Kayaba Ku-4
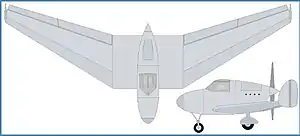
The Kayaba Ku-4 was a research aircraft built in Japan in 1940 to investigate the possibilities of tailless aircraft designs. It followed designer Hidemasa Kimura's successful Ku-2 and Ku-3 designs for the Imperial Japanese Army. While these previous aircraft had been gliders, however, the Ku-4 was to be a powered by a pusher engine. It had a low, swept wing, and like the Ku-2, fins at the wingtips.
| Ku-4 | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Role | Research aircraft |
| National origin | Japan |
| Manufacturer | Kayaba Industry |
| Designer | Hidemasa Kimura |
| Status | Cancelled project |
Work on the prototype was well advanced by April 1941, but the following month, Kimura's relationship with the Army soured following the crash of the Ku-2. The Ku-4 was cancelled, and Kimura eventually received only ¥17,000 of the ¥200,000 that had been promised for the development of his tailless designs.
Specifications (as designed)
General characteristics
- Crew: One pilot
- Length: 3.42 m (11 ft 3 in)
- Wingspan: 9.80 m (32 ft 2 in)
- Wing area: 9.0 m2 (97 sq ft)
- Powerplant: 1 × piston engine , 90 kW (120 hp)
Performance
- Maximum speed: 180 km/h (110 mph, 96 kn)
- Range: 300 km (190 mi, 170 nmi)
References
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Kayaba Ku-4. |
- Wooldridge, E.T. "Japanese flying wings". History of the Flying Wing. Retrieved 29 April 2007.
- 日本飞翼的短暂研究
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.