Ernst Reinhold von Hofmann
Ernst Reinhold von Hofmann (Russian: Эрнст Ка́рлович Го́фман, tr. Ernst Karlovich Hofmann, 8 January 1801 – 23 May 1871) was a Russian geologist, geographer, explorer, and lecturer. He was a geologist who accompanied Otto von Kotzebue and his crew during his travels around the world from 1823 to 1826. After that, he made several travels to regions such as the Urals and Continental Europe and made note of orography and general geography. He was also a professor at Saint Petersburg State University and an associate professor at the University of Kiev.
Ernst Reinhold von Hofmann | |
|---|---|
 Hofmann in the 1860s | |
| Born | 8 January 1801 Paistu Parish, Russian Empire (present-day Estonia) |
| Died | 23 May 1871 (aged 70) Dorpat, Russian Empire (present-day Estonia) |
| Nationality | Russian |
| Other names | Ernst Karlovich Hofmann |
| Alma mater | Dorpat University |
| Scientific career | |
| Fields | Mineralogy, geology |
| Institutions | Saint Petersburg State University University of Kiev |
| Academic advisors | Moritz von Engelhardt |
| Signature | |
Early life and education
Hofmann was born on 8 January 1801 in Paistu Parish, in the Russian Empire, located in present-day Estonia. His father, Carl, was a pastor.[1] He grew up in Dorpat (now called Tartu) and attended a city gymnasium for primary school. He started studying medicine at the Dorpat University in 1819, but became fascinated with Moritz von Engelhardt's teaching and became a student of geology and mineralogy.[2]
Early travels and studies
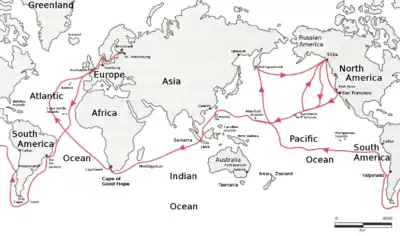
From 1823 to 1826, Hofmann circumnavigated the world with Otto von Kotzebue and other young students, including Emil Lenz.[1] The group departed from Kronstadt on 28 July 1823 on the sloop Enterprise. They dropped anchor in Portsmouth on 25 August and departed on 11 September, heading for Rio de Janeiro, which they docked into on 2 November. The group went around Cape Horn on 26 December. They anchored in the Bay of Concepción on 16 January 1824. They set out again on 3 February, after evading capture by Chilean authorities. They set out for the Tuamotus and sailed through the maze of atolls there, arriving on the island of Tahiti on 14 March. They arrived at Petropavlovsk on 8 June.[3] On 14 July, Hofmann was among a small group of travelers to make the first known ascent of the Avachinsky. The ascent was successful and they measured the summit's elevation as 7,200 feet above sea level. The group brought pieces of crystalline back to the ship to prove their ascent.[4] They left the Kamchatka Peninsula on 20 July and set out for Novo-Arkhangelsk, where they arrived on 10 August. It was there where they received word from Matvey Muravyev, chief manager of the Russian-American Company, that they wouldn't be needed until 1 March of next year, when trading season began. After a month on the island of Sitka, they departed and set out to California, which at the time wasn't well-explored. This differed from the original plan, as the group wanted to explore the Northwest Passage but the conditions proved to be too dangerous. The group also visited Hawaii in the six-month period of free time that they had. In Hawaii, the group stocked up on fresh food and conducted scientific observations. They returned to Novo-Arkhangelsk on 24 February 1825 and dropped anchor near a fortress for five months, guarding a portion of the city. They were to move when a decree reached Alaska on 30 July, permitting American ships to come to Russian American waters. The ship left the city on 11 August and headed for Honolulu, where they stopped for four days before moving to the Marshall Islands on 19 September. On 6 October the group observed and mapped the Ralik chain, which was regarded by explorers as relatively mysterious. The group were also the first Westerners to observe the Eschscholtz Atoll on 9 October. The group stopped in Guam for three days, starting in 19 October. The group arrived in Manila on 8 November and stayed so the ship could be repaired. The group left the Philippines on 10 January 1826. They passed the Sunda Strait on 25 January and ventured through the Indian Ocean, rounding the Cape of Good Hope on 16 March and arriving at Saint Helena eleven days later. They entered Portsmouth on 3 June and reached Kronstadt on 10 July.