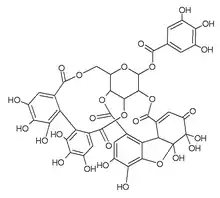
Granatin B
Granatin B is an ellagitannin found in the fruit of Punica granatum (pomegranate).[2][3] It is a molecule having an enantiomeric dehydrohexahydroxydiphenoyl group.[4]
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C41H28O27 | |
| Molar mass | 952.648 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
It is a highly active carbonic anhydrase inhibitor.[2]
References
- www.chemicalbook.com
- Satomi, H.; Umemura, K.; Ueno, A.; Hatano, T.; Okuda, T.; Noro, T. (1993). "Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors from the pericarps of Punica granatum L". Biological & Pharmaceutical Bulletin. 16 (8): 787–790. doi:10.1248/bpb.16.787. PMID 8220326.
- Steinmetz, W. E. (2010). "NMR assignment and characterization of proton exchange of the ellagitannin granatin B". Magnetic Resonance in Chemistry. 48 (7): 565–570. doi:10.1002/mrc.2615. PMID 20535776. S2CID 19592324.
- Okuda, T.; Hatano, T.; Nitta, H.; Fujii, R. (1980). "Hydrolysable tannins having enantiomeric dehydrohexahydroxydiphenoyl group: Revised structure of terchebin and structure of granatin B". Tetrahedron Letters. 21 (45): 4361. doi:10.1016/S0040-4039(00)77858-0.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.