Erivan Khanate
The Erivan Khanate[lower-alpha 1] (Persian: خانات ایروان – Xānāt-e Iravān; Armenian: Երևանի խանություն – Yerevani khanut’yun; Azerbaijani: İrəvan xanlığı – ایروان خانلیغی), also known as Chokhur-e Sa'd,[2][lower-alpha 2] was a khanate (i.e. province) that was established in Afsharid Iran in the eighteenth century. It covered an area of roughly 19,500 km2,[2] and corresponded to most of present-day central Armenia, of the Iğdır Province, Kağızman district of the Kars Province of present-day Turkey and the Sharur and Sadarak districts of the Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic of the present-day Azerbaijan Republic.
Erivan Khanate خانات ایروان – Xānāt e Iravān | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1747–1828 | |||||||||
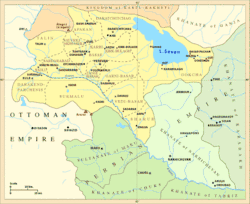 Erivan Khanate c. 1800. | |||||||||
| Status | Khanate Under Iranian suzerainty[1] | ||||||||
| Capital | Erivan (Yerevan) | ||||||||
| Common languages | Persian (official), Azerbaijani, Kurdish, Armenian | ||||||||
| History | |||||||||
• Established | 1747 | ||||||||
• Disestablished | 1828 | ||||||||
| |||||||||
The provincial capital of Erivan was a center of the Iranian defenses in the Caucasus during the Russo-Iranian Wars of the 19th century.[2] As a result of the Iranian defeat in the last Russo-Iranian war, it was occupied by Russian troops in 1827[4] and then ceded to the Russian Empire in 1828 in accordance with the Treaty of Turkmenchay. Immediately following this, the territories of the former Erivan Khanate and the Nakhchivan Khanate were joined to form the Armenian Oblast of the Russian Empire.
History
Administration
During the Iranian rule, the kings (shahs) appointed the various governors to preside over their domains, thus creating an administrative center. These governors usually carried the title of "khan" or "beglarbeg",[5] as well as the title of sardār (“chief”). Prior to the establishment of the khanate (i.e. province),[6] the Iranians had used the Erivan Province (also known as Chokhur-e Sa'd) to govern roughly the same area. Both the Safavid era province, as well as the administrative entity of the Zand and Qajar era, were alternatively known by the name of Chokhur-e Sa'd.[3]
In the Qajar era, members of the royal Qajar dynasty were appointed as governors of the Erivan khanate, until the Russian occupation in 1828.[7] The heads of the provincial government of the Erivan Khanate were thus directly related to the central ruling dynasty.[8] Administratively, the khanate was divided into fifteen administrative districts called maḥals with Persian as its official language.[9][10][11] The local bureaucracy was modeled on that of the central government, located in Tehran.[12]
Together with the Nakchivan Khanate, the area made up part of Iranian Armenia (also known as Persian Armenia).[13][lower-alpha 3] The Erivan Khanate made up the bulk of Iranian Armenia.[15] The remaining fringes of historic Armenia under Iranian rule were part of the Karabakh Khanate, Ganja Khanate, and Kartli-Kakheti.[13]
Events and ceding to Russia
Nader Shah (r. 1736-1747) organized the region into four khanates; Erivan, Nakhchivan, Karabakh, and Ganja.[16] Following his death in 1747, the territory became part of the Zands.[17] After the Zand period, it passed to the Iranian Qajars. During the Qajar period, the khanate was considered to be quite prosperous.[2] After the Russians annexed Kartli-Kakheti and initiated the Russo-Persian War of 1804-1813, Erivan became, "once more", a center of the Iranian defenses in the Caucasus.[2]
In 1804, Russian general Pavel Tsitsianov attacked Erivan, but a "superior" Iranian army, under the command of crown prince Abbas Mirza, repelled the attack.[2] In 1807, the central Iranian government of king Fath-Ali Shah Qajar (r. 1797-1834) appointed Hossein Khan Sardar as the new governor (khan) of Erivan, and made him the commander-in-chief (hence, sardar) of the Iranian forces to the north of the river Aras.[7][18]
_mint_(obverse).jpg.webp)
_mint_(reverse).jpg.webp)
