Gloster Goldfinch
The Gloster Goldfinch was a single-engined single-seat high-altitude biplane fighter of all-metal construction from the later 1920s. It did not reach production and only one was built.
| Goldfinch | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Role | Single-seat fighter |
| National origin | United Kingdom |
| Manufacturer | Gloster Aircraft Company |
| Designer | H.P. Folland |
| First flight | Summer 1927 |
| Number built | 1 |
Development
In January 1926 the Air Ministry funded Gloster Aircraft to produce an all-metal version of their Gamecock for a high altitude fighter role, hence requiring a supercharged engine. The result was the Goldfinch, a single-bay biplane with unequal span wings of marked stagger. Unsurprisingly, this aircraft had a strong similarity to the Gamecock and in particular to the Gamecock II with its narrow-chord ailerons. Because of the supercharged engine the fuselage was longer forward of the cockpit. The tail also was slightly different, the tailplane having rounded trailing tips and the fin, initially, was very broad in chord and short in height.[1][2]
Only one Goldfinch was built but there were two rather different versions. The first build had all-metal wings but a fuselage of mixed metal and wood construction. Both the wings and fuselage were fabric covered. The fuselage was then rebuilt entirely of metal, apart from its covering and lengthened. The rebuild also brought a revised fin and rudder, with a narrower, higher fin of simpler overall shape.[3] Throughout, the Goldfinch was powered by a supercharged 450 hp (335 kW) Bristol Jupiter VIIF driving a 9 ft (2.74 m) two-bladed fixed-pitch propeller.[1][2]
The Goldfinch first flew in May 1927,[4] and in December it went to RAF Martlesham Heath for trials where it proved fast and high with a rapid climb rate,[1] and generally good manoeverability, although spinning behaviour was substandard.[5] Gloster's submitted it as a contender for Air Ministry specification F.9/26 for an all-metal day-and-night fighter, but it failed to meet the required load and fuel requirements and was eliminated quite early. The Bristol Bulldog was the eventual winner,[1][2] with the Goldfinch being used for trials at Martlesham Heath until October 1928.[6]
Specifications
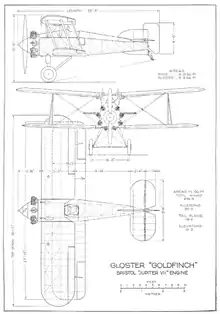
Data from James 1971, p. 148
General characteristics
- Crew: one
- Length: 22 ft 3 in (6.7 m)
- Wingspan: 30 ft 0 in (9.14 m)
- Height: 10 ft 6 in (3.19 m)
- Wing area: 274.3 sq ft (25.56 m2)
- Empty weight: 2,058 lb (933 kg)
- Gross weight: 3,236 lb (1,467 kg)
- Powerplant: 1 × Bristol Jupiter VIIF 9-cylinder supercharged radial , 450 hp (335 kW)
Performance
- Maximum speed: 172 mph (276 km/h, 149 kn) at 10,000 ft (3,048 m)
- Service ceiling: 26,960 ft (8,217 m)
- Rate of climb: 1,250 ft/min (6.35 m/s) to 20,000 ft (6,096 m)
Armament
- 2×synchronised 0.303 in (7.7 mm) Vickers machine guns firing forward
Notes
- James 1971, pp. 145–8
- Flight 4 October 1928
- Flight 4 October 1928: the g/a drawings show the early fin and the photographs the later arrangement
- Jarrett 1997, pp. 48–49.
- Jarrett 1997, p. 50.
- Jarrett 1997, p. 51.
References
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Gloster Goldfinch. |
- James, Derek N. (1971). Gloster Aircraft since 1917. London: Putnam Publishing. ISBN 0-370-00084-6.
- Jarrett, Philip. "Limited Editions:Gloster Goldfinch". Aeroplane Monthly. No. January 1997. London: IPC. pp. 46–51.
- "THE GLOSTER "GOLDFINCH"". Flight. No. 4 October 1928. pp. 845–849.