Galena and Chicago Union Railroad
The Galena and Chicago Union Railroad (G&CU) was a railroad running west from Chicago to Freeport, Illinois, never reaching Galena, Illinois. A later route went to Clinton, Iowa. Incorporated in 1836, the G&CU became the first railroad built out from Chicago.
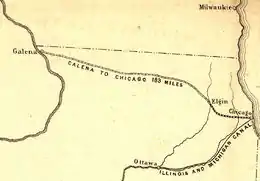 Original plan from Chicago to Galena | |
| Overview | |
|---|---|
| Locale | northern Illinois |
| Dates of operation | 1836 (chartered); 1848 (in service)–1864 |
| Successor | Chicago and North Western |
| Technical | |
| Track gauge | 4 ft 8 1⁄2 in (1,435 mm) standard gauge |
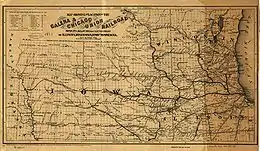
History
The first railroad constructed out of Chicago, the Galena and Chicago Union, was chartered January 16, 1836, to connect Chicago with the lead mines at Galena. "The Pioneer," the first locomotive on the road, arrived at Chicago on October 10, 1848, nearly thirteen years after the charter was granted. In 1850, the Galena and Chicago Union Railroad was completed as far as Elgin. The railroad and the Illinois and Michigan Canal were vital in the development of Chicago, and the population of the city tripled in the six years after the opening of the canal. Eventually other railroads were built and Chicago became the largest railroad center in the world.
In 1862 the G&CU leased in perpetuity the Cedar Rapids and Missouri Railroad which was to be the first railroad to reach Council Bluffs, Iowa and the First Transcontinental Railroad. The 1862 map by G. Woolworth Colton shown here lays out the various lines in operation at that time.[1] The G&CU consolidated with the Chicago and North Western Railway in 1864, which merged with the Union Pacific Railroad over a century later in 1996.
Today, the G&CU's main line between Chicago and West Chicago is a busy commuter service, jointly operated by Union Pacific and Metra as the Union Pacific / West Line.
Construction
The railroad was constructed starting in March 1848, and was completed to Freeport in 1853. The first westbound train out of Chicago departed on October 25, 1848, pulled by a used Baldwin-built locomotive named Pioneer.[2][3] When construction reached the Fox River at Elgin in 1850 passengers going farther west could transfer to the stagecoach lines. The railroad extended to Rockford by 1851 and ended construction at Freeport in 1853. The Illinois Central Railroad, using the G&CU construction crew, completed the Freeport to Galena route in 1854 following the stage route already established by Frink, Walker and Company.
Depots
Stations between Chicago and Freeport included the following:
- Chicago, Illinois (1848. Depot at Kinzie and Canal Streets north of the Chicago River was converted to an employees' reading room 1853. Second depot at Kinzie and Wells Streets burned in 1871. The Merchandise Mart now occupies the site)
- Garfield Park (1848. formerly Central Park)
- Oak Park, Illinois (1848. formerly Oak Ridge, Cicero)
- Melrose Park, Illinois (1849) formerly Melrose
- Berkeley, Illinois (1849. Formerly Proviso)
- Elmhurst, Illinois (1849. Formerly Cottage Hill)
- Lombard, Illinois (1849. Babcock's Grove)
- Glen Ellyn, Illinois (1849. Formerly Danby)
- Wheaton, Illinois (1849)
- Winfield, Illinois (1849–1854. Hedges Station)
- West Chicago, Illinois (1849. Turner Junction. Hotel and roundhouse 1853)
- Wayne, Illinois (1850)
- South Elgin, Illinois (1850. formerly Clintonville)
- Elgin, Illinois (1850)
- Gilberts, Illinois (1855. Gilbert's Station)
- Huntley, Illinois (1851)
- Union, Illinois (1851)
- Marengo, Illinois (1851)
- Garden Prairie, Illinois (1853)
- Belvidere, Illinois (1851)
- Cherry Valley, Illinois (1853)
- Rockford, Illinois (1851)
- Winnebago, Illinois (1853)
- Pecatonica, Illinois (1853)
- Nevada, Ridott Township, Stephenson County, Illinois (1853. Depot was moved to Ridott 10 July 1860. Nevada no longer exists)
- Ridott, Illinois (1860)
- Freeport, Illinois (1853)
From West Chicago to Clinton:
- La Fox, Illinois (1859)
- Elburn, Illinois (1854, formerly Blackberry)
- Maple Park, Illinois (1854, formerly Lodi)
- Cortland, Illinois (1854)
- DeKalb, Illinois (1854)
- Malta, Illinois (1855, formerly Milton)
- Creston, Illinois (1855, Formerly Dement)
- Rochelle, Illinois (1855, formerly Hang Town)
- Flagg, Illinois(1856)
- Ashton, Illinois (1855, formerly Ogle)
- Franklin Grove, Illinois (1855)
- Nachusa, Illinois (1855)
- Dixon, Illinois (1855)
- Nelson, Illinois (1858)
- Sterling, Illinois (1855)
- Galt, Illinois (1857)
- Agnew, Illinois (1860)
- Como, Illinois (1855. Depot was moved to Agnew in 1860)
- Round Grove, Illinois (1855)
- Lyndon, Illinois (1857)
- Morrison, Illinois (1855)
- Union Grove, Illinois (1859)
- Fulton, Illinois (1855. Line was moved to East Clinton after C&NW takeover)
- Clinton, Iowa (1855)
Crystal Lake Branch
- East Dundee, Illinois (1854)
- Algonquin, Illinois (1855)
- Crystal Lake, Illinois (1855)
Aurora Branch
- Batavia, Illinois (1872)
- Aurora, Illinois (1888)
St. Charles Branch
- Geneva, Illinois (1854)
- St. Charles, Illinois (1871)
References
- "Map Showing the Location of the Galena & Chicago Union Railroad with its Branches & Connections in Illinois, Wisconsin, Iowa and Minnesota. Engraved & Printed by G. Woolworth Colton, No. 18 Beekman St., N.Y." 1862. Described in Robert A. Holland (2005) Chicago in Maps 1612 to 2002.. New York: Rizzoli International Publications. pp. 74–75. ISBN 0-8478-2743-7 Original map is located in the Library of Congress, Washington D.C.
- Rivanna Chapter, National Railway Historical Society (2005), This Month in Railroad History - October. Retrieved October 25, 2005.
- Chicago Historical Society, History Lab Collections - Riding the Rails Archived 2006-05-27 at the Wayback Machine. Retrieved October 25, 2005.
Sources
- Cronon, William (1992). Nature's metropolis: Chicago and the great west (reprint ed.). W. W. Norton & Company. ISBN 0-393-30873-1. examines the economic effects of the railroad (among other things).
- A Chronological History of Chicago: 1673- Compiled by Chicago Municipal Reference Library, City of Chicago, updated by Municipal Reference Collection, Chicago Public Library
- The Northern Counties Gazetteer and Directory for 1855–6: A Complete and Perfect Guide to Northern Illinois Containing a Concise Description of the Cities, Towns & Principal Villages... (1855). 189 Lake Street, Chicago. Reprinted on demand by Pranava Books, India. August 2019.