Hossein Khan Sardar was one of the most important individuals in the government of then incumbent king Fath-Ali Shah Qajar.[19] A capable administrator, his long tenure as governor is considered to be an era of prosperity, during which he made the khanate a model province.[2] His local bureaucracy, modeled on that of the central government in Tehran, was efficient, and restored the confidence of the local Armenians in the Iranian rule.[2][12]
In 1808 the Russians, now led by general Ivan Gudovich, attacked the city once again; this attempt was repelled as well.[2] By the Treaty of Gulistan (1813), which ended the 1804-1813 war, Iran lost most of its Caucasus territories; Erivan and Tabriz were now the main headquarters of the Iranian efforts to regain the territories lost to Russia.[2]
About a decade later, in violation of the Gulistan Treaty, the Russians invaded the Erivan Khanate.[20][21] This sparked the final bout of hostilities between the two; the Russo-Persian War of 1826-1828. In the early stages of this war, the Iranians were successful in recovering many of the territories that were lost in 1813; however, the Russian offensive of 1827, in which the superior Russian artillery played a decisive role, resulted in the Iranians being defeated at Abbasabad, Sardarabad as well Erivan.[2] Erivan was taken by the Russians on 2 October 1827.[2] In February 1828, Iran was forced to sign the Treaty of Turkmenchay, which resulted in the cession of the khanate (as well as the other remaining territories to the north of the Aras River) to the Russians.[2] After the fall of the Soviet Union, the Aras River became and remained the border between Iran and Armenia.[2]
Provincial capital
Erivan city was reportedly "quite prosperous" in the Qajar era.[2] It covered roughly one square mile, whereas its direct environs (incl. gardens) further extended some eighteen miles.[2] The city itself had, according to Kettenhofen et al. / Encyclopædia Iranica, three mahals, more than 1,700 houses, 850 stores, almost ten mosques, seven churches, ten baths, seven caravanserais, five squares, as well as two bazars and two schools.[2] During the governorship of Hossein Khan Sardar, Erivan's fortifications were reportedly the strongest in the entire country.[22] Its enormous fortress, which was located on "high ground" and was surrounded by thick walls, as well as moats and cannons, helped to prevent the Russian advance for some time.[2] Of the city's two most prominent mosques, one was built in 1687 in the Safavid period, whereas the largest mosque of the city, the Blue Mosque, was built in the 18th century after the establishment of the khanate, and is considered to be a prominent architectural remnant of the era.[23] The palace of the khan was situated nearby one of the mosques.[2]
During Hossein Khan Sardar's governorship, Erivan's population steadily rose.[24] Just before the Russian conquest, its population was approaching 20,000 inhabitants.[25] In contrast, in 1897, some seventy years after the establishment of Russian rule, and with the Armenian resettlements, Erivan only had approximately 14,000 inhabitants.[25][lower-alpha 4]
Demographics
Per article III of the Turkmenchay Treaty, the Iranians had to give the tax records of the lost Caucasus territories to the Russians.[14] However, these records only represented the families that lived in these territories, as well as tax quotas ("būniche"), and thus were not an "accurate count" of the number of people that lived in these provinces, including Iranian Armenia.[14]
The Russians therefore immediately conducted a thorough statistical account of the population of the Erivan Khanate, now renamed to the "Armenian Oblast".[14] Ivan Chopin headed the survey team which gathered the administrative census (Kameral'noe Opisanie') for the newly established Russian administration in Erivan. Based on the Persian administrative records of the Erivan Khanate as well as interviews, the Kameral'noe Opisanie is considered to be "the only accurate source for any statistical or ethnographical data" on the territories that comprised Iranian Armenia, on the situation before and immediately after the Russian conquest.[14]
