Green junglefowl
The green junglefowl (Gallus varius), also known as Javan junglefowl, forktail or green Javanese junglefowl, is the most distantly related and the first to diverge at least 4 million years ago among the four species of the Junglefowl.[2] Hybridization with domestic chicken has also been reported.[2] Green junglefowl is a medium-sized (up to 75 cm long) bird in the pheasant family Phasianidae.
| Green junglefowl | |
|---|---|
_(7936877492).jpg.webp) | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Galliformes |
| Family: | Phasianidae |
| Genus: | Gallus |
| Species: | G. varius |
| Binomial name | |
| Gallus varius Shaw, 1798 | |
 | |
| : Gallus varius
| |
Description
The colouration of the green junglefowl is sexually dimorphic. The male's plumage is dark and blackish at a distance. A closer view reveals an iridescent mantle of gleaming scales reminiscent in colour and pattern to those seen in the ocellated turkey and green peafowl. Each scale is vivid blue at its base and moves through various shades of gold and bronzed green. Specialized plumes framing the throat of the male green junglefowl are highly light-reflective and appear violet at the proximal and sky blue at the distal edges. The lesser coverts of the wing are a striking burnt orange with bronzed black centers. The distal edges of the greater secondary coverts are vivid ocher.
| |||||||||||||||||||||
| Cladogram showing the species in the genus Gallus.[2][3] |
Like the related red junglefowl, the breast and ventral regions are a dense, light-absorbing black. Like its closer relative the Sri Lankan junglefowl, the male green junglefowl exhibits vivid 'windows' of bare facial skin that contrast against the dark scarlet red of the face. The green junglefowl exhibits an ice blue center in its comb. A region of electric yellow facial skin extends below each ear, delineating the plumed hackles from gular lappet. Its head is topped by a light blue comb, which turns purple or red towards the top. Its wattle is also of the same colour but is bordered with blue on the edges and yellow closer to the throat. The female is mostly brown with occasional green feathers and has no comb.
Distribution and habitat

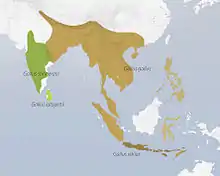
The green junglefowl is endemic to Java, Bali, Lombok, Komodo, Flores, Rinca and small islands linking Java with Flores, Indonesia. It has been introduced to the Cocos (Keeling) Islands where there is a small wild population. It is found from a natural altitude of 0–2000 m in subtropical/tropical lowland moist forest, shrubland and arable land, and has been seen flying from island to island in its native range, where it lives and breeds along coastal areas.
Behaviour
The green junglefowl usually lives in groups of two to five in the wild led by a dominant male, who takes the flock to feed and drink and then back into the cover of the forest. In the night the flock roosts in bamboo stands at 15–20 feet above the forest floor. In the breeding season the dominant males in each flock are challenged by other males without flocks. The two males clap their wings and crow loudly while fighting each other with their spurs.

Relationship with humans
The green junglefowl is being maintained and increasingly bred in captivity as its genetic diversity is disappearing. This is because these birds are bred with domestic chickens by many people, producing a hybrid known as the bekisar. The bekisar has become very popular in the East Java province and has become a mascot of the area. A recent genetic study revealed evidence of genetic introgressive hybridization from green junglefowl to domestic chicken.[2]
The captive green junglefowl requires warm aviaries with much foliage and cover due to their shy nature, and are fed with grains and seeds, as well as fruit and insects; these are the same type of food they would feed on in the wild. This bird has also been known for a long time as a pet animal because of its beauty and unique call.
Status and conservation
The green junglefowl is evaluated as least concern on the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.
References
- BirdLife International (2012). "Gallus varius". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2012. Retrieved 26 November 2013.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Lawal, R.A.; et al. (2020). "The wild species genome ancestry of domestic chickens". BMC Biology. 18 (13): 13. doi:10.1186/s12915-020-0738-1. PMID 32050971.
- Tiley, G.P.; Pandey, A.; Kimball, R.T.; Braun, E.L.; Burleigh, J.G. (2020). "Whole genome phylogeny of Gallus: Introgression and data‑type effects". Avian Research. 11 (7). doi:10.1186/s40657-020-00194-w.
External links
- "Green Junglefowl Gallus varius". BirdLife International.
- "Green junglefowl information and picture". gbwf.org. Archived from the original on 4 February 2006.
- "Information about the green junglefowl". feathersite.com.
- "Captive breeding of Green Jungle Fowl (Gallus varius)". seaza.org. TMII Bird Park. Archived from the original on 12 September 2009.
