gedit
gedit (/ˈdʒɛdɪt/ or /ˈɡɛdɪt/)[3] is the default text editor of the GNOME desktop environment and part of the GNOME Core Applications. Designed as a general-purpose text editor, gedit emphasizes simplicity and ease of use, with a clean and simple GUI, according to the philosophy of the GNOME project.[4] It includes tools for editing source code and structured text such as markup languages.[4]
 | |
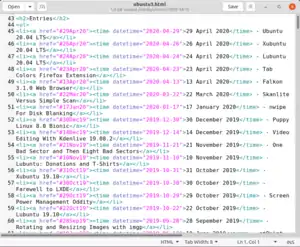 gedit 3.36.1 showing a web page with syntax highlighting | |
| Developer(s) | Paolo Maggi Paolo Borelli Steve Frécinaux Jesse van den Kieboom James Willcox Chema Celorio Federico Mena Quintero |
|---|---|
| Initial release | February 12, 1999 |
| Stable release | 3.38.3[1] (29 January 2021) [±] |
| Preview release | 40.alpha[2] (26 January 2021) [±] |
| Repository | |
| Written in | C, Python |
| Type | Text editor |
| License | GNU General Public License |
| Website | wiki |
It is free and open-source software under the GNU General Public License version 2 or later.[4]
gedit is also available for macOS and Windows.
By July 2017, gedit was not being maintained by any developers, but in August 2017 two developers volunteered to commence work on it again.[5][6][7]
Features
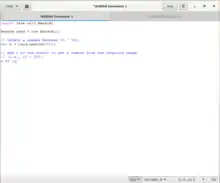
gedit includes syntax highlighting via GtkSourceView[8] for various program code and text markup formats including MediaWiki.[9][10] gedit also has GUI tabs for editing multiple files. Tabs can be moved between various windows by the user. It can edit remote files using GVfs libraries; (GnomeVFS is now deprecated). It supports a full undo and redo system as well as search and replace.[11] Other typical code oriented features include line numbering, bracket matching, text wrapping, current line highlighting, automatic indentation and automatic file backup.[11]
The features of gedit include multi language spell checking via Enchant and a flexible plugin system allowing the addition of new features, for example snippets and integration with external applications including a Python or Bash terminal.[11] A number of plugins are included in gedit itself, with more plugins in the gedit-plugins package and online.[12]
Since version 3.20 gedit uses gspell for spell checking.[13][14]
gedit has an optional side pane displaying the list of open files and (in a different tab of the side pane) a file browser. It also has an optional bottom pane with a Python console and (using gedit-plugins) terminal. gedit automatically detects when an open file is modified on disk by another application and offers to reload that file. Using a plugin (in gedit-plugins package), gedit can save and load sessions, which are lists of currently open tabs.[12]
gedit supports printing, including print preview and printing to PostScript and PDF files. Printing options include text font, and page size, orientation, margins, optional printing of page headers and line numbers, as well as syntax highlighting.[15]
In late 2013 and early 2014 the application received major upgrades for Gnome 3.12, with a new, cleaner user interface and code base improvements to make it work better with other desktop interfaces, such as Unity.[16]
Valencia is a gedit plugin that turns gedit into a lightweight IDE for Vala.[17]
Architecture
Being part of the GNOME Core Applications, gedit 3 uses the GTK 3.x and GNOME 3.x libraries. The GNOME integration includes drag and drop to and from GNOME Files.
gedit uses the GNOME help system for documentation. It also uses virtual file system and GNOME printing framework.[18]
In December 2008, gedit binaries were made available for macOS and Windows.[19]
The last version for Windows 32-bit was 2.30.1, released in 2014.[20] Standalone releases for 64-bit Windows continued, with Version 3.20.1 released in 2016.[21]
Current versions of gedit (3.0+) for Windows are also available through MSYS2 and can be installed via the built-in Pacman package manager.[22]
References
- Catanzaro, Michael (29 January 2021). "GNOME 3.38.3 released!". GNOME Mail Services (Mailing list). Retrieved 30 January 2021.
- Petridis, Jordan (26 January 2021). "GNOME 40.alpha Released". GNOME Mail Services (Mailing list). Retrieved 26 January 2021.
- Borelli, Paolo (19 April 2006). "Re: [gedit-list] Pronouncing gedit" (Email). GNOME Mail Services. The GNOME Project. Retrieved 25 April 2014.
- The GNOME Project (October 2015). "gedit". Retrieved 2015-10-28.
- "[gedit-list] gedit is unmaintained, some thoughts". mail.gnome.org. Retrieved 2017-08-05.
- "Gedit Text Editor is No Longer Maintained - OMG! Ubuntu!". OMG! Ubuntu!. 2017-07-27. Retrieved 2017-08-02.
- The GNOME Project (27 August 2017). "About gedit maintenance". wiki.gnome.org. Retrieved 29 December 2017.
about gedit maintenance: gedit has been marked as unmaintained recently, now two new developers have proposed their help to become new maintainers. If you want to help, reach us on the IRC channel or the mailing list, thanks!
- "GtkSourceView home page".
- Wikipedia:Text editor support § gedit
- jpfleury. "Syntax highlighting for MediaWiki in gedit". GitHub. Retrieved 2016-10-21.
- "gedit: a powerful, underrated text editor for everybody", Free Software Magazine Archived 2008-05-18 at the Wayback Machine 15 February 2008
- "Lists of gedit plugins". wiki.gnome.org. Retrieved 2015-10-28.
- "gspell website".
- "Blog post: gspell news".
- "Printing with gedit". Library.gnome.org. 2011. Retrieved 2020-02-23.
- Sneddon, Joey-Elijah (15 January 2014). "Gedit Text Editor Finally Gets a UI Revamp". News Organization. Retrieved 15 January 2014.
- "Valencia home page".
- "Free Software Directory - gedit". Directory.fsf.org. 2005-10-03. Retrieved 2020-02-23.
- "Club Silencio » Late Christmas gift for Windows users". Blogs.gnome.org. 2008-12-25. Retrieved 2009-03-13.
- "ftp.gnome.org". ftp.gnome.org. Retrieved 22 March 2019.
- "ftp.gnome.org". ftp.gnome.org. Retrieved 22 March 2019.
- "How to build your GTK+ application on Windows". Blogs.gnome.org. 2014-08-01. Retrieved 2015-11-30.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Gedit. |