[3] He was awarded the Order of Saint Vladimir in 1929 for his participation in the circumnavigation.[5] Hofmann later recorded his geological findings in his article, "Geognostische Beobachtungen auf einer Reise um die Welt in den Jahren 1823-26" (English: Geognostic observations on a trip around the world in the years 1823-26).[2]
With Gregor von Helmersen, Hofmann travelled to the Southern Ural region in 1828, by request of Georg Ludwig Cancrin, the Minister of Finance.[2] While there, the pair became the first to create an orographic map of the region.[6] In 1831, they published "Geognostische Untersuchung der Süd-Uralgebirges" (English: Geognostic study of the southern Ural Mountains) in Berlin.[2] While in Europe with Helmersen, Hofmann travelled to Saxony, Bohemia, the Harz, Austria, Northern Italy, Switzerland, and the Rhineland and met such figures as Gustav Rose and Christian Gottfried Ehrenberg.[1]
Later career and professorship
Having returned from Berlin, Hofmann became a lecturer of geology and mineralogy at his alma mater, Dorpat University, in 1833. He also headed the department of the subject, following the resignation of Moritz von Engelhardt due to illness in 1835. He became a Master of Philosophy in 1837, with his dissertation "Geognostische Beobachtungen auf einer Reis von Dorpat bis Abo" (English: Geognostic observations on a trip from Dorpat to Abo). He left Dorpat that year and headed to the University of Kiev, where he taught for five years. He also conducted studies in Kiev and the surrounding area.[2] He became a member of the Corps of Mining Engineers in 1842. In 1843, he conducted studies in Eastern Siberia and researched the gold-bearing placer deposits and collected information on its geology, vegetation, fauna, and ethnography.[6] He wrote a work on his findings in 1847.[7] In 1844, he conducted research around the Kemijoki.[2] In 1845, he became a professor at Saint Petersburg State University, a position he held until 1863.[5]
The latter part of his career was spent mainly researching the Ural region. In 1847, he led a Russian Geographical Society expedition to the Northern Urals. He won the first-ever Constantine Medal in 1849 as a result of the expedition.[8] From 1853 until 1859 he travelled to the Middle Urals every summer. He created maps and recorded geological details of different areas in the region. He also wrote many works about his findings in the resulting years.[2] In 1861, he became the director of the Imperial Mineralogical Society and served the position until 1865. In 1869, he became lieutenant general of the Corps of Mining Engineers.[6]
He died on 23 May 1871, at the age of 70.[9] Hofmann Island is claimed to be named after him.[6]
References
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Ernst Reinhold Hofmann. |
- "Hofmann, Ernst". Deutsche Biographie (in German). Retrieved 15 November 2020.
- "Гофман, Эрнест Карлович". Brockhaus and Efron Encyclopedic Dictionary (in Russian). Retrieved 15 November 2020.
- Kaputsin, I.V. "Новое путешествие вокруг света в 1823 - 1826 гг" (in Russian). Retrieved 16 November 2020.
- "190 лет первовосхождению на Авачинский вулкан". Volcanoes of Kamchatka (in Russian). Retrieved 16 November 2020.
- "Гофман Эрнст Карлович". Saint Petersburg State University (in Russian). Retrieved 16 November 2020.
- "ГОФМАН ЭРНСТ КАРЛОВИЧ. НАСЛЕДИЕ КАРТОГРАФОВ УРАЛА". Russian Geographical Society (in Russian). Retrieved 16 November 2020.
- "ГОФМАН, ЭРНЕСТ КАРЛОВИЧ (ERNST REINHOLD HOFMANN, 1801 -1871)". Shartash Megaliths (in Russian). Retrieved 16 November 2020.
- "CONSTANTINE MEDAL OF THE IRGS". Russian Geographical Society. Retrieved 16 November 2020.
- Helmersen, Gregor von (1874). Ernst Hofmann : Nekrolog. Retrieved 16 November 2020.