Laetare Sunday
Laetare Sunday (/liːˈtɛːri/ or /lʌɪˈtɑːri/)[1] is the fourth Sunday in the season of Lent, in the Western Christian liturgical calendar. Traditionally, this Sunday has been a day of celebration, within the austere period of Lent. This Sunday gets its name from the first few words (incipit) of the traditional Latin entrance (Introit) for the Mass of the day. "Laetare Jerusalem" ("Rejoice, O Jerusalem") is Latin from Isaiah 66:10.
| Laetare Sunday | |
|---|---|
| Observed by | Western Christianity |
| Type | Western Christian |
| Observances | Church services; feasts/parties |
| Date | Fourth Sunday of Lent (21 days before Easter Sunday) |
| 2020 date | March 22 |
| 2021 date | March 14 |
| 2022 date | March 27 |
| 2023 date | March 19 |


History
The term "Laetare Sunday" is used by most Roman Catholic and Anglican churches, particularly those with Latin liturgical traditions. The word comes from the Latin laetare, the singular imperative of laetari: "to rejoice".
Laetare Hierusalem et conventum facite omnes qui diligitis eam; gaudete cum laetitia, qui in tristitia fuistis, ut exsultetis et satiemini ab uberibus consolationis vestrae. Psalm: Laetatus sum in his quae dicta sunt mihi: in domum Domini ibimus.
Rejoice ye with Jerusalem; and be ye glad for her, all ye that delight in her: exult and sing for joy with her, all ye that in sadness mourn for her; that ye may suck, and be satisfied with the breasts of her consolations. Psalm: I was glad when they said unto me, We will go into the house of the Lord.
Alternative names
This Sunday is currently also known as Mothering Sunday,[4] Refreshment Sunday, mid-Lent Sunday (in French mi-carême) and Rose Sunday (either because the golden rose (sent by Popes to Catholic sovereigns) used to be blessed at this time, or because the use of rose-colored (rather than violet) vestments was permitted on this day).
Historically, the day was also known as "the Sunday of the Five Loaves," from the story of the miracle of the loaves and fishes. Before the adoption of the modern "common lectionaries", this narrative was the traditional Gospel reading for this Sunday in Roman Catholic, Lutheran, Anglican, and Old Catholic churches.
The station church at Rome for this day was Santa Croce in Gerusalemme, one of the seven chief basilicas; the Golden Rose, sent by Popes to Catholic sovereigns, used to be blessed at this time and for this reason the day was sometimes called Dominica de Rosa.
Customs

In Roman Catholic, Anglican, Lutheran and Old Catholic churches flowers may appear on the high altar and the organ may be played as a solo instrument. Priests are given the option to wear rose-colored vestments at Mass held on this day in place of the violet vestments normally worn during Lent.[5] The term "rose" is used to describe this lighter shade of the color violet in the Roman Rite.[6]
The Sunday is considered a day of relaxation from normal Lenten rigours; a day of hope with Easter at last within sight. Traditionally, weddings (otherwise banned during Lent) could be performed on this day,[7] and servants were released from service for the day to visit their mothers (hence 'Mothering Sunday').
The Laetare Medal is announced, and gains its name from, Laetare Sunday.[8]
Date
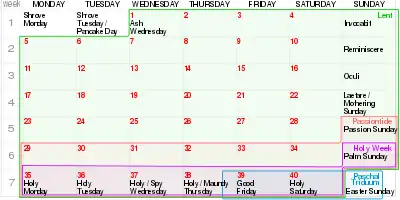
Laetare Sunday is exactly 21 days before Easter Sunday, a moveable feast based on the cycles of the moon. The date can be any between 1 March and 4 April inclusive; occurrence in April is considered to be uncommon; the last occurrence was on 3 April 2011 and the next will be on 4 April 2038, after which it will not occur again until 1 April 2057 – occurrences in April are printed in the below list in bold type. The earliest occurrence of Laetare Sunday in the twenty-first century was on 2 March 2008,[9] and the latest will be on 4 April 2038.
Laetare Sunday occurs on these dates:
- 2019 – 31 March
- 2020 – 22 March
- 2021 – 14 March
- 2022 – 27 March
- 2023 – 19 March
- 2024 – 10 March
- 2025 – 30 March
- 2026 – 15 March
- 2027 – 7 March
- 2028 – 26 March
- 2029 – 11 March
- 2030 – 31 March
- 2031 – 23 March
- 2032 – 7 March
- 2033 – 27 March
- 2034 – 19 March
- 2035 – 4 March
- 2036 – 23 March
- 2037 – 15 March
- 2038 – 4 April
- 2039 – 20 March
- 2040 – 11 March
- 2041 – 31 March
- 2042 – 16 March
- 2043 – 8 March
- 2044 – 27 March
- 2045 – 19 March
- 2046 – 4 March
- 2047 – 24 March
- 2048 – 15 March
- 2049 – 28 March
- 2050 – 20 March
- 2051 – 12 March
- 2052 – 31 March
- 2053 – 16 March
- 2054 – 8 March
- 2055 – 28 March
- 2056 – 12 March
- 2057 – 1 April
- 2058 – 24 March
- 2059 – 9 March
- 2060 – 28 March
- 2061 – 20 March
- 2062 – 5 March
- 2063 – 25 March
- 2064 – 16 March
- 2065 – 8 March
- 2066 – 21 March
- 2067 – 13 March
- 2068 – 1 April
- 2069 – 24 March
- 2070 – 9 March
- 2071 – 29 March
- 2072 – 20 March
- 2073 – 5 March
- 2074 – 25 March
- 2075 – 17 March
- 2076 – 29 March
- 2077 – 21 March
- 2078 – 13 March
- 2079 – 2 April
- 2080 – 17 March
- 2081 – 9 March
- 2082 – 29 March
- 2083 – 14 March
- 2084 – 5 March
- 2085 – 25 March
- 2086 – 10 March
- 2087 – 30 March
- 2088 – 21 March
- 2089 – 13 March
- 2090 – 26 March
- 2091 – 18 March
- 2092 – 9 March
- 2093 – 22 March
- 2094 – 14 March
- 2095 – 3 April
- 2096 – 25 March
- 2097 – 10 March
- 2098 – 30 March
- 2099 – 22 March
- 2100 – 7 March
See also
References
- "Laetare". Oxford English Dictionary (Online ed.). Oxford University Press. (Subscription or participating institution membership required.)
- Higdon, David Leon (1972). "The Wife of Bath and Refreshment Sunday". Papers on Language and Literature. 8 (2): 199–201.
- Burgess, Francis (1921). The English Gradual, part 2. London: Plainchant Publications Committee.
- Dunning, Andrew (26 March 2017). "The medieval origins of Mothering Sunday". Medieval manuscripts blog. The British Library.
- The traditional use of rose-pink vestments on this day by Anglican clergy is suggested in the liturgical colour sequence notes of Common Worship of which an on-line version may be found here (see near bottom of page).
- "Homiletic Directory". Congregation for Divine Worship and the Discipline of the Sacraments. 2015. Third Sunday of Advent, Fourth Sunday of Lent.
- See for example, Laetare Sunday extract
- Dame, Marketing Communications: Web | University of Notre. "About". The Laetare Medal. Retrieved 2021-02-01.
- https://www.catholicculture.org/culture/liturgicalyear/calendar/day.cfm?date=2008-03-02
- Catholic Encyclopedia: "Laetare Sunday"