Jespersen's Cycle
Jespersen's Cycle (JC) is a series of processes in historical linguistics, which describe the historical development of the expression of negation in a variety of languages, from a simple pre-verbal marker of negation, through a discontinuous marker (elements both before and after the verb) and in some cases through subsequent loss of the original pre-verbal marker. The pattern was formulated in Otto Jespersen's 1917 book Negation in English and Other Languages,[1] and named after him in Swedish linguist Östen Dahl's 1979 article Typology of Sentence Negation.[2]
Introduction
The linguist Otto Jespersen began his book with the words:
The history of negative expressions in various languages makes us witness the following curious fluctuation: the original negative adverb is first weakened, then found insufficient and therefore strengthened, generally through some additional word, and this in turn may be felt as the negative proper and may then in the course of time be subject to the same development as the original word.
The process has since been described for many languages in many different families, and is particularly noticeable in languages which are currently at stage II (both the original and the additional word obligatory) such as French, Welsh, and some dialects of Arabic and Berber.
The fact that different languages can be seen to be in different stages of the process, and that sometimes, as Jespersen says, the whole process can begin again after renewal, prompted Dahl to name the process "Jespersen's cycle". The observation was however made earlier, most noticeably by Antoine Meillet, who used the term 'spiral'.
The process
There are three stages, labelled I, II and III:
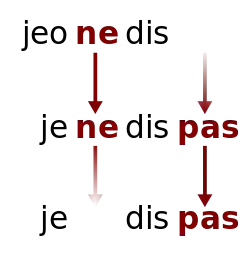
In Stage I, negation is expressed by a single pre-verbal element:
(Examples from different periods of French, all from Lucas (2007)):
jeo
I
ne
NEG
dis.
say
(Old French)
'I do not say'
In Stage II both a preverbal and a postverbal element are obligatory:
je
I
ne
NEG
dis
say
pas.
NEG
(modern standard French)
'I do not say'
In Stage III the original preverbal element becomes optional or is lost altogether:
je
I
dis
say
pas.
NEG
(modern colloquial French)
'I do not say'
Examples
French is well known to use a bipartite negative, e.g. "Je ne sais pas" = "I don't know", lit. "I not know not". (The second negative element originally had a semantic connection with the verb: "Je ne marche pas" originally meant "I don't walk a step".) Welsh has a very similar pattern, "Ni wn i ddim, literally "Not know I nothing". In both languages, the colloquial register is at a more advanced stage in the cycle, and the first part (ne or ni(d)) is very frequently omitted. In formal Welsh registers, by contrast, ni(d) tends to be used without ddim. This is not true of formal registers of modern French, but the use of ne on its own survives in certain set expressions (e.g. n'importe quoi: "no matter what/anything") and with certain verbs (e.g. "Elle ne cesse de parler": "She doesn't stop talking").
English too passed through Jespersen's cycle early in its history: for example "I didn't see" would be expressed in Old English as ic ne seah; then strengthened with the word nauȝt (from Old English nawiht "no thing") as Middle English I ne sauȝ nauȝt; then leading to Early Modern English I saw not.[3][4] The same development occurred in the other Germanic languages such as German and Dutch, which produced their respective postposed negative particles nicht and niet, first duplicating and eventually ousting the original preposed negative particle ne / ni.[5]
Modern English’s do-support and contraction of “do not” to “don’t” in colloquial speech could be argued as moving English back toward Stage I of Jespersen’s Cycle—“I didn’t see”. Incipient signs of a further step may be seen in sentences like "I didn't say a word" or "I don't know shit", in which the final word does not specify the object of the verb, but mainly serves to reinforce the negative.
Central Atlas Tamazight, a Berber language spoken principally in Central Morocco, uses a bipartite negative construction (e.g. /uriffiɣ ʃa/ 'he didn't go out' — the underlined elements together convey the negative) which apparently was modeled after proximate Arabic varieties.[6][7]
The Chamic languages, spoken in parts of Cambodia, Vietnam, and Hainan, may also be undergoing Jespersen's cycle.[8]
Italian and the various Italian regional languages are also undergoing a similar transformation, where even all three stages can be seen in action at once: The standard language is generally at stage I, with, e. g., Non gliel'ho detto (I haven't told him/her). This can become Non gliel'ho mica detto colloquially, but with a difference in meaning (stage II) and also (stage III) Gliel'ho mica detto (sub-standard and only regionally in some varieties) or Mica gliel'ho detto (colloquial, but with identical meaning as stage II), mica originally meaning "in the least". In Western Lombard, the archaic no l'hoo vist (I haven't seen him/it) has long since become l'hoo minga vist or l'hoo vist no with no change in meaning.
References
- Jespersen 1917.
- Dahl, Östen (1979). "Typology of Sentence Negation". Linguistics. 17: 79–106. doi:10.1515/ling.1979.17.1-2.79.
- Kastovsky, Dieter. 1991. Historical English syntax. P. 452
- Van Gelderen, Elly. 2006. A history of the English language. P. 130
- Jäger, Agnes. History of German negation. P. 103–104
- Lucas 2007.
- "Contact-induced grammatical change: towards an explicit account" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2009-06-07. Retrieved 2009-06-07. (389 KB), p. 2.
- "Bipartite negatives in Chamic" (PDF). (11.5 MB), p. 313.
Bibliography
- Jespersen, Otto (1917). Negation in English and Other Languages. Copenhagen: Høst.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Lucas, Christopher (2007). "Jespersen's Cycle in Arabic and Berber". Transactions of the Philological Society. 105: 398–431. doi:10.1111/j.1467-968x.2007.00189.x.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- van der Auwera, Johan. (2009) 'The Jespersen Cycles', Cyclical change, ed. by E. van Gelderen. Amsterdam: Benjamins, 35-71.
