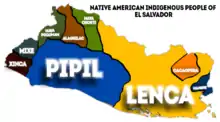
Lenca
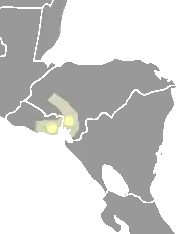
The Lenca are a Mesoamerican indigenous people of southwestern Honduras and eastern El Salvador in Central America. They once spoke the Lenca language, which is now nearly extinct. In Honduras, the Lenca are the largest indigenous group, with an estimated population of 100,000. El Salvador's Lenca population is estimated at about 37,000.
 Lenca at a market in La Esperanza, Honduras | |
| Total population | |
|---|---|
| 137,000 | |
| Regions with significant populations | |
| ~100,000 | |
| 37,000 | |
| Languages | |
| Honduran Spanish • Salvadoran Spanish • Formerly Lencan languages | |
| Religion | |
| Roman Catholic, Traditional tribal religion | |

The pre-Conquest Lenca had frequent contact with various Mayan groups as well as other indigenous peoples of the territory of present-day Mexico and Central America. The origin of Lenca populations has been a source of ongoing debate among anthropologists and historians. Research has been directed to gaining archaeological evidence of the pre-colonial Lenca.
Culture
_(20400434566).jpg.webp)
Lenca culture developed for centuries preceding the Spanish conquest. Like other indigenous groups of Central America, they gradually changed their cultural relationships to the land.[1][2][3]
While there are ongoing political problems in contemporary Central America over indigenous land rights and identity, the Lenca have retained many of their pre-Columbian traditions. Although their indigenous language is nearly extinct, and their culture has changed in other ways over the centuries due to the Spanish influence, the Lenca continue to preserve some traditional ways and identify as indigenous peoples. There are programs and dictionaries to help revitalize the language and traditional Lenca culture.
Economy
Modern Lenca communities are centered on the milpa crop-growing system. Lenca men engage in agriculture, including the cultivation of coffee, cacao, tobacco, varieties of plantains, and gourds. Other principal crops are maize, wheat, beans, squash, sugarcane, and chili peppers. In El Salvador peanuts are also cultivated. Within their communities, Lenca traditionally expect all members to participate in communal efforts.[4][5]
While there has been a growing national acceptance of indigenous rights and culture in both Honduras and El Salvador, the Lenca continue to struggle in both nations over indigenous land rights. In the mid-1990s, indigenous activists formed political groups in order to petition the government over issues of land ownership and indigenous rights. Due to the unresolved land issues and constitutional amendments in those countries that favor land ownership by large-scale investors and agro-industrialists, there has been a decreasing amount of land for indigenous peoples. Many Lenca men have had to find employment in neighboring cities.[4]
Many Lenca communities still have their communal land. They devote the majority of cultivation to commodity crops raised for export to foreign markets. Most Lenca still use traditional agricultural practices on their own crops, as well as the crops for investors.[2]
Material culture
During the Pre-Columbian Era, Lencan pottery was very similar to that of other Mesoamerican groups, especially Mayan pottery and that of several groups from central Mexico. Today, Lencan pottery is very distinctive. Handcrafted by Lenca women, the modern traditional pottery is considered an ethnic marking of their culture, as is common among traditional peoples. Many handmade pieces are sold at very high prices in the United States and Europe.
In the mid-1980s, NGO cooperatives of women artisans were created in order to market their pottery. To increase sales of their works, the cooperatives were encouraged to orient their designs and styles to meet the tastes of urban buyers and to expand their market. In the 21st century, Lenca women are making modern painted pottery (often painted black and white) not based on traditional designs in an effort to appeal to foreign buyers.[2]
Traditional Lencan pottery is still made by women in the town of Gracias, Honduras and the surrounding villages, most notably in La Campa. The pieces are usually a dark orange or brick color. Visitors can watch demonstrations of how traditional pottery is made.
Spirituality
The contemporary Lenca primarily practice Roman Catholicism, adopted, often by force, during the colonial Spanish era after the first war. As with other indigenous groups], their practices often incorporate Pre-Hispanic traditions, and some Lenca communities retain more exclusively indigenous traditions. Similarly to the beliefs of other indigenous peoples in Mesoamerica, the Lenca consider sacred mountains and hills to be holy places. Many Lenca have profound respect and adoration for the sun. Their main gods were Ilanguipuca (great father), Itanipuca (great mother), and Icelacam (god of time).
Some traditional practices are associated with the cultivation and harvest of crops. During different crop seasons, for instance, Lenca men participate in ceremonies where they consume chicha and burn incense.[5]
Guancasco
Guancasco is the annual ceremony by which neighboring communities, usually two, gather to establish reciprocal obligations in order to confirm peace and friendship. The guancascos take many forms and have adopted many Catholic representations, but they also include traditional customs and representations. Processions and elaborate exchanges of greetings and Honduran folk dancing are performed for the statue of the patron saint of the town. Towns in central and western Honduras such as Yamaranguila, La Campa, La Paz and Tencoa, all host the annual celebration.[6][7]
Creation story
In the Lenca Putum story it is said that Aku created everything.