Muslims (Persian, Turkic groups and Kurds) formed an absolute majority in Iranian Armenia, comprising some 80% of the population, whereas Christian Armenians formed some 20% of the population.[26][lower-alpha 5] According to the Kameral'noe Opisanie, the settled and semi-settled Muslim population numbered more than 74,000.[28] However, there are flaws regarding this number, as it doesn't account for the settled and semi-settled Muslims that left immediately after the Iranian defeat.[28] For example, basically the entire Persian ruling elite and the military officer apparatus, "most of whom resided in the administrative centers", migrated to mainland Iran after the defeat.[28] Furthermore, a number of the Turkic and Persian soldiers had perished in the 1826–1828 war, which lead to the Russian conquest of the Erivan and Nakchivan Khanates.[28] According to estimations, some 20,000 Muslims had left Iranian Armenia or were killed during the 1826–1828 war.[28] According to professor of history George Bournoutian, it can therefore be taken for granted that the combined Persian and Turkic (settled and semi-settled) population of Iranian Armenia amounted some 93,000, instead of 74,000.[28]
The total Muslim population of Iranian Armenia (incl. semi-settled, nomadic, and settled), prior to the Russian invasion and conquest, amounted "roughly over" 117,000.[29] Some 35,000 of these, were thus not present (i.e. emigration, killed during the war) after the Russians decisively arrived.[29]
| Ethnic Group | Count |
|---|---|
| Armenians[lower-alpha 6] | 20,073 |
| Kurds | 25,237 |
| Persian elite/army[lower-alpha 7] | 10,000 |
| Turkic groups (settled and semi-settled)[lower-alpha 8] | 31,588 |
| Turkic groups (nomads)[lower-alpha 9] | 23,222 |
| Total | 110,120 |
After the Russian administration took hold of Iranian Armenia, the ethnic make-up shifted, and thus for the first time in more than four centuries, ethnic Armenians started to form a majority once again in one part of historic Armenia.[33] Some 35,000 Muslims of over 100,000 emigrated from the region, while some 57,000 Armenians from Iran proper and Turkey (see also; Russo-Turkish War of 1828–1829) arrived after 1828.[34] Due to these new significant demographic shifts, in 1832, the number of Armenians had matched that of the Muslims.[26] Anyhow, it would be only after the Crimean War and the Russo-Turkish War of 1877–1878, which brought another influx of Turkish Armenians, that ethnic Armenians once again established a solid majority in Eastern Armenia.[35] Nevertheless, the city of Erivan remained having a Muslim majority up to the twentieth century.[35] According to the traveller H. F. B. Lynch, the city was about 50% Armenian and 50% Muslim (Azerbaijanis and Persians) in the early 1890s.[2]
Persians
The Persians were the elite in the region, and were part of the settled population.[28] The term "Persians" in this specific matter refers to the ruling hierarchy of the khanate, and does not necessarily denote the ethnic composition of the group.[27] There were thus ethnic "Persians" and "Turks" among the ruling "Persian" elite of the khanate.[27] This ruling elite were primarily the members of the governors' household, his close associates, the officer corps, the members of the local Persian bureaucracy, and some of the prosperous merchants.[24] The Persian ruling elite was a minority among the Muslims in the khanate.[27] During the 1826–1828 war, which lead to the Russian conquest, a number of the Persian ruling elite was killed; the remaining number, basically migrated "in toto" to Iran proper after the Russians decisively gained control of the province.[28][24][lower-alpha 10]
Turkics
The Turkics[lower-alpha 11] were the largest group in the khanate, but they were composed of three branches; settled, semi-settled, and nomadic.[28] Alike the Persian ruling elite, a number of them had perished in the 1826–1828 war against the Russians.[28] The principal settled Turkic groups in the khanate were the Bayat, Kangarlu, Ayrumlu, Ak Koyunlu, Qara Qoyunlu, Qajars, as well as the "Turkified Qazzaqs" (i.e. Karapapakh).[37] A large number of the Turkic groups, numbering some 35,000, were some sort of nomads.[29] Alike the Kurds, some of the Turkic groups had specific areas where they moved to for summer and winter.[29] The Turkic nomads were important to the local Persian governors for their animal husbandry, handicrafts and horses which they provided for the cavalry.[38] The settled Turkics made up a large percentage of the workers in the agricultural sector.