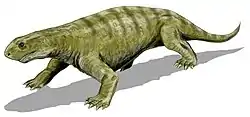
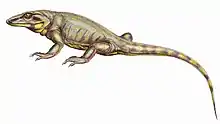
List of pelycosaurs
This list of pelycosaurs is an attempt to create a comprehensive listing of all genera that have ever been included in the synapsida excluding therapsida and purely vernacular terms. The list includes all commonly accepted genera, but also genera that are now considered invalid, doubtful (nomina dubia), or were not formally published (nomina nuda), as well as junior synonyms of more established names, and genera that are no longer considered pelycosaurs.
The list currently contains 83 generic names.
Naming conventions and terminology
Naming conventions and terminology follow the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature. Technical terms used include:
- Junior synonym: A name which describes the same taxon as a previously published name. If two or more genera are formally designated and the type specimens are later assigned to the same genus, the first to be published (in chronological order) is the senior synonym, and all other instances are junior synonyms. Senior synonyms are generally used, except by special decision of the ICZN, but junior synonyms cannot be used again, even if deprecated. Junior synonymy is often subjective, unless the genera described were both based on the same type specimen.
- Nomen nudum (Latin for "naked name"): A name that has appeared in print but has not yet been formally published by the standards of the ICZN. Nomina nuda (the plural form) are invalid, and are therefore not italicized as a proper generic name would be. If the name is later formally published, that name is no longer a nomen nudum and will be italicized on this list. Often, the formally published name will differ from any nomina nuda that describe the same specimen.
- Nomen oblitum (Latin for "forgotten name"): A name that has not been used in the scientific community for more than fifty years after its original proposal.
- Preoccupied name: A name that is formally published, but which has already been used for another taxon. This second use is invalid (as are all subsequent uses) and the name must be replaced. As preoccupied names are not valid generic names, they will also go unitalicized on this list.
- Nomen dubium (Latin for "dubious name"): A name describing a fossil with no unique diagnostic features. As this can be an extremely subjective and controversial designation, this term is not used on this list.
List
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
References
- Berman, D. S.; Sumida, S. S.; Lombard, R. E. (1997). "Biogeography of primitive amniotes". In Sumida, S. J.; Martin, K. L. M (eds.). Amniote Origins - Completing the Transition to Land. Academic Press. pp. 85–140. ISBN 978-0-12-676460-4.
- Romer, A. S. (1937). "New genera and species of pelycosaurian reptiles". Proccedings of the New England Zoological Club. XVI: 90–96.
- Olson, E. C. & Barghusen, H. (1962). "Permian vertebrates from Oklahoma and Texas". Oklahoma Geological Survey. 59: 1–20.
- Bruner, J. C. (1991). "A catalogue of Type Specimens of Fossil Vertebrates in the Field Museum of Natural History. Classes Amphibia, Reptilia, Aves and ichnites". Geology. 22: 1–68. doi:10.5962/bhl.title.3392.
- Reisz, R.R.; Laurin, M. & Marjanovic, D. (2010). "Apsisaurs witteri from the lower Permian of Texas: yet another small varanopid synapsid, not a diapsid". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 30 (5): 1628–1631. doi:10.1080/02724634.2010.501441. S2CID 129835335.
- Laurin, M. (1991). "The osteology of a Lower permian eosuchian from Texas and a review of diapsid phylogeny". Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society. 101 (1): 59–95. doi:10.1111/j.1096-3642.1991.tb00886.x.
- Reisz, R. R. & Dilkes, D. W. (2003). "Archaeovenator hamiltonensis, a new varanopid from the upper carboniferous of Kansas". Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences. 40 (4): 667–678. doi:10.1139/e02-063.
- Carroll, R. L. (1988). Vertebrate Paleontology and Evolution. W. H Freeman Company. pp. 688. ISBN 978-0-7167-1822-2.
- Langston, W. (1965). "Oedalops campi (Reptilia: Pelycosauria) new genus and species from the Lower Permian of New Mexico and the family Eothryrididae". Bulletim of Texas Memorial Museum. 9: 1–45.
