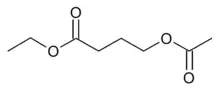
Ethyl acetoxy butanoate
Ethyl acetoxy butanoate (EAB) is a volatile chemical compound found as a minor component of the odour profile of ripe pineapples, though in its pure form it has a smell more similar to sour yoghurt.[1] It can be metabolized in humans into GHB, and thus can produce similar sedative effects.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Ethyl 4-(acetyloxy)butanoate | |
| Other names
Ethyl 4-acetoxybutanoate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H14O4 | |
| Molar mass | 174.196 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
It is synthesised by the reaction of gamma-butyrolactone and ethyl acetate with sodium ethoxide.[2]
See also
References
- Umano RP, Hagi Y, Nakahara K, Shoji A, Shibamoto T. Volatile constituents of green and ripened pineapple (Ananas comosus). J Agric Food Chem 1992; 40:599-603. doi:10.1021/jf00016a014
- 常温下4-乙酰氧基丁酸乙酯的催化合成方法. 1994. CN1047589C
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.