pace of growth increased, giving rise to "incentive and rewards" solutions, in Europe and Asia, in addition to Expense management, solutions, with the development of Ticket Car in Latin America.
Following the split of Accor's hotel and prepaid services businesses, Accor Services became Edenred in June 2010.[3] The new group became independent, defined its corporate mission project and was listed on NYSE Euronext Paris on July 2, 2010. Jacques Stern was appointed chairman and chief executive officer.
The group sped up its transformation by making digital technology a pillar of its strategy and launched the Ticket Restaurant® card in France in April 2014. As of 2015, 78% of the group's business volume around the world was generated from digital solutions.[4][5]
Edenred also launched new solutions including Ticket Plus Card in Germany (staple goods: food, fuel, meals), Ticket Cultura® in Brazil (cultural goods and services),[6] Fides Cloud® Loyalty Software solutions in India which is managed by its subsidiary Accentiv India Pvt. Ltd.[7]
Moreover, Edenred consolidated its development strategy for its Expense management activity, by finalizing the acquisition of a 34% stake in UTA in Germany and by establishing a major partnership in Brazil with Daimler[8] in 2015.
Bertrand Dumazy became Chairman and Chief Executive Officer of Edenred on October 26, 2015.[9]
On May 31, 2016, Edenred finalized its acquisition of Embratec's operations in Brazil, creating a leading player in this fast-growing segment.[10]
In January 2017, Edenred takes over UTA majority, one of the leading providers of fuel and service cards in Europe.[11]
On June 14, 2017, Edenred unveiled its new global identity. The group will market all of its solutions in 42 countries under the Edenred brand.[12]
Ownership
According to the company website: 94.6% institutional investors, 4.8% individual shareholders, 0.6% own shares.[13]
Expansion
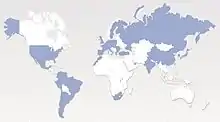
Edenred currently operates in 45 countries and over 8,000 employees. Has been operating in Venezuela for 26 years. The group has moved into new countries since 2010: Finland in 2011, Japan in 2012, Russia, the United Arab Emirates in 2014 and Moldova in 2018.[15]
Challenge to Public Procurement in the UK
In 2014, Edenred initiated a high court case in which it argued that the UK Treasury was in breach of EU public procurement law in varying a contract with Atos IT Services Ltd to take account of changes in tax-free childcare law, without initiating a new procurement process. Their case was taken to the Supreme Court in 2015 but Edenred were unsuccessful, the court ruling that the modifications made to Atos' contract were not "substantial".[16]
References
Footnotes
- Date of demerger from Accor.
Citations
- "Company Description: Edenred". businessweek.com. BusinessWeek. Retrieved 12 August 2012.
- "Information about the Edenred group". www.edenred.com. Retrieved 2015-11-13.
- "press release Edenred" (PDF).
- "PR HY2015" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2015-11-17.
- "Edenred 2017 annual results press release" (PDF). Edenred.
- "PR Ticket Cultura".
- "Loyalty Programs from India's No. 1 in loyalty services". Accentiv' India. Retrieved 2020-09-03.
- "Edenred / Daimler Reuters".
- "B.Dumazy / Edenred Reuters".
- http://www.edenred.com/en/medias/news-and-press-releases/edenred-finalizes-its-alliance-embratec-brazil
- https://www.uta.com/tankkarte/0/12255E528CAAB35DC12580AE0022D870/$FILE/PR_Edenred_UTA_EN_final.docx
- http://www.edenred.com/en/medias/news-and-press-releases/edenred-unveils-new-global-identiy
- "Edenred capital structure". Archived from the original on 2017-06-06.
- "Edenred Worldwide - The Edenred Group". www.edenred.com. Retrieved 2015-11-13.
- "Edenred to issue meal benefits in the Republic of Moldova in 2018". Business review.
- Supreme Court, Edenred (UK Group) Limited and another (Appellants) v Her Majesty’s Treasury and others (Respondents) [2015 UKSC 45], published 1 July 2015, accessed 12 December 2020
External links
![]() Media related to Edenred at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Edenred at Wikimedia Commons