[39] Together with the Kurds, the nomadic Turkic groups used about half the territory of the khanate for their pastoral way of life.[40] There was rivalry between the leading Turkic groups.[41] Due to the nomadic nature of many of the Turkic groups, they were located in many of the districts. They were abundantly presented in the central and northern parts of the khanate, where they "controlled the marginal grazing lands".[41] There was a traditional sense of hostility between the Turkic nomads and the Kurds.[41] The Karapapakh and the Ayrumlu were the largest Turkic nomad groups; most of them were resettled in Azerbaijan (historic Azerbaijan, also known as Iranian Azerbaijan) with the help of Abbas Mirza, after 1828.[42]
Kurds
Regarding the Kurds, the Kameral'noe Opisanie lists more than 10,000 inhabitants (of various tribes), and notes that some 15,000 had migrated after the Russian annexation.[28] The total Kurdish population (pre-war) would therefore amount over 25,000 individuals.[28] The Kurds were nomadic by tradition, similar to a large number of the Turkic groups.[43] Together with the nomadic Turkic groups, the Kurds used about half the territory of the khanate for their pastoral way of life.[40] The Kurds were primarily of three religious affiliations; Sunni, Shia, and Yezidi.[44] There was a traditional sense of hostility between the Kurds and the Turkic nomads.[41]
Armenians
Christians Armenians formed a minority in the khanate, comprising some 20%, and formed no majority in any of the mahals (districts).[26][lower-alpha 12] The utter vast majority of the Armenians, some 80% of their total number, were located in the districts (mahals) of Kirk-Bulagh, Karbi-Basar, Surmalu, and Sardarabad.[45] As with other minorities in Western Asia, they lived close to their "religious and administrative centers".[45] There were also Armenians in the provincial capital of Erivan.[45] There were reportedly no Armenians in the Sharur and Sa'dlu districts and only "very few" in Garni-Basar, Gökcha, Aparan, Talin, Sayyidli-Akhsakhli, and Vedi-Basar.[45]
Many events had led to the demise of the Armenian population from the region. Until the mid-fourteenth century, Armenians had constituted a majority in Eastern Armenia.[46] At the close of the fourteenth century, after Timur's campaigns, Islam had become the dominant faith, and Armenians became a minority in Eastern Armenia.[46]
Shah Abbas I's deportation of much of the population from the Armenian Highlands in 1605 was one later event, when as many as 250,000 Armenians were removed from the region.[47] To repopulate the frontier region of his realm, Shah Abbas II (1642–1666) permitted the Turkic Kangarlu tribe to return. Under Nader Shah (r. 1736-1747), when the Armenians suffered excessive taxation and other penalties, many emigrated, particularly to India.[48]
Even though both Muslims and Armenians practiced the various professions, it were the Armenians who dominated the trade and professions in the khanate.[33][2] They were thus of major economic significance to the Iranian administration.[2] Though the Armenians sympathised with the Christian Russians, they were indifferent to them as a whole; immediate concerns, both rural and urban Armenians, was limited to socio-economic "well-being".[49] As long as the living conditions in the khanate were considered to be appropriate, the majority of Armenians felt no urge to take any actions.[49] An example of this can be seen in 1808; when the Russians launched another siege in that year, in a 2nd attempt to take the city from the Iranians, the Armenians displayed "general neutrality".[50]
Partial Armenian autonomy
Armenians in the territory of the Khanate lived under the immediate jurisdiction of the melik of Erivan, from the House of the Melik-Aghamalyan family, who had the sole right to govern them with the authorization of the shah. The inception of the melikdom of Erivan appears only after the end of the last Ottoman-Safavid war in 1639 and seems to have been a part of an overall administrative reorganization in Iranian Armenia after a long period of wars and invasions. The first known member of the family is a certain Melik Gilan but the first certain holder of the title of "melik of Erivan" was Melik Aghamal and it may be from him that the house had taken its surname. One of his successors, Melik-Hakob-Jan, attended the coronation of Nader Shah in the Mugan plain in 1736.[2]
