Lahontan Valley
The Lahontan Valley is a basin in Churchill County, Nevada, United States.[1] The valley is a landform of the central portion of the prehistoric Lake Lahontan's lakebed of 20,000-9,000 years ago. The valley and the adjacent Carson Sink represent a small portion of the lake bed. Humboldt Lake is to the valley's northeast. Pyramid Lake is west. Walker Lake is to the south.
| Lahontan Valley | |
|---|---|
| Lahontan Basin | |
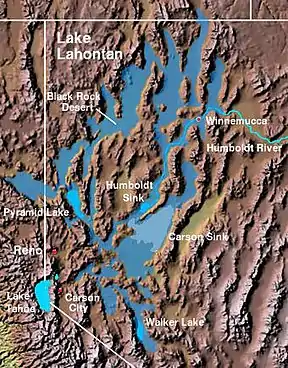 The Lahontan Valley is adjacent to the Carson Sink and southwest of the Humboldt Sink. | |
 Lahontan Valley  Lahontan Valley | |
| Floor elevation | 4,006 m (13,143 ft)[1] |
| Geography | |
| Country | United States |
| State | Nevada |
| District | Churchill County |
| Coordinates | 39°34′0″N 118°50′0″W |
| Traversed by | U.S. Route 50 |
Description

The Lahontan Valley is mostly uninhabited desert, aside from the city of Fallon and the Fallon Paiute-Shoshone Reservation. There is sparse habitation in farmland around the Carson River and irrigation canals surrounding Fallon, an arc of farms around the Soda Lakes volcano, the railroad junction at Hazen and the ghost town of Stillwater. There is a geothermal power plant at Soda Lake and combined geothermal/solar plant at Stillwater. During the era of the California trail the Lahontan and adjacent valleys to the northwest were called the Forty Mile Desert.
The valley derives its name from Louis-Armand de Lom d'Arce de Lahontan, Baron de Lahontan, a French soldier.[2]
Forty Mile Desert
The Forty Mile Desert is a California Gold Rush name for Nevada's Lahontan Valley and the adjoining area to the northwest. Emigrants following the California Trail west came into the Lahonton Valley via the Humboldt River. West of the river's end in the Humboldt Sink, the trail forked, with one branch leading towards the Carson River and the other towards the Truckee River.[3] Regardless of which route they took, the travelers would have to endure about 40 miles (64 km) of desert without usable water.[4] The Truckee route traversed the area starting at modern Lovelock, reaching the waters of the Truckee River near modern Wadsworth. This path is along a series of smaller valleys separated from the main part of the Lahontan Valley by the Hot Springs Mountains. Modern Interstate 80 closely approximates this path. The Carson route across the Lahontan Valley proceeds south from modern Lovelock towards an area west of modern Fallon called Ragtown, which had the last usable water on the Carson River.[5] The First Transcontinental Railroad (modern Overland Route) and U.S. Route 95 loosely follow the Carson route.
Per a state historical marker at a rest area at the junction of I-80 and US 95, the Forty Mile Desert was the most dreaded part of the California Trail. If possible, it was crossed at night. An 1850 survey counted 953 graves along this portion of the trail, along with thousands of animal skeletons and abandoned belongings of the desperate travelers.[4][6]
References
- U.S. Geological Survey Geographic Names Information System: Lahontan Valley
- Federal Writers' Project (1941). Origin of Place Names: Nevada (PDF). W.P.A. p. 11.
- Nevada Road and Recreation Atlas (Map). 1:250000. Benchmark Maps. 2003. p. 47. ISBN 0-929591-81-X.
- "Forty Mile Desert". Nevada State Historic Preservation Office. Retrieved April 12, 2020. State Historical Marker No. 26.
- "Ragtown". Nevada State Historic Preservation Office. Retrieved April 12, 2020. State Historical Marker No. 19.
- "Forty Mile Desert - Virtual Tour". Oregon-California Trails Association. Archived from the original on 2011-07-25. Retrieved 2011-07-26.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Lahontan Valley. |
- Carson Trail at Emigrant Trails West, photo tour of southern wagon route across Forty Mile Desert
- Truckee Trail at Emigrant Trails West, photo tour of northern wagon route across Forty Mile Desert