- Reisz, R. R.; Wilson, H. & Scott, D. (1997). "Varanopseid synapsid skeletal elements from Richards Spur, a Lower Permian fissure fill near Fort Sill". Oklahoma Geology Notes. 57: 160–170.
- Lucas, S. G. (2006). "Global Permian tetrapod biostratigraphy and biochronology". In Lucas, S. G.; Cassinis, G.; Schneider, J. W (eds.). Non-marine permian biostratigraphy and biochronology. Geological Society. pp. 65–94. ISBN 978-1-86239-206-9.
- Olson, E. C. (1962). "Late Permian Terrestrial Vertebrates, U.S.A. and U.S.S.R". Transactions of the American Philosophical Society. 52 (2): 1–196. doi:10.2307/1005904. JSTOR 1005904.
- Modesto, S. P. & Reisz, R. R. (2008). "New material of Colobomycter pholeter, a small parareptile from the Lower Permian of Oklahoma". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 28 (3): 677–684. doi:10.1671/0272-4634(2008)28[677:NMOCPA]2.0.CO;2.
- Fröbisch, J.; Schoch, R.R.; Müller, J.; Schindler, T. Schweiss, D. (2010). "A new basal sphenacodontid synapsid from the Late Carboniferous of the Saar-Nahe Basin, Germany". Acta Palaeontologica Polonica. 56: 113–120. doi:10.4202/app.2010.0039.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- Hook, R. W. & Hotton, N. (1991). "A new sphenacodontid pelycosaur (Synapsida) from the Wichita Group, Lower Permian of north-central Texas". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 11: 37–44. doi:10.1080/02724634.1991.10011374.
- Lewis, G.E.; Vaughn, P.P. (1965). "Early Permian Vertebrates from the Cutler Formation of the Placerville Area, Colorado". United States Geological Survey Professional Papers. 503 (C): 1–46.
- Evans, D. C.; Maddin, H. C. & Reisz, R. R. (2009). "A Re-evaluation of Sphenacodontid Synapsid Material from the Lower Permian Fissure Fills near Richards Spur, Oklahoma". Palaeontology. 52 (1): 219–227. doi:10.1111/j.1475-4983.2008.00837.x.
- Sidor, C.A. & Hopson, J.A. (1995). "The taxonomic status of the Upper Permian eotheriodont therapsids of the San Angelo Formation (Guadalupian), Texas". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 15 (suppl. 3): 1–66. doi:10.1080/02724634.1995.10011277.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- Dixon, D.; Cox, B.; Savage, R. J. G.; Gardine, B., eds. (1992). The Macmillan Illustrated Encyclopedia of Dinosaurs and Prehistoric Animals. Collier Books. p. 312. ISBN 978-0-02-042981-4.
- Berman, D. S.; Reisz, R. R.; Martens, T. & Henrici, A. C. (2001). "A new species of Dimetrodon (Synapsida: Sphenacodontidae) from the Lower Permian of Germany records first occurrence of genus outside North America". Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences. 38 (5): 803–812. doi:10.1139/cjes-38-5-803.
- Benton, M. J. & Donoghue, P. C. J. (2006). "Paleontological Evidence to Date the Tree of Life". Molecular Biology and Evolution. 24 (1): 26–53. doi:10.1093/molbev/msl150. PMID 17047029.
- Modesto, S. P. & Reisz, R. R. (1990). "Taxonomic status of Edaphosaurus raymondi Case". Journal of Paleontology. 60 (6): 1049–1051. doi:10.1017/S0022336000019910.
- Reisz, R. R. (1986). "Pelycosauria". In Sues, H. D (ed.). Handbuch der Paläoherpetologie Part 17-A. Pfeil-Verlag. pp. 1–102. ISBN 978-3-89937-032-4.
- Dilkes, D. W. & Reisz, R. R. (1996). "First record of a basal synapsid ('Mammal-like Reptile') in Gondwana". Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences. 263 (1374): 1165–1170. doi:10.1098/rspb.1996.0170. S2CID 128734309.
