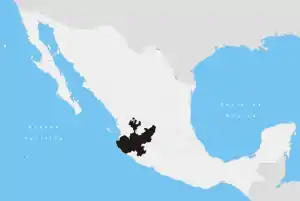
El Arenal, Jalisco
El Arenal is a town and municipality in the state of Jalisco in central-western Mexico. El Arenal is known as the gateway to the so-called "blue agave" region in the Jaliscan Highlands (Los Altos de Jalisco). The municipality has an area of approximately 182 square kilometres (70 sq mi).
El Arenal | |
|---|---|
Municipality and city | |
 | |
 Coat of arms | |
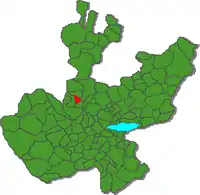 Location of the municipality in Jalisco | |
 El Arenal Location in Mexico | |
| Coordinates: 20°42′N 103°37′W | |
| Country | |
| State | Jalisco |
| Area | |
| • Total | 181.81 km2 (70.20 sq mi) |
| Population (2005) | |
| • Total | 13,574 |
As of 2005, the municipality had a total population of 13,574.[1]
The Tequila Factories
The municipality includes La Providencia (claimed to be the first to export tequila to Europe), Cascahuín, Don Rigo and Don Valente factories.
Toponymy
Its name derives from the terrestrial conditions of the first settlement, since there was a lot of sand in the valley.
Coat of arms
The municipal coat of arms is divided into four quarters. In the upper part there are some mounds of sand, an abundant material at the time of the first settlement, which gave its name to the municipality, and an agave plant, the cultivation of which has become economically important in the region. In the lower sections are the figures of a milpa (cultivated field ) and a cow, representing local agriculture, the main economic activity. In the upper central part, crowning the shield, the legend appears: "Homeland, Loyalty and Work", values ascribed to the natives of this municipality.
The City Council ran a contest for the best design of a coat of arms in commemoration of the 69th anniversary of the constitution of the municipality, with the winning design being submitted by Ana Elda Rosas Jiménez. The official coat of arms of the municipality was approved in the Cabildo session of May 30, 1992.
History
Its primitive settlers were Nahoa s. Shortly before the arrival of the conquerors, the Purépecha people found the region in its failed attempt to seize the salt flats on the beaches. Archeological studies indicated that the area may have been the center of the civilization that built the Guachimontones pyramids.[2] The founders of modern El Arenal were: Familias Ruiz, Castañeda, Ocampo, Ibarra, Rosales, and Sanchez, Donato Ruiz, Miguel Rosales Armas, Enrique Rosales Sánchez and his brother Emiliano; Manuel Ruiz and Andrés Ibarra. Its name derives from the ground conditions of the first settlement, since there was a lot of sand in the valley. Until 1922, El Arenal was a delegation of the municipality of Amatitán. By decree number 2270, published on June 5 of 1923, the El Arenal police station was made a municipality.
In 1925 the main square was built, having opened the streets and the beginning of the construction of the temple. In 1938, by decree number 4421, the municipality of El Arenal expands its large settlements.
Physical geography
Situation
The municipality of Arenal is located in the northwest of the state, at coordinates 20º42'44 to 20º52'15 north latitude and 103º37'04 at 103º42'45 west longitude, at an altitude of 1450 meters above sea level.
Delimitation
It borders the municipalities of Amatitán to the north and west, to the south with Tala and to the east it borders Zapopan.
Extension
The extension of the El Arenal municipality is 181.81 km².
Geology
It is considered within the Tertiary Period; The subsoil is made up of limestone, extrusive igneous rocks, rhyolite, andesite, basalt, tuff and volcanic gap.
Topography
Most of the municipality has semi-flat areas with elevations of 1550 to 1600 meters above sea level. They are followed in proportion by flat areas with elevations from 1400 to 1550 meters above sea level, and in a minimal proportion are rugged areas with elevations from 1600 to 1840 meters above sea level.
Hydrography
Belonging to the Lerma-Chapala-Santiago basin and the sub-basin of the Santiago-Cuisillos-Juchipila rivers; Its main currents are the Salado and Arenal rivers and the Las Tortugas, Arenal, Agua Dulce and Laguna Colorada streams.
Floors
The composition of the soil corresponds to those of the haplic Feozem type associated with the eutrophic Regosol and pelvic Vertisol.
Climate
The climate of the municipality has been classified as semi-dry; with winter and spring dry and semi-warm, with no defined winter season. The average annual temperature is 20 °C., And an average rainfall of 1,103.6 mm, with rainfall in the months of June and July. The prevailing winds are in the northwest direction. The annual average of days with frosts is 13.
Flora and fauna
The hills are covered with oak and spiny low vegetation. The hills and hillsides are covered with huizache, nopal, granjeno, cat's claw and some fruit trees. The fauna is represented by species such as deer, squirrel, rabbit, reptile and other minor species.
Natural resources
The natural wealth that the municipality has is represented by 900 hectares of forest. Its mineral resources are deposits of non-metallic elements: lime, quarry, sand, gravel, clay, kaolin, diatamite, quartz and feldspar.
Social and communications infrastructure
Health care is provided by the Ministry of Health of the State Government and by the Mexican Social Security Institute (IMSS). The social welfare area is covered by the System for the Integral Development of the Family (DIF), through the Municipal Committee in support of its different programs. There are grocery stores in the municipal seat and other locations. In the municipal head there is a public market where the inhabitants of smaller towns buy products. There is also a civic plaza, sports centers and recreational centers. There are also sites with natural attractions such as the Las Tinajas temporary spa and the Las Tortugas dam. Home ownership is fundamentally private. Counting much of them with the services of drinking water, electricity and drainage. The predominant materials in the construction of the houses are mostly adobe and in a smaller proportion of partition walls, with tile roofs and brick vaults. With regard to basic services, 93.5% of the inhabitants have drinking water; in sewerage the coverage is 94.4% and in the electricity service 97.4%. Ground transportation can be done through the Mexico-Guadalajara-Nogales highway. It has a network of rural roads and dirt roads in the towns. The municipality is integrated into the state rail network, through the Guadalajara-Nogales-Mexicali line of the Pacific Rail System (recently privatized company). It has the service of direct line of trucks, as well as buses of passage. Regarding the media, there is mail, telegraph, telephone, radiotelephony and radio and television signal.
Economy
The corn and agave crops stand out. Cattle of meat, milk and for work, pig and poultry are raised. The most developed industrial activity in this municipality is the elaboration of tequila. The manufacture of food products is also important and cold meats are packed. The mining resources available to the municipality are represented by non-metallic minerals such as lime, quarry, sand, gr
Tourism
Santa Quintera is a hacienda located northeast of the town of El Arenal. The hacienda contains both agave fields as well as rocky hills with pine and holm oak forest. It is also home to the Mesa Alta archeological zone belonging to the Volador culture. It contains two Mesoamerican ballcourts along with a circular pyramid.[2]
References
- "El Arenal". Enciclopedia de los Municipios de México. Instituto Nacional para el Federalismo y el Desarrollo Municipal. Archived from the original on March 9, 2007. Retrieved April 13, 2009.
- "Santa Quiteria: Jalisco's next tourism magnet or sad example of patrimonicide?". Mexico News Daily. August 7, 2020. Retrieved August 20, 2020.