Archaeology
Until recently, archaeological research and investigation of Lenca settlements had been limited. In studies of how the indigenous and colonial cultures affected each other, more attention had been given to colonial-era settlements influenced by Europeans. In addition, many indigenous sites are isolated and difficult to access. Researchers may also have difficulty conducting excavations because the sites are found in agricultural fields under cultivation. Surface evidence in rural areas reveals that pre-Columbian indigenous settlements existed in many regions. Many surface-visible earthwork mounds have been damaged from being plowed over by rural farmers.
The evidence for pre-Columbian Lenca has come from research and excavation of several sites in Honduras and El Salvador. It shows that Lenca occupation was characterized by a relatively continuous pattern of growth.
The Comayagua Valley is located at the highland basin linking the Pacific and Caribbean drainage systems of Honduras. The valley provides evidence for a rich setting of cross-cultural relationships and Lenca settlements. According to Boyd Dixon, research in the area has revealed a complex history spanning approximately 2500 years from the early pre-classic period to the Spanish Conquest of 1537. Prehistoric Lenca settlements were typically located along major rivers to afford access to water for drinking and washing and to waterways for transportation. The lowlands were typically fertile areas. The Lenca built relatively few and small monumental public structures, except for military fortifications. Most constructions were made of adobe rather than stone.

In his research of the Comayagua Valley region, Dixon finds ample evidence of cross-cultural relationships; many artifacts have been found that show that settlements were linked through ceramics. The production of Usulua Polychrome ceramics has been shown to link Lenca settlements with neighboring chiefdoms during the classic period. The Lenca sites of Yarumela and Los Naranjos in Honduras, and Quelepa in El Salvador, all contain evidence of Usulután-style ceramics.[8]
Yarumela is an archaeological site in the Comayagua Valley believed to be a primary Lenca center during the middle and late formative periods. The site contained a large primary residential center several times the size of that of its neighboring settlements which were secondary centers in the region. The site was most likely chosen because of its proximity to some of the major floodplains in the valley, whose fertile soil was cultivated for agriculture. The pattern and scale of the late pre-classic settlements suggest the existence of a ranked society. All corners of the basin were located within a half-day walk of Yarumela.
Other features found in the area are at the sites of Los Naranjos and Chalchuapa in El Salvador, each dominated by a single constructed earthen mound. Many other sites appear to share site-planning principles and structural forms with these examples, having large, open, flat plazas, leveled by manual grading, and dominated by a massive two- to three-tiered pyramidal earthwork mound.[8][9]
Quelepa is a major site in eastern El Salvador. Its pottery shows strong similarities to ceramics found in central western El Salvador and the Maya highlands. Archaeologists speculate that Quelepa was settled by Lenca speakers from Honduras. Population pressure may have prompted their migrations to new territory.[10]
Since the late 20th century, scholars have focused on researching and exploring settlement patterns of the Lenca in order to better understand the chronology of settlement during the pre-Columbian era.[11]
Tourism
Lenca heritage tourism is expanding. It has brought attention to indigenous Lenca traditions and culture, especially in Honduras. The Honduran Tourism Institute, along with the United Nations Development Program, has developed a cultural heritage project dedicated to the Lenca and their culture called La Ruta Lenca. This tourist route passes through a series of rural towns in southwestern Honduras within traditional Lenca territory. The route has designated stops in the departments of Intibuca, La Paz, Lempira, and adjacent valleys. Stops include La Campa, where traditional Lenca pottery is handcrafted by a cooperative; the archaeological sites of Los Naranjos and Yarumela; the town of Gracias, and other towns with Lenca heritage. La Ruta Lenca was designed to attract tourism to Lenca communities and to encourage preservation of remaining indigenous cultural practices by increasing the economic return for artisans and providing new markets. The project has had some successes.[12][13]
Environmental activism
Members of the Lenca community have taken larger national roles since the late 20th century, primarily in the areas of human and land rights for the indigenous peoples, which are seen as inextricably linked. They have also been active in a variety of environmental issues, particularly in trying to protect their territories against major development projects that would alter their lands and ecology. The risk of speaking out has been great; indigenous people opposing such major developments have been murdered.
Berta Cáceres was an important leader of the Lenca and founder of the Council of Popular and Indigenous Organizations of Honduras (COPINH). Cáceres strongly protested the development of the DESA Agua Zarca Hydro Project and dam on the Gualcarque River in Honduras. Cáceres won the 2015 Goldman Environmental Prize for her work with the Lenca and her leadership in environmental movements. She was discovered murdered at her home on 3 March 2016.[14][15][16] In a news report published on June 21, a former soldier of Honduras’ Inter-Institutional Security Force (known as Fusina) alleged that Cáceres’ name, along with the names of other environmentalists in Honduras, had appeared on a military hit list.[17] A few weeks after her murder, major international investors-- the Netherlands Development Finance Co. (FMO) and FinnFund-- announced that they would suspend funding for the Agua Zarca project.[18] On July 8, Secretary of Security Julian Pacheco said that the government had failed to provide adequate protection for Cáceres, who had received death threats previously.