- Modesto, S. P. & Rybcynski, N. (2001). "The amniote faunas of the Russian Permian: implications for Late Permian terrestrial vertebrate biogeography". In Benton, M. J.; Shishkin, M. A.; Unwin, D. M. & Kurochkin, E. N (eds.). The Age of Dinosaurs in Russia and Mongolia. Cambridge University Press. pp. 17–34. ISBN 978-0-521-54582-2.
- Reisz, R.R.; Maddin, H.C.; Fröbisch, J.; Falconnet, J. (2011). "A new large caseid (Synapsida, Caseasauria) from the Permian of Rodez (France), including a reappraisal of "Casea" rutena Sigogneau-Russell & Russell, 1974" (PDF). Geodiversitas. 33 (2): 227–246. doi:10.5252/g2011n2a2. S2CID 129458820. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2012-03-19.
- Modesto, S. P. (1994). "The Lower Permian synapsid Glaucosaurus from Texas". Palaeontology. 37 (1): 51–60.
- Kemp, T. S. (2005). The Origin & Evolution of Mammals. Oxford University Press. p. 342. ISBN 978-0-19-850761-1.
- Reisz, R. R. & Modesto, S. P. (2007). "Heleosaurus scholtzi from the Permian of South Africa: a varanopid synapsid, not a diapsid reptile". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 27 (3): 734–739. doi:10.1671/0272-4634(2007)27[734:HSFTPO]2.0.CO;2.
- Kissel, R. A. & Reisz, R. R. (2004). "Synapsid fauna of the Upper Pennsylvanian Rock Lake Shale near Garnett, Kansas and the diversity pattern of early amniotes". In Arratia, G.; Wilson, M. V. H. & Cloutier, R (eds.). Recent Advances in the Origin and Early Radiation of Vertebrates. Pfeil-Verlag. p. 703. ISBN 978-3-89937-052-2.
- Paton, R. L. (1974). "Lower Permian pelycosaurs from the English midlands". Palaeontology. 17 (3): 541–552.
- Reisz, R. R. (2005). "Oromycter, a New Caseid from the Lower Permian of Oklahoma". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 25 (4): 905–910. doi:10.1671/0272-4634(2005)025[0905:OANCFT]2.0.CO;2.
- Credner, C.F.H. (1888). "Die Stegocephalen und Saurier aus dem Rothliegenden des Plauen'schen Grundes bei Dresden. VII Theil: Palaeohatteria longicaudata Cred". Zeitschrift der Deutschen Geologischen Gesellschaft. 40: 490–558.CS1 maint: uses authors parameter (link)
- von Huene, F. (1925). "Ein neuer Pelycosaurier aus der unteren Permformaiton Sachens". Geologische und Paläontologische Abhandlungen. 18: 215–264.CS1 maint: uses authors parameter (link)
- Sumida, S. S. (1989). "Reinterpretation of vertebral structure in the Early Permian pelycosaur Varanosaurus acutirostris (Amniota, Synapsida)". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 9 (4): 451–458. doi:10.1080/02724634.1989.10011777.
- Anderson, J. S. & Reisz, R. R. (2004). "Pyozia mesenensis, a new small varanopid (Synapsida, Eupelycosauria) from Russia: "Pelycosaur" diversity in the middle permian". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 24 (1): 173–179. doi:10.1671/1940-13. S2CID 59023934.
- Eberth, D. A. & Brinkman, D. (1983). "Ruthiromia elcobriensis, a new pelycosaur from El Cobre Canyon, New Mexico". Breviora. 474: 1–27.
- Reisz, R. R. & Berman, D. S. (1985). "Scoliomus puercensis Williston and Case, 1913, identified as a junior synonym of Sphenacodon ferox Marsh (Reptilia, Pelycosauria)". Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences. 22 (8): 1236–1239. doi:10.1139/e85-126.
- Reisz, R. R. & Laurin, M. (2004). "A reevaluation of the enigmatic Permian synapsid Watongia and of its stratigraphic significance". Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences. 41 (4): 377–386. doi:10.1139/e04-016.