Hombrechtikon
Hombrechtikon is a municipality in the district of Meilen in the canton of Zürich in Switzerland.
Hombrechtikon | |
|---|---|
 | |
 Coat of arms | |
Location of Hombrechtikon 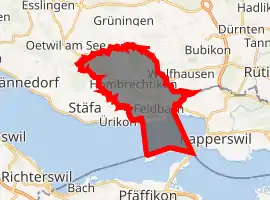
| |
 Hombrechtikon 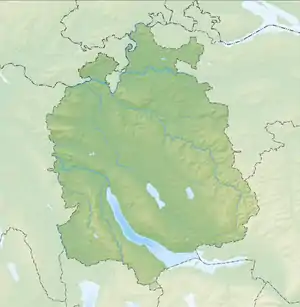 Hombrechtikon | |
| Coordinates: 47°15′N 8°46′E | |
| Country | Switzerland |
| Canton | Zurich |
| District | Meilen |
| Area | |
| • Total | 12.19 km2 (4.71 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 464 m (1,522 ft) |
| Population (2018-12-31)[2] | |
| • Total | 8,756 |
| • Density | 720/km2 (1,900/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+01:00 (Central European Time) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+02:00 (Central European Summer Time) |
| Postal code(s) | 8634 |
| SFOS number | 0153 |
| Localities | Feldbach |
| Surrounded by | Bubikon, Freienbach (SZ), Grüningen, Jona (SG), Oetwil am See, Rapperswil (SG), Stäfa |
| Website | www SFSO statistics |

_IMG_5502.jpg.webp)
History
Hombrechtikon is first mentioned in 1200 as Humbrechtigkon. In 1217 it was mentioned as Hunbrechticon.[3]
Geography

.jpg.webp)
Hombrechtikon has an area of 12.2 km2 (4.7 sq mi). Of this area, 60.6% is used for agricultural purposes, while 14.9% is forested. Of the rest of the land, 18.7% is settled (buildings or roads) and the remainder (5.8%) is non-productive (rivers, glaciers or mountains).[4] In 1996 housing and buildings made up 13.9% of the total area, while transportation infrastructure made up the rest (4.8%).[5] Of the total unproductive area, water (streams and lakes) made up 1.2% of the area. As of 2007 15.8% of the total municipal area was undergoing some type of construction.[5]
The municipality is located between Lake Zurich and the Zürcher Oberland. The land is very hilly, which prevented a large, single village from forming. There at least 97 different hamlets and individual farm houses scattered throughout the municipality. Some of the largest are Lützelsee (first mentioned in 745 as Lucikinse) and Feldbach (first mentioned in 873 as Velepach).[3]
Demographics
Hombrechtikon has a population (as of 31 December 2019) of 8,775.[6] As of 2007, 16.7% of the population was made up of foreign nationals. As of 2008 the gender distribution of the population was 49.2% male and 50.8% female. Over the last 10 years the population has grown at a rate of 11.6%. Most of the population (as of 2000) speaks German (88.9%), with Italian being second most common ( 2.4%) and Albanian being third ( 1.7%).
In the 2007 election the most popular party was the SVP which received 44.1% of the vote. The next three most popular parties were the SPS (13.6%), the FDP (11.7%) and the CSP (10.7%).
The age distribution of the population (as of 2000) is children and teenagers (0–19 years old) make up 25.5% of the population, while adults (20–64 years old) make up 60.8% and seniors (over 64 years old) make up 13.7%. The entire Swiss population is generally well educated. In Hombrechtikon about 77.9% of the population (between age 25-64) have completed either non-mandatory upper secondary education or additional higher education (either university or a Fachhochschule). There are 2948 households in Hombrechtikon.[5]
Hombrechtikon has an unemployment rate of 2.12%. As of 2005, there were 260 people employed in the primary economic sector and about 87 businesses involved in this sector. 983 people are employed in the secondary sector and there are 93 businesses in this sector. 1305 people are employed in the tertiary sector, with 224 businesses in this sector.[4] As of 2007 41.6% of the working population were employed full-time, and 58.4% were employed part-time.[5]
As of 2008 there were 2,314 Catholics and 3,419 Protestants in Hombrechtikon. In the 2000 census, religion was broken down into several smaller categories. From the census, 51.4% were some type of Protestant, with 47.4% belonging to the Swiss Reformed Church and 4% belonging to other Protestant churches. 28.9% of the population were Catholic. Of the rest of the population, 0% were Muslim, 6% belonged to another religion (not listed), 2.9% did not give a religion, and 10.6% were atheist or agnostic.[5]
The historical population is given in the following table:[3]
| year | population |
|---|---|
| 1634 | 617 |
| 1772 | 1,501 |
| 1850 | 2,649 |
| 1900 | 2,292 |
| 1950 | 3,079 |
| 1980 | 6,001 |
| 2000 | 7,246 |
Geography
The village Feldbach and the train station are located on Lake Zürich. Hombrechtion is perched above the lake besides Pfannenstiel. On a plateau, the protected moorlands Uetziker Ried and Lützelsee are located, as well Seeweidsee is situated in the municipality.
Transportation
Hombrechtikon-Feldbach railway station is a stop of the S-Bahn Zürich on the line S7.
Heritage sites of national significance
There are seven sites in Hombrechtikon that are listed as Swiss heritage sites of national significance. The houses in the town include; the Hof Oberhaus at Seestrasse 2&4, the Hürlimannhaus at Lützelsee 2&4, the Landstiz Rosenberg at Alte Landstrasse 1&3, the Menzihaus at Lützelsee 3 and the Eglihaus at Lutikon 1-3. The town's Reformed church is also on the list. The neolithic and early Bronze Age settlement at Feldbach is the last site on the list. The entire hamlet of Lützelsee and the Feldbach area are part of the Inventory of Swiss Heritage Sites.[7] The prehistoric settlement Seegubel at Feldbach is part of the Prehistoric Pile dwellings around the Alps, a UNESCO World Heritage Site.[8]
References
- "Arealstatistik Standard - Gemeinden nach 4 Hauptbereichen". Federal Statistical Office. Retrieved 13 January 2019.
- "Ständige Wohnbevölkerung nach Staatsangehörigkeitskategorie Geschlecht und Gemeinde; Provisorische Jahresergebnisse; 2018". Federal Statistical Office. 9 April 2019. Retrieved 11 April 2019.
- Hombrechtikon in German, French and Italian in the online Historical Dictionary of Switzerland.
- Swiss Federal Statistical Office Archived 2016-01-05 at the Wayback Machine accessed 10-Aug-2009
- Statistics Zurich (in German) accessed 4 August 2009
- "Ständige und nichtständige Wohnbevölkerung nach institutionellen Gliederungen, Geburtsort und Staatsangehörigkeit". bfs.admin.ch (in German). Swiss Federal Statistical Office - STAT-TAB. 31 December 2019. Retrieved 6 October 2020.
- Swiss inventory of cultural property of national and regional significance Archived 2010-06-28 at the Wayback Machine 04.05.2010 version, (in German) accessed 14 August 2011
- UNESCO World Heritage Site - Prehistoric Pile dwellings around the Alps
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Hombrechtikon. |
- Official website (in German)
- Hombrechtikon in German, French and Italian in the online Historical Dictionary of Switzerland.
.jpg.webp)
