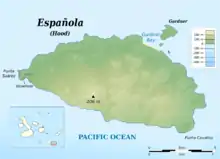
Española Island
Española Island (Spanish: Isla Española) is part of the Galápagos Islands.[1] The English named it Hood Island[2] after Viscount Samuel Hood. It is located in the extreme southeast of the archipelago and is considered, along with Santa Fe, one of the oldest, at approximately four million years. A popular tourist stop, Isla Española is the most southerly island in the Galápagos Archipelago. The climate is very dry, like most of the Archipelago. But due to the flatness of the island, it is the driest of these islands, with only a few inches of rain per year. It is about a 10- to 12-hour trip by boat from Isla Santa Cruz.
 Española Island | |
| Geography | |
|---|---|
| Location | Galápagos Islands, Ecuador |
| Coordinates | 1.38°S 89.68°W |
| Archipelago | Galápagos Islands |
| Administration | |


Wildlife
Tourists come to see the waved albatrosses (from March to January, almost the entire world population breeds on the island) and the mating dances of blue-footed boobies. Two spots are especially popular with visitors: Bahía Gardner, which has a lovely beach; and Punta Suárez, of interest because of its varied bird-life. This island has its own species of animals, such as the Hood mockingbird, which has a longer and more curved beak than the one on the central islands; the Española lava lizard; and the marine iguana of the subspecies venustissimus, which has red markings on its back. There are also swallow-tailed gulls, Galapagos hawks and other birds. The island has been recognised as an Important Bird Area (IBA) by BirdLife International.[3]
While Española Island is one of the oldest of the Galápagos Islands, this island is dying, slowly becoming a rocky, barren land with little or no vegetation. But this does give large bays, with sand and soft shingle which attracts a healthy number of Galápagos sea lions. In January 2020, it was widely reported that a male Galápagos tortoise named Diego fathered and resurrected the island tortoise population, saving the diminishing species from near extinction.[4]
In popular culture
- American author Herman Melville mentions the island in his novella The Encantadas, or Enchanted Isles (1854).
- The novel La iguana (1982) by Spanish writer Alberto Vázquez-Figueroa takes place in the island. The novel was later cinematized as Iguana by American film director Monte Hellman (1988).[5]
References
- "Española". Galapagos Conservancy. galapagos.org. Retrieved 2 June 2017.
- "Hood (Espanola)". About Galapagos. aboutgalapagos.nathab.com. Retrieved 2 June 2017.
- "Isla Española". BirdLife Data Zone. BirdLife International. 2021. Retrieved 21 January 2021.
- Picheta, Rob. "This tortoise had so much sex he saved his species. Now he's going home". CNN. Retrieved 2020-01-12.
- Cole, Jack (October 2, 2014). "Iguana". Slant Magazine. slantmagazine.com. Retrieved 2 June 2017.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Española Island. |
 Espanola (Galápagos) travel guide from Wikivoyage
Espanola (Galápagos) travel guide from Wikivoyage- Espanola Island
- Espanola wildlife and visitor sites Galapagosonline.com*
- Fauna at Gardner Bay
- Rory Carroll (27 June 2010), "Galápagos giant tortoise saved from extinction by breeding programme: Reintroduction of species that Charles Darwin saw raises conservation hopes for other wildlife", The Observer