Under the melik of Erivan were a number of other meliks in the khanate, with each maḥall inhabited by Armenians having its own local melik. The meliks of Erivan themselves, especially the last, Melik Sahak II, were among the most important, influential and respected individuals in the khanate and both Christians and Muslims alike sought their advice, protection and intercession. Second in importance only to the khan himself, they alone among the Armenians of Erivan were allowed to wear the dress of an Iranian of rank. The melik of Erivan had full administrative, legislative and judicial authority over Armenians up to the sentence of the death penalty, which only the khan was allowed to impose. The melik exercised a military function as well, because he or his appointee commanded the Armenian infantry contingents in the khan's army. All the other meliks and village headmen (tanuters) of the khanate were subordinate to the melik of Erivan and all the Armenian villages of the khanate were required to pay him an annual tax.[2]
List of Khans

- 1736–40 Tahmasp II
- 1740–47 Nader Shah
- 1745–48 Mehdi-Khan Qasemlu
- 1748–50 Hasan Ali-khan
- 1750–80 Hoseyn Ali Khan
- 1752–55 Khalil Khan
- 1755–62 Hasan Ali Khan Qajar
- 1762–83 Hoseyn Ali Khan
- 1783–84 Gholam Ali (son of Hasan Ali)
- 1784–1804 Mohammad Khan
- 1804–06 Mehdi-Qoli Khan
- 1806–07 Mohammad Khan Maragai
- 1807–28 Hossein Qoli Khan Qajar
See also
Notes
- Also spelled as "Iravan Khanate" or "Erevan Khanate".
- The comparable administrative entity of the Safavid era, the Erivan Province, was also known as "Chokhur-e Sa'd".[3]
- Ordubad was added by the central government to the Nakhchivan Khanate in the early 19th century.[14]
- Reasons behind this were; the large Muslim migration primarily to Iran proper, higher taxes, the rise of Tiflis and Baku as new commercial centers in the region, the "cessation of the war economy" that had been initiated by the Iranians, and, of course, the end of Erivan's strategic importance.[25]
- There were also a handful of Georgians, Jews, Circassians, some Russians, as well as some other peoples of the Caucasus; they were not of any statistical significance.[27]
- Number includes the "few Gypsies of Erevan".[31]
- The term "Persians" in this specific matter refers to the ruling hierarchy of the khanate, and does not necessarily denote the ethnic composition of the group.[27] There were thus ethnic "Persians" and "Turks" among the ruling "Persian" elite of the khanate.[27]
- Mentioned as "Turko-tatars" or "Turks".[32] The khanate had a few Persian peasants, all of whom are included in this group.[31]
- Mentioned as "Turko-tatars" or "Turks".[32]
- Indeed, in his 1840 review of the statistical data in the "Overview of Russian Domain in the Transcaucasus" published in 1837, in response to the listing of Persians as an ethnic group residing in the Armenian Oblast, Ivan Chopin notes that there were no "Persians" in the province and that the Muslim population there was of either Turkic or Kurdish stock.[36]
- Also variously referred to as "Turko-tatars" or "Turks".[32]
- There is a chance that the Karbi-basar mahal, with the ecclesiastical center of Uch-Kilisa ("Etchmiadzin") could have had an Armenian majority.[35]
References
- Bournoutian, George A. (2016). The 1820 Russian Survey of the Khanate of Shirvan: A Primary Source on the Demography and Economy of an Iranian Province prior to its Annexation by Russia. Gibb Memorial Trust. p. xvii. ISBN 978-1909724808.
Serious historians and geographers agree that after the fall of the Safavids, and especially from the mid-eighteenth century, the territory of the South Caucasus was composed of the khanates of Ganja, Kuba, Shirvan, Baku, Talesh, Sheki, Karabagh, Nakhichivan and Yerevan, all of which were under Iranian suzerainty.
- Kettenhofen, Bournoutian & Hewsen 1998, pp. 542–551.
- Floor 2008, pp. 86, 170.
- Muriel Atkin. Russia and Iran, 1780-1828 (U of Minnesota Press, 1980), p. 89; "The new khan of Yerevan, Hosein Qoli, was one of the most able men in Fath' Ali's government and ruled Yerevan from 1807 until its conquest by the Russians in 1827."
