Enneagram of Personality
The Enneagram of Personality, or simply the Enneagram (from the Greek words ἐννέα [ennéa, meaning "nine"] and γράμμα [grámma, meaning something "written" or "drawn"[1]]), is a model of the human psyche which is principally understood and taught as a typology of nine interconnected personality types. Although the origins and history of many of the ideas and theories associated with the Enneagram of Personality are a matter of dispute, contemporary Enneagram theories are principally derived from the teachings of the Bolivian psycho-spiritual teacher Oscar Ichazo from the 1950s and the Chilean psychiatrist Claudio Naranjo from the 1970s. Naranjo's theories were also influenced by some earlier teachings about personality by George Gurdjieff and the Fourth Way tradition.
| Part of a series on |
| Psychology |
|---|
 |
|
As a typology the Enneagram defines nine personality types (sometimes called "enneatypes"), which are represented by the points of a geometric figure called an enneagram,[2] which indicate connections between the types. There are some different schools of thought among Enneagram teachers and their understandings are not always in agreement.[2]
The Enneagram of Personality has been widely promoted in both business management and spirituality contexts through seminars, conferences, books, magazines, and DVDs.[3][4] In business contexts it is generally used as a typology to gain insights into workplace interpersonal dynamics; in spirituality it is more commonly presented as a path to higher states of being, essence, and enlightenment. Both contexts say it can aid in self-awareness, self-understanding and self-development.[3]
There has been limited formal psychometric analysis of the Enneagram and the peer-reviewed research that has been done has not been widely accepted within the relevant academic communities.[5]
History
The origins and historical development of the Enneagram of Personality are matters of dispute. Wiltse and Palmer[6] have suggested that similar ideas to the Enneagram of Personality are found in the work of Evagrius Ponticus, a Christian mystic who lived in 4th century Alexandria. Evagrius identified eight logismoi ("deadly thoughts") plus an overarching thought he called "love of self". Evagrius wrote, "The first thought of all is that of love of self (philautia); after this, [come] the eight."[7] In addition to identifying eight deadly thoughts, Evagrius also identified eight "remedies" to these thoughts.[6]
G. I. Gurdjieff (died 1949) is credited with making the word enneagram and the enneagram figure commonly known[8] (see Fourth Way enneagram). He did not, however, develop the nine personality types associated with the Enneagram of Personality.
Oscar Ichazo (1931–2020) is generally recognized as the principal source[8] of the contemporary Enneagram of Personality which is largely derived from some of Ichazo's teachings, such as those on ego-fixations, holy ideas, passions and virtues. The Bolivian-born Ichazo began teaching programs of self-development in the 1950s. His teaching, which he calls "Protoanalysis", uses the enneagram figure among many other symbols and ideas. Ichazo founded the Arica Institute which was originally based in Chile before moving to the United States[2] and coined the term "Enneagram of Personality".[3]
Claudio Naranjo (1932–2019) was a Chilean-born psychiatrist who first learned about the Enneagram of Personality from Ichazo at a course in Arica, Chile. He then began developing and teaching his own understanding of the Enneagram in the United States in the early 1970s, influencing others including some Jesuit priests who adapted the Enneagram for use in Christian spirituality. Ichazo disowned Naranjo and the other teachers on what he felt were misinterpretations and uses of the Enneagram. Among Naranjo's early students there are also differing understandings of Enneagram theory.[2] Numerous other authors also began publishing widely read books on the Enneagram of Personality in the 1980s and 1990s, including Don Richard Riso (1987), Helen Palmer (1988), Eli Jaxon-Bear (1989), Elizabeth Wagele (1994), and Richard Rohr (1995).
