Indene
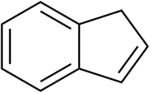
Indene is a flammable polycyclic hydrocarbon with chemical formula C9H8. It is composed of a benzene ring fused with a cyclopentene ring. This aromatic liquid is colorless although samples often are pale yellow. The principal industrial use of indene is in the production of indene/coumarone thermoplastic resins. Substituted indenes and their closely related indane derivatives are important structural motifs found in many natural products and biologically active molecules, such as sulindac.[3]
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
1H-Indene | |
| Systematic IUPAC name
Bicyclo[4.3.0]nona-1,3,5,7-tetraene | |
| Other names
Benzocyclopentadiene Indonaphthene | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| 635873 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.002.176 |
| 27265 | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C9H8 | |
| Molar mass | 116.16 |
| Appearance | Colorless liquid[1] |
| Density | 0.997 g/mL |
| Melting point | −1.8 °C (28.8 °F; 271.3 K) |
| Boiling point | 181.6 °C (358.9 °F; 454.8 K) |
| Insoluble | |
| Acidity (pKa) | 20.1 (in DMSO)[2] |
| −80.89×10−6 cm3/mol | |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | Flammable |
| Flash point | 78.3 °C (172.9 °F; 351.4 K) |
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |
PEL (Permissible) |
none[1] |
REL (Recommended) |
TWA 10 ppm (45 mg/m3)[1] |
IDLH (Immediate danger) |
N.D.[1] |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds |
Benzofuran, Benzothiophene, Indole |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Isolation
Indene occurs naturally in coal-tar fractions boiling around 175–185 °C. It can be obtained by heating this fraction with sodium to precipitate solid "sodio-indene". This step exploits indene's weak acidity evidenced by its deprotonation by sodium to give the indenyl derivative. The sodio-indene is converted back to indene by steam distillation.[4]
Reactivity
Indene readily polymerises. Oxidation of indene with acid dichromate yields homophthalic acid (o-carboxylphenylacetic acid). It condenses with diethyl oxalate in the presence of sodium ethoxide to form indene–oxalic ester, and with aldehydes or ketones in the presence of alkali to form benzofulvenes, which are highly coloured. Treatment of indene with organolithium reagents give lithium indenyl compounds:
- C9H8 + RLi → LiC9H7 + RH
Indenyl is a ligand in organometallic chemistry, giving rise to many transition metal indenyl complexes.[5]
See also
References
- NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0340". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- Bordwell FG (1988). "Equilibrium acidities in dimethyl sulfoxide solution". Accounts of Chemical Research. 21 (12): 456–463. doi:10.1021/ar00156a004. Bordwell pKa Table in DMSO Archived 2008-10-09 at the Wayback Machine
- Wu, Jie; Qiu, Guanyinsheng (2014). "Generation of Indene Derivatives by Tandem Reactions". Synlett. 25 (19): 2703–2713. doi:10.1055/s-0034-1379318.
- Collin, Gerd; Mildenberg, Rolf; Zander, Mechthild; Höke, Hartmut; McKillip, William; Freitag, Werner; Imöhl, Wolfgang. "Resins, Synthetic". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH.
- O'Connor, Joseph M.; Casey, Charles P. (1987). "Ring-Slippage Chemistry of Transition Metal Cyclopentadienyl and Indenyl Complexes". Chemical Reviews. 87 (2): 307–318. doi:10.1021/cr00078a002.
External links
- W. v. Miller, Rohde (1890). "Zur Synthese von Indenderivaten". Berichte der Deutschen Chemischen Gesellschaft. 23 (2): 1881–1886. doi:10.1002/cber.18900230227.
- W. v. Miller, Rohde (1890). "Zur Synthese von Indenderivaten". Berichte der Deutschen Chemischen Gesellschaft. 23 (2): 1887–1902. doi:10.1002/cber.18900230228.
- Finar, I. L. (1985). Organic Chemistry. Longman Scientific & Technical. ISBN 0-582-44257-5.