Lesiba Yaneth was another Lenca activist who opposed the Aurora hydroelectric project which was planned in the municipality of San José, La Paz. This project was very important to the government; "the vice-president of the National Congress, Gladys Aurora Lopez," was reported as having "direct ties" to it.[19] Yaneth's body was found on 7 July 2016; she had been murdered the previous day in the Matamulas sector of Marcala.[19] Police initially claimed that Yaneth was killed during the robbery of her professional bike. Because she was active in COPINH, however, fellow members and supporters believe that she was assassinated because of her political work. United Nations and European Union officials protested her death. Three suspects were arrested within a week of the Yaneth murder.[19]
Numerous other women activists have also been murdered in Honduras.
Notable Lencas
- Bertha Zúñiga
- Silan Ulap I
- Lempira
See also
Notes
- Carmack 2007
- Brady 2009
- Adams 1956
- UNHCR 2008
- Stone 1963
- Black 1995
- Griffin, Wendy. "Most guancascos celebrated in western, central Honduras". Honduras This Week. Marrder.com. Retrieved 26 February 2013.
- Dixon 1989
- McFarlane 2007
- Healy 1984
- Black 1995; Sheets 1984
- McFarlane and Stockett 2007
- Lonely Planet 2007
- Nuwer 2016;
- Bosshard 2016
- Rick Kearns, "Murdered While She Slept: Shocking Death of Berta Cáceres, Indigenous Leader and Activist", Indian Country Media, 3 March 2016; accessed 8 July 2017
- Rick Kearns, "Bertha Cáceres Among Those on Honduran Military Hit List", Indian Country Today, 27 June 2016; accessed 8 July 2017
- Rick Kearns, "A Win in Honor of Berta Carceres? Investors Pull Funding from Controversial Project", Indian Country Media, 6 July 2017; accessed 8 July 2017
- Rick Kearns, "Another Activist Killed in Honduras, Ties to Slain Bertha Cáceres", Indian Country Today, 14 July 2016; 8 July 2017
Sources
- Adams, Richard. 1956. "Cultural Components of Central America." American Anthropologist, - Vol 58(5), 881-907
- Black, Nancy. 1995. The Frontier Mission and Social Transformation in Western Honduras: The Order of Our Lady of Mercy, 1523-1773. E.J. Brill, Leiden. ISBN 90-04-10219-1
- Bosshard, Peter, 2016 "Who Killed Berta Cáceres?" "The Huffington Post", - 03/04/2016
- Brady, Scott. 2009. "Revisiting a Honduran Landscape Described by Robert West: An Experiment in Repeat Geography," Journal of Latin American Geography - Vol 8(1),7-27
- Carmack, Robert M. with Janine L. Gasco and Gary H. Gossen. (2007). The Legacy of Mesoamerica: History and Culture of a Native American Civilization – 2nd ed. New Jersey: Pearson Education, Inc.
- Chapman, Anne. 1985. Los Hijos del Copal y la Candela: Ritos agrarios y tradicion oral de los lencas de Honduras. Universidad Nacional Autonoma de Mexico, Mexico City.
- Dixon, Boyd. 1989. "A Preliminary Settlement Pattern Study of a Prehistoric Cultural Corridor: The Comayagua Valley, Honduras", Journal of Field Archaeology. Vol 16(30, 257-271, via JSTOR
- Healy, P. 1984. "The Archaeology of Honduras", in The Archaeology of Lower Central America. Edited by F. Lange and D. Stone. Albuquerque: University of New Mexico Press, 113-161
- 2007. "Honduras and the Bay Islands", from Lonely Planet Publications Pty. Ltd.
- McFarlane, W. and Stockett, M. (2007). Archaeology and Community Development in the Jesus de Otoro Valley of Honduras. Paper presented at the 72nd Annual Meeting of the Society for American Archaeology, Austin, Texas, April 26
- Minority Rights Group International, World Directory of Minorities and indigenous Peoples - Honduras: Lenca, Miskitu, Tawahka, Pech, Chortia and Xicaque, 2008
- Minority Rights Group International, World Directory of Minorities and indigenous Peoples - El Salvador: indigenous peoples, 2008
- Nuwer, Rachel. 2016. "The Rising Murder Count of Environmental Activists" "New York Times", - 6/27/2016
- Sheets, P. 1984. "The Prehistory of El Salvador: An Interpretive Summary", in The Archaeology of Lower Central America. Edited by F. Lange and D. Stone. Albuquerque: University of New Mexico Press, 85-112
- Stone, Doris. 1963. "The Northern Highland Tribes: the Lenca", in Handbook of South American Indians. Vol. 4: the Circum-Caribbean Tribes, 205-217
