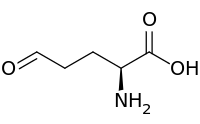
Glutamate-5-semialdehyde
Glutamate-5-semialdehyde is a non-proteinogenic amino acid involved in the biosynthesis of proline and arginine (via ornithine), as well as in the biosynthesis of antibiotics, such as carbapenems. It is synthesized by the reduction of glutamyl-5-phosphate by glutamate-5-semialdehyde dehydrogenase.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(2S)-2-Amino-5-oxopentanoic acid | |
| Other names
L-Glutamate gamma-semialdehyde; gamma-Glutamyl semialdehyde | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C5H9NO3 | |
| Molar mass | 131.131 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
See also
References
- Baich A (1971). "The biosynthesis of proline in Escherichia coli: phosphate-dependent glutamate -semialdehyde dehydrogenase (NADP), the second enzyme in the pathway". Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 244 (1): 129–34. doi:10.1016/0304-4165(71)90129-2. PMID 4399189.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.
