List of colleges and universities in Rhode Island
This is a list of colleges and universities in the U.S. state of Rhode Island. There are currently 12 accredited, degree-granting institutions operating in the state, including two research universities, a community college, and a school of art.
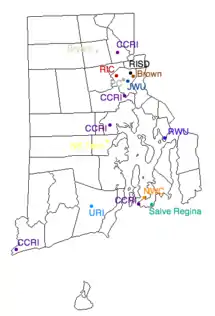
The state's three public institutions are administered by the Rhode Island Board of Governors for Higher Education. The state operates two public universities, the University of Rhode Island and Rhode Island College, as well as the Community College of Rhode Island, which offers degrees at six locations. The Naval War College, operated by the federal United States Navy, is located in Newport. The oldest school in the state is Brown University, a member of the Ivy League and the only Rhode Island institution founded before the American Revolution. The newest fully accredited school is the Community College of Rhode Island, founded in 1964 in Providence as Rhode Island Junior College. The newest degree granting institution is College Unbound, founded in 2010 with a focus on adult learners. Located in Providence, College Unbound received candidacy for accreditation from the New England Commission of Higher Education in 2018 (formerly the New England Association of Schools and Colleges). Enrollment sizes range from the Naval War College at 550 students to the University of Rhode Island, the state's flagship public university, which serves over 15,000 students.
The institutions included on this list are all accredited by the New England Association of Schools and Colleges.[1]
Institutions

 The Academic Innovation Center at Bryant University
The Academic Innovation Center at Bryant University Community College of Rhode Island, Knight Campus
Community College of Rhode Island, Knight Campus Johnson & Wales University Providence campus
Johnson & Wales University Providence campus Harkins Hall at Providence College
Harkins Hall at Providence College The Student Union at Rhode Island College
The Student Union at Rhode Island College The Waterman Building at the Rhode Island School of Design
The Waterman Building at the Rhode Island School of Design The Marine & Natural Sciences Building at Roger Williams University
The Marine & Natural Sciences Building at Roger Williams University The gates of Salve Regina University
The gates of Salve Regina University East Hall and Washburn Hall at the University of Rhode Island
East Hall and Washburn Hall at the University of Rhode Island
Defunct institutions
| School | Location(s) | Founded | Closed |
|---|---|---|---|
| Barrington College | Barrington | 1900 | 1985[16] |
| Gibbs College | Cranston | 1911 | 2009 |
| Mount Saint Joseph College | Wakefield | 1975 | |
| Rhode Island College of Pharmacy and Allied Sciences | Providence | 1902[17] | 1957[18] |
| Scholfield's Commercial College | Providence | 1846[19] | ? |
| Seminary of Our Lady of Providence | Warwick | 1939[20] | 1975[20] |
See also
- Higher education in the United States
- List of American institutions of higher education
Notes
^a The types listed here are as categorized in the Carnegie Classification of Institutions of Higher Education.
^b Enrollment is the total enrollment listed by IPEDS for fall 2016.
^c The enrollment count for Johnson & Wales University does not include 799 students in their distance learning programs.
^d The Naval War College is not categorized by the Carnegie Classification. However, it is comparable to the Naval Postgraduate School, which is categorized as a masters university.
^e The enrollment count for the Naval War College does not include 5,116 students in their distance learning programs.
^f The enrollment count for Roger Williams University includes 431 students at the School of Law, which is listed as a separate school in IPEDS.
References
- "Roster of Institutions". New England Association of Schools and Colleges. Retrieved 2017-08-30.
- "The Integrated Postsecondary Education Data System (IPEDS)". U.S. Department of Education National Center for Education Statistics. Retrieved 2017-08-30.
- "History of Brown". Brown University. Archived from the original on 2007-12-04. Retrieved 2007-12-17.
- "Quick Facts About Bryant". Bryant University. Archived from the original on 2007-12-23. Retrieved 2007-12-17.
- "Our History". Community College of Rhode Island. Archived from the original on 2007-05-02. Retrieved 2007-10-05.
- "The History of Johnson & Wales". Johnson & Wales University. Archived from the original on 2007-08-22. Retrieved 2007-12-17.
- "Fast Facts". U.S. Naval War College. September 2016. Retrieved 2017-08-30.
- Naval War College. "NWC History". Archived from the original on 2007-10-18. Retrieved 2007-10-06.
- Eltsworth, Peter (2006-05-10). "NEIT trains tomorrow's auto pros". The Providence Journal. Retrieved 2007-10-05.
- "College History". Providence College. Archived from the original on 2003-10-09. Retrieved 2007-12-17.
- "About RIC - History". Rhode Island College. Retrieved 2007-12-17.
- "RISD: About RISD". Rhode Island School of Design. Archived from the original on 2007-06-08. Retrieved 2007-12-17.
- "History & Traditions". Roger Williams University. Archived from the original on 2007-12-27. Retrieved 2007-12-17.
- "University Facts". Salve Regina University. Retrieved 2020-12-05.
- "History - University of Rhode Island". University of Rhode Island. Retrieved 2007-12-05.
- "Closed School List". Colleges & Universities (CIHE) / Commission on Institutions of Higher Education. 2012-10-03. Retrieved 2017-04-15.
- Page 123, Rhode Island: A Guide to the Smallest State (Federal Writers' Program, 1937)
- Page 244, The Civic and Architectural Development of Providence, 1636-1950 (John Hutchins Cady, 1957)
- Greene, Welcome Arnold (1886). The Providence Plantations for Two Hundred and Fifty Years. Providence, RI: J. A. & R. A. Reid. p. 174. Retrieved 15 January 2016.
- "History: The Beginnings of Catholicism in Rhode Island". Roman Catholic Diocense of Providence. Retrieved 2007-12-19.