ITCH
ITCH is a HECT domain E3 ubiquitin ligase that is ablated in non-agouti-lethal 18H (aka Itchy) mice.[5][6] Itchy mice develop a severe immunological phenotype after birth that includes hyperplasia of lymphoid and hematopoietic cells, and stomach and lung inflammation.[7][8] In humans ITCH deficiency causes altered physical growth, craniofacial morphology defects, defective muscle development, and aberrant immune system function.[9] ITCH contains multiple amino acids that are phosphorylated and ubiquitinated.[10]
Regulation by post-translational modifications
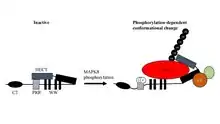
ITCH is regulated by MAPK8.[11] MAPK8 regulates JUNB protein turnover by MAPK8-dependent phosphorylation of ITCH and a subsequent conformational change in ITCH. This mechanism is discrete from the direct activation of Jun family transcription factors by direct phosphorylation. ITCH serves as a paradigm for our understanding of the regulation of the ubiquitylation machinery by direct protein phosphorylation of its components. Importantly, this regulatory process controls the balance of Th2 cytokine secretion by negatively regulating JUNB levels and Interleukin 4 transcription.
References
- GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000078747 - Ensembl, May 2017
- GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000027598 - Ensembl, May 2017
- "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- Perry WL, Hustad CM, Swing DA, O'Sullivan TN, Jenkins NA, Copeland NG (February 1998). "The itchy locus encodes a novel ubiquitin protein ligase that is disrupted in a18H mice". Nature Genetics. 18 (2): 143–6. doi:10.1038/ng0298-143. PMID 9462742. S2CID 9438916.
- https://swissmodel.expasy.org/repository/uniprot/Q96J02
- Melino G, Gallagher E, Aqeilan RI, Knight R, Peschiaroli A, Rossi M, et al. (July 2008). "Itch: a HECT-type E3 ligase regulating immunity, skin and cancer". Cell Death and Differentiation. 15 (7): 1103–12. doi:10.1038/cdd.2008.60. PMID 18552861. S2CID 2626150.
- Aki D, Zhang W, Liu YC (July 2015). "The E3 ligase Itch in immune regulation and beyond". Immunological Reviews. 266 (1): 6–26. doi:10.1111/imr.12301. PMID 26085204. S2CID 42110767.
- Lohr NJ, Molleston JP, Strauss KA, Torres-Martinez W, Sherman EA, Squires RH, et al. (March 2010). "Human ITCH E3 ubiquitin ligase deficiency causes syndromic multisystem autoimmune disease". American Journal of Human Genetics. 86 (3): 447–53. doi:10.1016/j.ajhg.2010.01.028. PMC 2833372. PMID 20170897.
- "ITCH (human)". www.phosphosite.org. Retrieved 2020-10-27.
- Karin M, Gallagher E (2005). "From JNK to pay dirt: jun kinases, their biochemistry, physiology and clinical importance". IUBMB Life. 57 (4–5): 283–95. doi:10.1080/15216540500097111. PMID 16036612. S2CID 25508987.
External links
- ITCH+protein,+human at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)