Figure
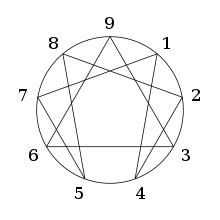
The enneagram figure is usually composed of three parts; a circle, an inner triangle (connecting 3-6-9) and an irregular hexagonal "periodic figure" (connecting 1-4-2-8-5-7). According to esoteric spiritual traditions,[9] the circle symbolizes unity, the inner triangle symbolizes the "law of three" and the hexagon represents the "law of seven" (because 1-4-2-8-5-7-1 is the repeating decimal created by dividing one by seven in base 10 arithmetic).[10] These three elements constitute the usual enneagram figure.[11]
Nine types
The table below offers some of the principal characteristics of the nine types along with their basic relationships. This table expands upon Oscar Ichazo's ego fixations, holy ideas, passions, and virtues[12] primarily using material from Understanding the Enneagram: The Practical Guide to Personality Types (revised edition) by Don Richard Riso and Russ Hudson.[13] Other theorists may disagree on some aspects. The types are normally referred to by their numbers, but sometimes their "characteristic roles" (which refers to distinctive archetypal characteristics) are used instead.[14] Various labels for each type are commonly used by different authors and teachers. The "stress" and "security" points (sometimes referred to as the "disintegration" and "integration" points) are the types connected by the lines of the enneagram figure and are believed by some to influence a person in more adverse or relaxed circumstances. According to this theory, someone with a primary One type, for example, may begin to think, feel and act more like someone with a Four type when stressed or a Seven type when relaxed.
| Type | Characteristic role | Ego fixation | Holy idea | Basic fear | Basic desire | Temptation | Vice/Passion | Virtue | Stress/ Disintegration | Security/ Integration |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Reformer, Perfectionist | Resentment | Perfection | Corruptness, imbalance, being bad | Goodness, integrity, balance | Hypocrisy, hypercriticism | Anger | Serenity | 4 | 7 |
| 2 | Helper, Giver | Flattery (Ingratiation) | Freedom, Will | Being unloved | To feel love | Deny own needs, manipulation | Pride | Humility | 8 | 4 |
| 3 | Achiever, Performer | Vanity | Hope, Law | Worthlessness | To feel valuable | Pushing self to always be "the best" | Deceit | Truthfulness, Authenticity | 9 | 6 |
| 4 | Individualist, Romantic | Melancholy (Fantasizing) | Origin | Having no identity or significance | To be uniquely themselves | To overuse imagination in search of self | Envy | Equanimity (Emotional Balance) | 2 | 1 |
| 5 | Investigator, Observer | Stinginess (Retention) | Omniscience, transparency | Helplessness, incapability, incompetence | Mastery, understanding | Replacing direct experience with concepts | Avarice | Non-Attachment | 7 | 8 |
| 6 | Loyalist, Loyal Skeptic | Cowardice (Worrying) | Faith | Being without support or guidance | To have support and guidance | Indecision, doubt, seeking reassurance | Fear | Courage | 3 | 9 |
| 7 | Enthusiast, Epicure | Planning (Anticipation) | Wisdom, Plan | Being unfulfilled, trapped, deprived | To be satisfied and content | Thinking fulfillment is somewhere else | Gluttony | Sobriety | 1 | 5 |
| 8 | Challenger, Protector | Vengeance (Objectification) | Truth | Being controlled, harmed, violated | Self-protection | Thinking they are completely self-sufficient | Lust (Forcefulness) | Innocence | 5 | 2 |
| 9 | Peacemaker, Mediator | Indolence (Daydreaming) | Love | Loss, fragmentation, separation | Wholeness, peace of mind | Avoiding conflicts, avoiding self-assertion | Sloth (Disengagement) | Action | 6 | 3 |
Wings
Most, but not all, Enneagram of Personality theorists teach that a person's basic type is modified, at least to some extent, by the personality dynamics of the two adjacent types as indicated on the enneagram figure. These two types are often called "wings". A person with the Three personality type, for example, is understood to have points Two and Four as their wing types. The circle of the enneagram figure may indicate that the types or points exist on a spectrum rather than as distinct types or points unrelated to those adjacent to them. A person may be understood, therefore, to have a core type and one or two wing types which influence but do not change the core type.[15][16]
Connecting lines
For some Enneagram theorists the lines connecting the points add further meaning to the information provided by the descriptions of the types. Sometimes called the "security" and "stress" points, or points of "integration" and "disintegration", some theorists believe these connected points also contribute to a person's overall personality. From this viewpoint, therefore, at least four other points affect a person's overall personality; the two points connected by the lines to the core type and the two wing points.[17][18] The earlier teachings about the connecting lines are now rejected or modified by many Enneagram teachers, including Claudio Naranjo who developed them.
