Exclusive economic zone of Spain
Spain's exclusive economic zone (EEZ) (spanish: Zona económica exclusiva de España) is the 30th largest in the world with 1,039,233 km2 (401,250 sq mi).[1] It is mostly in the Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea. This is approximately double the entire Spanish land area. Together the land and sea surface would account for approximately 0.3% of the world's land surface.
Geography
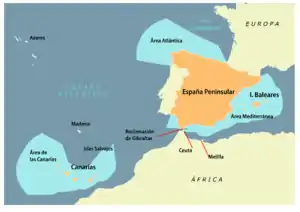
The Spanish EEZ is divided into three compact regions: the Cantabrian and Atlantic regions (Área Atlántica), the Mediterranean together with the Gulf of Cádiz region (Área mediterránea junto) and the dependent area of the Canary Islands (Áreas de las Canarias).[2] It is located in the Mediterranean Sea (Balearic Sea, Alboran Sea) and the Atlantic Ocean (Bay of Biscay). The most notable areas are the Canary Islands, the Balearic Islands and the north western area in the Bay of Biscay.
Disputes
Algeria
Algeria in 17 April 2018 establishes an exclusive economic zone (EEZ) off its coasts by Presidential Decree No. 18-96 of 2 Rajab 1439 corresponding to 20 March 2018.[3][4] The permanent Mission of Spain to the United Nations in 27 July 2018 declares his disagreement with the EEZ announced by Algeria and that the Government of Spain hereby indicates its willingness to enter into negotiations with the Government of Algeria with a view to reaching a mutually acceptable agreement on the outer limits of their respective exclusive economic zones,[5] The same was done by the Italian mission in 28 November 2018.[6] The two countries indicated that the Algerian measure had been taken unilaterally and without consulting them.
25 November 2018 The Algerian Ministry of Foreign Affairs sent an oral note in response to the Spanish protest, explains that the Algerian Government does not recognize the largely exorbitant coordinates contained in Royal Decree 236/2013, which overlap with the coordinates of Presidential Decree n° 18–96 establishing an exclusive economic zone off the coast of Algeria. The Algerian Government wishes to emphasize that the unilateral delimitation carried out by Spain is not in conformity with the letter of the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea and has not taken into consideration the configuration, the specific characteristics and the special circumstances of the Mediterranean Sea, in particular for the case of the two countries whose coasts are located face to face, as well as the objective rules and relevant principles of international law to govern the equitable delimitation of the maritime areas between Algeria and Spain, in accordance with article 74 of the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea. Algeria expressed its willingness to negotiate for a just solution[7]
20 June 2019 a communication from Algeria addressed to the Italian embassy[8] and the Spain embassy in Algiers[9] to show their eligibility in her exclusive economic zone.
Portugal
Spain disputes the EEZ's southern border, maintaining that it should be drawn halfway between Madeira and the Canary Islands. But Portugal exercises sovereignty over the Savage Islands, a small archipelago north of the Canaries, claiming an EEZ border further south. Spain objects, arguing that the Savage Islands do not have a separate continental shelf,[10] citing article 121 of the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea.[11]
United Kingdom
The British colony of the United Kingdom claims that Gibraltar has jurisdiction over the territorial waters annexed to the Rock. Spain argues that the Treaty of Utrecht would only give the British jurisdiction over the internal waters of the port. This discussion would lead both parties to a diplomatic conflict that returned after a fishing dispute in 2013.[12]
References
- "Sea Around Us – Fisheries, Ecosystems and Biodiversity". Retrieved 1 April 2017.
- "Aguas jurisdiccionales españolas – Convenio internacional del Derecho del Mar". Retrieved 1 February 2019.
- Deposit by Algeria of a list of geographical coordinates of points, pursuant to article 75, paragraph 2, of the Convention
- Presidential Decree No. 18-96 of 2 Rajab 1439 corresponding to March 20, 2018 establishing an exclusive economic zone off the Algerian coast.
- Letter from Spain to the Secretary-General of 27 July 2018
- Letter from Italy to the Secretary-General of November 28 2018
- oral note of the Algerian Ministry of Foreign Affairs response to the Spanish protest
- Communication from Algeria addressed to Italy dated 20 June 2019
- Communication from Algeria addressed to Spain dated 20 June 2019
- Lacleta Muñoz, José Manuel: "Las fronteras de España en el mar". Documentos de trabajo 34-2004, Real Instituto Elcano
- "PREAMBLE TO THE UNITED NATIONS CONVENTION ON THE LAW OF THE SEA". Retrieved 1 April 2017.
- "Spain threatens Court of Justice suit over Gibraltar fishing dispute". UPI News. 16 September 2013.