Krafla
Krafla is a volcanic caldera of about 10 km in diameter with a 90 km long fissure zone, in the north of Iceland in the Mývatn region which is situated on the Iceland Hotspot atop the Mid-Atlantic Ridge at the divergent boundary between the North American Plate and the Eurasian Plate. Its highest peak reaches up to 818 m and it is 2 km in depth. There have been 29 reported eruptions in recorded history.
| Krafla | |
|---|---|
 Aerial view of Krafla (mountain) and Krafla caldera with Leirhnjúkur in 2008 | |
| Highest point | |
| Elevation | 650 m (2,130 ft) |
| Coordinates | 65°44′0″N 16°47′0″W |
| Geography | |
 Location in Iceland | |
| Location | Iceland |
| Geology | |
| Mountain type | Caldera |
| Last eruption | September 1984 |
Overview
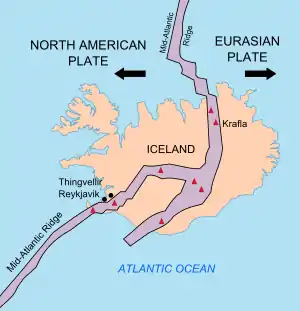
Iceland is a place where it is possible to see plate tectonics at work. It sits astride the Mid-Atlantic Ridge; the western part of the island nation is part of the roughly westward-moving North American plate, while the eastern part of the island is part of the roughly eastward-moving Eurasian Plate. The north-south axis of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge splits Iceland in two, roughly north to south. Along this ridge many of Iceland's most active volcanoes are located; Krafla is one of these.[1]
Krafla includes the crater Víti, one of two well-known craters by this name in Iceland (the other is in Askja). The Icelandic word "víti" means "hell". In former times, people often believed hell to be under volcanoes. Víti has a green lake inside of it.
South of the Krafla area, but not actually within the caldera is Námafjall, a mountain, beneath which is Hverir, a geothermal area with boiling mudpools and steaming fumaroles.
The Mývatn fires occurred between 1724–1729, when many of the fissure vents opened up. The lava fountains could be seen in the south of the island and a lava flow destroyed three farms near the village of Reykjahlíð, although nobody was harmed.
Between 1975 and 1984 there was a volcanic episode within the Krafla volcano. It involved nine volcanic eruptions and fifteen uplift and subsidence events. This interrupted some of the Krafla drillfields. During these events a large magma chamber emerged. This has been identified by analysing the seismic activity.
Since 1977 the Krafla area has been the source of the geothermal energy used by a 60 MWe power station. A survey undertaken in 2006 indicated very high temperatures at depths of between 3 and 5 kilometres and these favourable conditions have led to the development of the first well from the Iceland Deep Drilling Project (IDDP), that found magma only 2.1 km deep.[2]
Photogallery
 Krafla volcanic area
Krafla volcanic area Lava flow during a rift eruption at Krafla, 1984
Lava flow during a rift eruption at Krafla, 1984 Lava ropes at Krafla, June 2007
Lava ropes at Krafla, June 2007 Steams at Krafla, June 2007
Steams at Krafla, June 2007 Sulfur deposits at Krafla, June 2007
Sulfur deposits at Krafla, June 2007 A general view of Krafla, June 2007
A general view of Krafla, June 2007 Mudpots at Hverir, Námafjall, August 2008
Mudpots at Hverir, Námafjall, August 2008 Lava at Krafla
Lava at Krafla Krafla area
Krafla area Boiling mudpools
Boiling mudpools Víti crater and lake
Víti crater and lake Small lake in Krafla
Small lake in Krafla
See also
References
- Kious, W. Jacquelyne; Tilling, Robert I. (February 1996). "This Dynamic Earth: The Story of Plate Techtonics. Chapter 3: Understanding plate motions - Divergent boundaries". United States Geological Survey. USGS. Retrieved 15 January 2020.
The volcanic country of Iceland, which straddles the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, offers scientists a natural laboratory for studying on land the processes also occurring along the submerged parts of a spreading ridge. Iceland is splitting along the spreading center between the North American and Eurasian Plates, as North America moves westward relative to Eurasia.
- http://www.iddp.is/ Iceland Deep Drilling Project
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Krafla (volcanic system). |
- Krafla in the Catalogue of Icelandic Volcanoes
- Volcanism
- Photos of Krafla and Reykjahlíð (among others)
- Univ. of Iceland: Information about Krafla
- Energy from magma at Krafla