Instinctual subtypes
Each of the personality types is usually understood as having three "instinctual subtypes". These subtypes are believed to be formed according to which one of three instinctual energies of a person is dominantly developed and expressed. The instinctual energies are usually called "self-preservation", "sexual" (also called "intimacy" or "one-to-one") and "social". On the instinctual level, people may internally stress and externally express the need to protect themselves (self-preservation), to connect with important others or partners (sexual), or to get along or succeed in groups (social).[19] From this perspective, there are twenty-seven distinct personality patterns, because people of each of the nine types also express themselves as one of the three subtypes.[20] An alternative approach to the subtypes looks at them as three domains or clusters of instincts that result in increased probability of survival (the "preserving" domain), increased skill in navigating the social environment (the "navigating" domain) and increased likelihood of reproductive success (the "transmitting" domain).[21] From this understanding the subtypes reflect individual differences in the presence of these three separate clusters of instincts.
It is believed people function in all three forms of instinctual energies but one may dominate. According to some theorists, another instinct may also be well-developed and the third often less developed.[22]
Criticism
While Enneagram teachings have attained some degree of popularity, they have also received criticism including accusations of being pseudoscience, subject to interpretation and difficult to test or validate scientifically, "an assessment method of no demonstrated reliability or validity".[23] The scientific skeptic Robert Todd Carroll included the Enneagram in a list of pseudoscientific theories that "can't be tested because they are so vague and malleable that anything relevant can be shoehorned to fit the theory".[24] However, in the book The Enneagram: a Journey of Self Discovery (1984), the nine types were categorized in accordance with the work of psychoanalyst Karen Horney, for a more scientific basis of the Enneagram.[25]
The Enneagram has also received criticism from some religious perspectives. In 2000, the United States Conference of Catholic Bishops' Committee on Doctrine produced a draft report on the origins of the Enneagram to aid bishops in their evaluation of its use in their dioceses. The report identified aspects of the intersection between the Enneagram and Roman Catholicism which, in their opinion, warranted scrutiny with potential areas of concern, stating, "While the enneagram system shares little with traditional Christian doctrine or spirituality, it also shares little with the methods and criteria of modern science... The burden of proof is on proponents of the enneagram to furnish scientific evidence for their claims."[26] Partly in response to some Jesuits and members of other religious orders teaching a Christian understanding of the Enneagram of Personality, a 2003 Vatican document called Jesus Christ, the Bearer of the Water of Life. A Christian Reflection on the 'New Age' said that the Enneagram "when used as a means of spiritual growth introduces an ambiguity in the doctrine and the life of the Christian faith."[27][28]
References
- "Strong's Greek: 1121. γράμμα (gramma) -- that which is drawn or written, i.e. a letter". biblesuite.com.
- "Page 569". in Ellis, Albert; Abrams, Mike; Dengelegi Abrams, Lidia (2008). "Religious, New Age, and Traditional Approaches to Personality". Personality theories: critical perspectives. SAGE. pp. 529–576. doi:10.4135/9781452231617.n17. ISBN 978-1-4129-7062-4.
Ichazo has disowned Naranjo, Palmer and the other Jesuit writers on the Enneagram on the grounds that his descriptions of the nine types represent ego fixations that develop in early childhood in response to trauma.
- Clarke, Peter (2004). Encyclopedia of new religious movements. Taylor & Francis. ISBN 0-203-48433-9.
- Kemp, Daren (2004). New age: a guide : alternative spiritualities from Aquarian conspiracy to Next Age. Edinburgh University Press. ISBN 978-0-7486-1532-2.
- Thyer, Dr Bruce A.; Pignotti, Monica (15 May 2015). Science and Pseudoscience in Social Work Practice. Springer Publishing Company. p. 49. ISBN 9780826177681.
- Wiltse, V.; Palmer, H. (July 2011). "Hidden in plain sight: Observations on the origin of the Enneagram". The Enneagram Journal. 4 (1): 4–37.
- Harmless, W.; Fitzgerald, R.R. (2001). "The saphhire light of the mind: The Skemmata of Evagrius Ponticus". Theological Studies. 62 (3): 498–529. doi:10.1177/004056390106200303.
- "International Enneagram Association - History". internationalenneagram.org. Archived from the original on 25 November 2012.
- Palmer, The Enneagram, p.36
- "The Theory of Process and The Law of Seven". rahul.net.
