Günzburg
Günzburg is a town in Bavaria, Germany. It is a Große Kreisstadt and the capital of the Swabian district Günzburg. This district was constituted in 1972 by combining the city of Günzburg – which had not previously been assigned to a Kreis (district) – with the district of Günzburg and the district of Krumbach.
Günzburg | |
|---|---|
 Market place | |
 Coat of arms | |
Location of Günzburg within Günzburg district 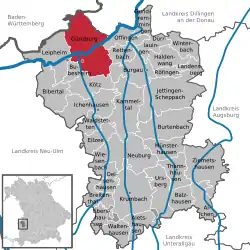 | |
 Günzburg  Günzburg | |
| Coordinates: 48°27.16′N 10°16.28′E | |
| Country | Germany |
| State | Bavaria |
| Admin. region | Schwaben |
| District | Günzburg |
| Government | |
| • Lord mayor | Gerhard Jauernig (SPD) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 55.40 km2 (21.39 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 478 m (1,568 ft) |
| Population (2019-12-31)[1] | |
| • Total | 21,028 |
| • Density | 380/km2 (980/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+01:00 (CET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+02:00 (CEST) |
| Postal codes | 89312 |
| Dialling codes | 08221 |
| Vehicle registration | GZ |
| Website | www.guenzburg.de |
Günzburg lies where the river Günz enters the Danube, and has a population of about 20,350.
Legoland Germany is located in Günzburg.
History
Günzburg was founded in about 70 BC by the Romans to defend the borders of their land along the Danube; it was known as Castellum Guntia, Gontia or Contia. The name comes from that of the Celtic goddess Gontia.[2] It consisted of a fort, later replaced by at least one other on the same site, a fairly large civilian settlement and most likely an important bridge over the Danube.
After the Romans left in the fifth century, the Alamanni tribe settled there. In around 700 the nearby castle of Ricinis was mentioned by the Cartographer of Ravenna as one of the five most important castles of Alemannia. In 1065 first documentary evidence appears of the town itself as Gunceburch.
In 1301 the town became part of the Habsburg house and was developed into the centre of the Margraviate of Burgau; for a time (1803–1805) it was even the capital of all Further Austria.
Very near Günzburg is the site where the "Leipheim Horde" was defeated by the Swabian army in 1525 during the German Peasants' War. The same site saw the first flight by a Messerschmitt Me 262 in 1942.
In 1770 the city was visited by French queen Marie Antoinette. She broke her journey towards France for two days and was joined by her father’s sister, Princess Anne Charlotte of Lorraine. Together, they made a pilgrimage to the church of Maria Königin Bild, near Limbach.
On 9 October 1805, elements of the Sixth Corps of Napoléon's Grande Armée assaulted Austrian positions in Günzburg. The first assault was initiated by the 25th Light Infantry and the 27th and 50th Infantry Regiments of the Line (under Pierre-Louis Binet de Marcognet), while the second consisted of only the 59th Infantry Regiment of the Line, under Mathieu de la Bassé; around one thousand Austrian prisoners were taken, and six guns captured. In 1806, through the Franco-Bavarian alliance, Günzburg was integrated into the Kingdom of Bavaria.
In April 1945, near the end of the Second World War, the city of Günzburg was bombed by the allies. Among other targets that were severely damaged or destroyed were the nearby town of Denzingen, the castle, and a munitions train that was in the train station.
Günzburg is the birthplace of Josef Mengele, medical officer at Auschwitz concentration camp.[3]
Günzburg has flourished, boasting a thriving downtown shopping area, scenic views of the nearby historic castle, and one of the top five Legoland theme parks in Germany. It is also home of the soccer player Stefano Celozzi, who moved to Günzburg in 2016.
Main sights




The attractions of Günzburg include the Church of Our Lady (Frauenkirche) built by Dominikus Zimmermann, the margraves' castle (the only Habsburg castle built in Germany), the Reisensburg fort, today the congress centre of the University of Ulm and the nearly-intact old town centre.
In 2002 Legoland built a theme park near the town.
Notable people
- Fred Benninger (1917–2004), executive of several companies in the United States
- Stefano Celozzi, (born 1988), footballer for VfL Bochum
- Diana Damrau (born 1971), opera singer, soprano
- Johann Eck (1494–1554), Reformation theologian
- Johann Eberlin von Günzburg (died 1533), reformist preacher and author, was born in the town around 1470
- Erhard Keller (born 1944), speed skater
- Petra Kelly (1947–1992), politician, peace activist and founding member of the party Greens
- Josef Mengele (1911–1979), a war criminal, the SS officer and Auschwitz physician was born in Günzburg. On 8 March 2005 a monument to his victims was erected in the town.
- Karl Mengele (1884–1959), father of a war criminal, concentration camp doctor Josef Mengele, temporarily owner of the Mengele agricultural Engineering company, in the 1950s, with 2,000 employees the largest employer in the region
- Franz Xaver Schwarz (1875–1947), Nazi politician, Reichsschatzmeister
- Tina Stöckle (1948–1982), activist in humanistic anti-psychiatry
Literature
- Wüst, Wolfgang: Historische Einleitung, in: Klaus Kraft: Landkreis Günzburg, Bd. 1: Stadt Günzburg (Die Kunstdenkmäler von Bayern, Teil Schwaben IX), München 1993, p. 1–49.
- Wüst, Wolfgang: Günzburg. Historischer Atlas von Bayern, Teil Schwaben, Reihe I, Bd. 13, München 1983, ISBN 3-7696-9933-5.
- Keller, Sven: Günzburg und der Fall Josef Mengele – Die Heimatstadt und die Jagd nach dem NS-Verbrecher. Oldenbourg Verlag, München 2003, ISBN 978-3-486-64587-3.
Freemen
- 1895 Prince Otto von Bismarck, German chancellor
- Josef Weizenegger (1924–2012), former county curator
- Karl Mengele (1884–1959), father of the concentration camp doctor Josef Mengele, temporarily owner Fa. Mengele Agrartechnik, in the 1950s, with 2,000 employees the largest employer in the region
- 1964 Ludwig Heilmeyer (1899–1969), internist, researcher and university teacher
- Georg Simnacher (1932–2014), district president in Swabia and president of the Bavarian districts
See also
References
- "Tabellenblatt "Daten 2", Statistischer Bericht A1200C 202041 Einwohnerzahlen der Gemeinden, Kreise und Regierungsbezirke". Bayerisches Landesamt für Statistik und Datenverarbeitung (in German). July 2020.
- Lauren Adams Gilmour, Pagans and Christians, Archaeopress, 2007, p. 24.
- Posner, Gerald L.; Ware, John (1986). Mengele: The Complete Story. New York: McGraw-Hill. p. 4. ISBN 0-07-050598-5.
External links
![]() Media related to Günzburg at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Günzburg at Wikimedia Commons