- Bournoutian 1992, p. xxiii. "The term khanate refers to an area that was governed by hereditary or appointed governors with the title of khan or beglerbegi who performed a military and/or administrative function for the central government. By the nineteenth century, there were nine such khanates in Transcaucasia (...)"
- Bournoutian 1980, pp. 1–2. "During the eighteenth century, Persian Armenia was composed of the provincial boundaries or Khanates (subdivided into Mahals) of Erevan and Nakhchivan (...)"
- Bournoutian 2002, p. 215. "Iranians, in order to save the rest of eastern Armenia, heavily subsidized the region and appointed a capable governor, Hosein Qoli Khan, to administer it."
- Bournoutian 2004, pp. 519–520.
- Swietochowski, Tadeusz (2004). Russian Azerbaijan, 1905-1920: The Shaping of a National Identity in a Muslim Community. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. p. 12. ISBN 978-0521522458.
(...) and Persian continued to be the official language of the judiciary and the local administration [even after the abolishment of the khanates].
- Pavlovich, Petrushevsky Ilya (1949). Essays on the history of feudal relations in Armenia and Azerbaijan in XVI - the beginning of XIX centuries. LSU them. Zhdanov. p. 7.
(...) The language of official acts not only in Iran proper and its fully dependant Khanates, but also in those Caucasian khanates that were semi-independent until the time of their accession to the Russian Empire, and even for some time after, was New Persian (Farsi). It played the role of the literary language of class feudal lords as well.
- Katouzian, Homa (2003). Iranian history and politics. Routledge. p. 128. ISBN 978-0415297547.
Indeed, since the formation of the Ghaznavids state in the tenth century until the fall of Qajars at the beginning of the twentieth century, most parts of the Iranian cultural regions were ruled by Turkic-speaking dynasties most of the time. At the same time, the official language was Persian, the court literature was in Persian, and most of the chancellors, ministers, and mandarins were Persian speakers of the highest learning and ability.
- Bournoutian 1982, p. 86. "The Khan Hosein Qoli Khan's efficient administration soon transformed the region. He modeled his bureaucracy on that of the central government, dividing power between tribal and settled groups (...) In essence the Erevan administration, like its counterpart in Tehran, was organized into three branches (...)"
- Bournoutian 1980, pp. 1–2.
- Bournoutian 1980, p. 2.
- Bournoutian 1980, pp. 1-2, 10, 13.
- Bournoutian 2006, pp. 214–215.
- Bournoutian 2006, p. 215.
- Bournoutian 2004, pp. 519–520. "ḤOSAYNQOLI KHAN SARDĀR-E IRAVĀNI; important governor in the early Qajar period (b. ca. 1742, d. 1831). (...) Requiring a strong and loyal governor to command the fortress of Erevan against the Russian advances during the first Russo-Persian War (1804-13), the shah appointed Ḥosaynqoli as the commander-in-chief (sardār) of the Persian forces north of the Araxes (Aras) River."
- Muriel Atkin. Russia and Iran, 1780-1828 (U of Minnesota Press, 1980), p. 89; "The khans of Yerevan and Nakhjavan were both removed in 1805 by the shah on the grounds of disloyalty. (...) The new khan of Yerevan, Hosein Qoli, was one of the most able men in Fath' Ali's government and ruled Yerevan from 1807 until its conquest by the Russians in 1827."
- Cronin, Stephanie, ed. (2013). Iranian-Russian Encounters: Empires and Revolutions since 1800. Routledge. p. 63. ISBN 978-0415624336.
Perhaps the most important legacy of Yermolov was his intention from early on to prepare the ground for the conquest of the remaining khanates under Iranian rule and to make the River Aras the new border. (...) Another provocative action by Yermolov was the Russian occupation of the northern shore of Lake Gokcha (Sivan) in the Khanate of Iravan in 1825. A clear violation of Golestan, this action was the most significant provocation by the Russian side. The Lake Gokcha occupation clearly showed that it was Russia and not Iran which initiated hostilities and breached Golestan, and that Iran was left with no choice but to come up with a proper response.
- Dowling, Timothy C., ed. (2015). Russia at War: From the Mongol Conquest to Afghanistan, Chechnya, and Beyond. ABC-CLIO. p. 729. ISBN 978-1598849486.