- Wagele, Enneagram Made Easy, pp. 1–11
- Ichazo, Oscar (1982). Interviews with Oscar Ichazo. Arica Institute Press. ISBN 978-0-916-55403-3.
- Riso, Don Richard; Hudson, Russ (2000). Understanding the Enneagram: The Practical Guide to Personality Types. Houghton Mifflin Harcourt. ISBN 978-0-618-00415-7.
Understanding the Enneagram: The Practical Guide to Personality Types, revised addition.
- Baron, Renee. What Type Am I: Discover Who You Really Are. p. 162.
- Riso, Wisdom of the Enneagram, p. 19.
- Wagner, Wagner Enneagram Personality Style Scales, p. 2.6.
- Riso, Wisdom of the Enneagram, pp. 87–88.
- Wagner, Wagner Enneagram Personality Style Scales, p. 30.
- Palmer, The Enneagram in Love and Work, p. 29
- Maitri, The Spiritual Dimension of the Enneagram, pp. 263–264
- "The Instincts: Taking a Broader View" Archived 7 July 2011 at the Wayback Machine, by Mario Sikora, Enneagram Monthly, June 2007.
- Riso, The Wisdom of the Enneagram, pp. 70–71
- "Page 64". in Thyer, Dr Bruce A.; Pignotti, Monica (2015). "Pseudoscience in Clinical Assessment". Science and Pseudoscience in Social Work Practice. pp. 33–74. doi:10.1891/9780826177698.0002. ISBN 978-0-8261-7768-1.
- Carroll, Robert (11 January 2011). The Skeptic's Dictionary: A Collection of Strange Beliefs, Amusing Deceptions, and Dangerous Delusions. John Wiley & Sons. p. 306. ISBN 978-1-118-04563-3.
- Wagner, Jerome. "Karen Horney Meets the Enneagram".
- "A Brief Report On The Origins Of The Enneagram", Draft from the U.S. bishops' Secretariat for Doctrine and Pastoral Practices, 10 October 2000, corrected 23 October 2001
- Richard Smoley, Jay Kinney (2006). Hidden Wisdom: A Guide to the Western Inner Traditions. Western Mystery Tradition Series (revised, illustrated ed.). Quest Books. p. 229. ISBN 978-0-8356-0844-2.
- "Jesus Christ, the Bearer of the Water of Life. A Christian Reflection on the 'New Age'" Archived 1 October 2013 at the Wayback Machine, Pontifical Council for Culture, Pontifical Council for Interreligious Dialogue
Further reading
- Almaas, A. H. (2000). Facets of Unity: The Enneagram of Holy Ideas. Shambhala. ISBN 0-936713-14-3.
- Goldberg, Michael J. (1999). 9 Ways of Working. Marlowe & Company. ISBN 1-56924-688-2.
- Maitri, Sandra (2005). The Enneagram of Passions and Virtues: Finding the Way Home. Tarcher. ISBN 1-58542-406-4.
- Naranjo, Claudio (1997). Transformation Through Insight: Enneatypes in Life. Hohm Press. ISBN 0-934252-73-4.
- Naranjo, Claudio (1994). Character and Neurosis: An Integrative View. Gateways/IDHHB, Inc. ISBN 0-89556-066-6.
- Palmer, Helen (1991). The Enneagram: Understanding Yourself and Others in Your Life. HarperSanFrancisco. ISBN 0-06-250683-8.
- Palmer, Helen (1996). The Enneagram in Love and Work: Understanding your Intimate and Business Relationships. HarperOne. ISBN 0-06-250721-4.
- Riso, Don Richard; Hudson, Russ (1999). Wisdom of the Enneagram. Bantam. ISBN 0-553-37820-1.
- Wagele, Elizabeth; Ingrid Stabb (2010). The Career Within You. HarperOne. ISBN 978-0-06-171861-8.
- Riso, Don Richard; Hudson, Russ (2000). Understanding the Enneagram; the practical guide to personality types. Houghton Mifflin Company. ISBN 0-618-00415-7.
- Daniels, David (2000). The Essential Enneagram. HarperOne. ISBN 0-06-251676-0.
- Gilbert, Eleonora (2015). Conversations on the Enneagram. Cherry Red Books. ISBN 978-1-909454-34-7.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Enneagram (Personality). |
- International Enneagram Association website
- "enneagram". The Skeptic's Dictionary.
