gamma-Hydroxybutyraldehyde
γ-Hydroxybutyraldehyde, also referred to as GHBAL, γ-hydroxybutaldehyde or γ-hydroxybutanal, is a chemical intermediate in the biosynthesis of the neurotransmitter γ-hydroxybutyric acid (GHB) from 1,4-butanediol (1,4-BD).[1] Like 1,4-BD, it also behaves as a prodrug to GHB when taken exogenously. However, as with all aliphatic aldehydes, γ-hydroxybutaldehyde is caustic and is strong-smelling and foul-tasting; thus, actual ingestion of this compound is likely to be unpleasant and result in severe nausea and vomiting.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
4-Hydroxybutanal | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.042.900 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C4H8O2 | |
| Molar mass | 88.106 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Metabolic pathway
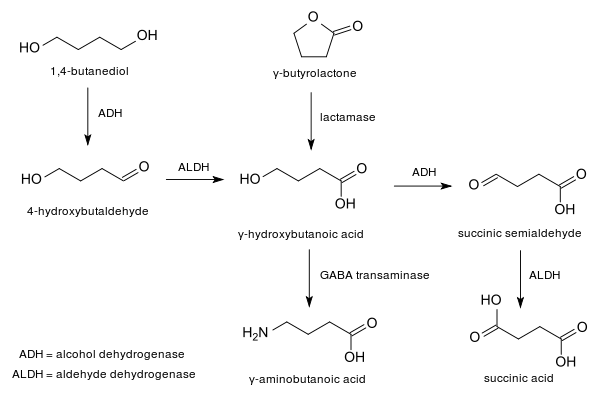
Metabolic pathway of GHB.
See also
References
- Thomas L. Lemke; David A. Williams (24 January 2012). Foye's Principles of Medicinal Chemistry. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 413–. ISBN 978-1-60913-345-0.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.