In May 1826, Russia therefore occupied Mirak, in the Erivan khanate, in violation of the Treaty of Gulistan.
- Hambly, Gavin (1991). "The traditional Iranian city in the Qājār period". In Avery, Peter; Hambly, Gavin; Melville, Charles (eds.). The Cambridge History of Iran (Vol. 7). Cambridge University Press. p. 552. ISBN 978-0521200950.
Erivan was renowned for its strong natural defences and the impressive fortifications maintained by its governor between 1807 and 1827, the famous sardār, Husain Qulī Khan, which were said to be the strongest in the country.
- Kettenhofen, Bournoutian & Hewsen 1998, pp. 542–551. "(...) built in 1776 near the end of Persian rule."
- Bournoutian 1992, p. 49.
- Bournoutian 1992, p. 62.
- Bournoutian 1980, pp. 12–13.
- Bournoutian 1980, p. 15.
- Bournoutian 1980, p. 3.
- Bournoutian 1980, p. 4.
- Bournoutian 1980, p. 12.
- Bournoutian 1992, p. 63.
- Bournoutian 1980, pp. 1–17.
- Bournoutian 1980, p. 14.
- Bournoutian 1980, pp. 11–13.
- Bournoutian 1980, p. 13.
- Ivan Chopin (1840). Нѣкоторыя замѣчания на книгу Обозрѣние российских владѣний за Кавказом; p. 6: "В Армянской области персиян вовсе нет. Тамошнее мусульманское народонаселение имеет происхождение татарское или курдинское", p. 111: "Ни одного персиянина нет в области".
- Bournoutian 1980, pp. 4, 15.
- Bournoutian 1980, pp. 5–6.
- Bournoutian 1992, p. 50.
- Bournoutian 1992, p. 51.
- Bournoutian 1992, p. 53.
- Bournoutian 1992, pp. 53–54.
- Bournoutian 1980, p. 4-5, 12.
- Bournoutian 1992, p. 54.
- Bournoutian 1992, p. 61.
- Bournoutian 1980, pp. 11, 13–14.
- An Ethnohistorical Dictionary of the Russian and Soviet Empires, James S. Olson, Greenwood(1994), p. 44
- An Historical Atlas of Islam by William Charles Brice, Brill Academic Publishers, 1981 p. 276
- Bournoutian 1992, pp. 91–92.
- Bournoutian 1992, p. 83.
Sources
- Bournoutian, George A. (1980). "The Population of Persian Armenia Prior to and Immediately Following its Annexation to the Russian Empire: 1826-1832". The Wilson Center, Kennan Institute for Advanced Russian Studies. Cite journal requires
|journal=(help) - Bournoutian, George A. (1982). Eastern Armenia in the Last Decades of Persian Rule 1807-1828: A Political and Socioeconomic Study of the Khanate of Erevan on the Eve of the Russian Conquest. Undena Publications. pp. 1–290. ISBN 978-0890031223.
- Bournoutian, George A. (1992). The Khanate of Erevan Under Qajar Rule: 1795-1828. Mazda Publishers. pp. 1–355. ISBN 978-0939214181.
- Bournoutian, George A. (2002). A Concise History of the Armenian People: (from Ancient Times to the Present). Mazda Publishers.
- Bournoutian, George A. (2004). "ḤOSAYNQOLI KHAN SARDĀR-E IRAVĀNI". Encyclopaedia Iranica, Vol. XII, Fasc. 5. pp. 519–520.
- Bournoutian, George A. (2006). A Concise History of the Armenian People (5 ed.). Costa Mesa, California: Mazda Publishers. ISBN 1-56859-141-1.
- Floor, Willem M. (2008). Titles and Emoluments in Safavid Iran: A Third Manual of Safavid Administration, by Mirza Naqi Nasiri. Washington, DC: Mage Publishers. ISBN 978-1933823232.
- Kettenhofen, Erich; Bournoutian, George A.; Hewsen, Robert H. (1998). "EREVAN". Encyclopaedia Iranica, Vol. VIII, Fasc. 5. pp. 542–551.