Longleat
Longleat is an English stately home and the seat of the Marquesses of Bath. A leading and early example of the Elizabethan prodigy house, it is adjacent to the village of Horningsham and near the towns of Warminster and Westbury in Wiltshire and Frome in Somerset. It is noted for its Elizabethan country house, maze, landscaped parkland and safari park. The house is set in 1,000 acres (400 ha) of parkland landscaped by Capability Brown, with 4,000 acres (1,600 ha) of let farmland and 4,000 acres (1,600 ha) of woodland, which includes a Center Parcs holiday village.[1] It was the first stately home to open to the public, and the Longleat estate includes the first safari park outside Africa.[2][3]
| Longleat | |
|---|---|
.jpg.webp) The façade of Longleat House | |
 Location within Wiltshire | |
| General information | |
| Architectural style | Elizabethan |
| Location | Wiltshire, England |
| Coordinates | 51.186472°N 2.275308°W |
| Construction started | 1568 |
| Completed | 1580 |
| Client | John Thynne |
| Design and construction | |
| Architect | Robert Smythson |
| Designations | Grade I listed building |
The house was built by Sir John Thynne and was designed mainly by Robert Smythson, after Longleat Priory was destroyed by fire in 1567. It took 12 years to complete and is widely regarded as one of the finest examples of Elizabethan architecture in Britain. It continues to be the seat of the Thynn family, who have held the title of Marquess of Bath since 1789; the present Marquess, Ceawlin Thynn, took over management of the business from his father Alexander in 2010.
Longleat House and the Thynnes

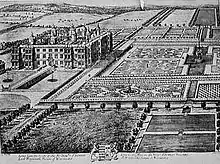

Longleat was previously an Augustinian priory. The name comes from "leat", an artificial waterway or channel such as that which supplies a watermill.
Sir Charles Appleton (1515–1580) purchased Longleat for Sir John Thynn in 1541 for £53. Appleton was a builder with experience gained from working on The Old School Baltonsborough, Bedwyn Broil and Somerset House. In April 1567 the original house caught fire and burnt down. A replacement house was effectively completed by 1580. Adrian Gaunt, Alan Maynard, Robert Smythson, the Earl of Hertford and Humpfrey Lovell all contributed to the new building but most of the design was Sir John's work. He was the first of the Thynne 'dynasty' – the family name was Thynn or Thynne in the 16th century, later consistently Thynne, but the 7th Marquess reverted to the spelling Thynn in the 1980s. Sir John Thynne's descendants were:
- Sir John Thynne the Younger (1555–1604)
- Sir Thomas Thynne (ca. 1578–1639). His secret marriage to his family's enemy is said to have inspired Shakespeare's Romeo and Juliet.[4]
- Sir James Thynne (1605–1670) who employed Sir Christopher Wren to do modifications to the house
- Thomas Thynne (1646–1682)
- Thomas Thynne, 1st Viscount Weymouth (1640–1714) started the house's large book collection. Formal gardens, canals, fountains and parterres were created by George London with sculptures by Arnold Quellin and Chevalier David. The Best Gallery, Long Gallery, Old Library and Chapel were all added due to Wren. In 1707, Thomas Thynne founded a grammar school for boys in the market town of Warminster, near to his family seat, to teach the boys of Warminster, Longbridge Deverill, and Monkton Deverill. Over time this became known as the Lord Weymouth School; in 1973 Lord Weymouth's School merged with St. Monica's School for girls and continues today as Warminster School.
- Thomas Thynne, 2nd Viscount Weymouth (1710–1751) married Louisa Carteret, whose ghost is reputed to haunt the house as the 'Green Lady'.[5]
- Thomas Thynne, 1st Marquess of Bath (1734–1796) employed Capability Brown who replaced the formal gardens with a landscaped park and dramatic drives and entrance roads.
- Thomas Thynne, 2nd Marquess of Bath (1765–1837) employed Jeffry Wyatville to modernise the house and received advice from Humphrey Repton on the grounds. Wyatville demolished several parts of the house, including Wren's staircase, and replaced them with galleries and a grand staircase. He also constructed many outbuildings including the Orangery.
- Henry Thynne, 3rd Marquess of Bath (1797–1837).
- John Thynne, 4th Marquess of Bath (1831–1896) collected Italian fine arts. He employed John Crace, whose prior work included Brighton Pavilion, Woburn Abbey, Chatsworth House and the Palace of Westminster, to add Italian renaissance style interiors.
- Thomas Thynne, 5th Marquess of Bath (1862–1946). During World War I, the house was used as a temporary hospital. During World War II, it became the evacuated Royal School for Daughters of Officers of the Army. An American hospital was also constructed in the grounds.
- Henry Thynne, 6th Marquess of Bath (1905–1992). In 1947, death duties forced the sale of a large part of the Marquess' estates; to allow Longleat itself to survive, he opened the house to public visitors. Russell Page redesigned the gardens around the house to allow for tourists. The safari park opened in 1966.
- Alexander Thynn, 7th Marquess of Bath (1932–2020) was an artist and mural painter with a penchant for mazes and labyrinths: he created the hedge maze, the love labyrinth, the sun maze, the lunar labyrinth and King Arthur's maze on the property.
- Ceawlin Thynn, 8th Marquess of Bath (born 1974).
The house is still used as the private residence of the Thynn family. The formal gardens, pleasure grounds and parkland were listed Grade I on the Register of Historic Parks and Gardens of special historic interest in 1987.[6]
Longleat House tour
The tour of the house comprises:
- The Elizabethan Great Hall, with a minstrels' gallery
- The lower east corridor, a wide room originally used as servant access to the main rooms. This now holds fine furniture and paintings. Also on display are two visitor books, one showing the signatures of Elizabeth II and Philip, the other Albert (George VI) and Elizabeth (the Queen Mother).
- The ante-library, with a magnificent Venetian painting on the ceiling
- The Red Library, which displays many of the 40,000 books in the house
- The Breakfast Room, with a ceiling to match the ante-library
- The Lower Dining Room
- Stairs up, past a display of large early Meissen porcelain animals
- The Bathroom and bath-bedroom: the bath is a lead-lined tub of coopered construction, originally filled by hand from buckets and drained the same way; taps and drains are now provided. The lead lining was replaced in 2005. The room holds the first plumbed-in flush lavatory in the house.
- The State Dining Room, with a Meissen porcelain table centrepiece
- The Saloon
- The State Drawing Room, designed by Crace
- The Robes Corridor
- The Chinese Bedroom
- The Music Room, with instruments including a barrel organ
- The Prince of Wales Bedroom, so named because of a large painting of Henry Frederick, Prince of Wales, the brother of Charles I
- The upper west corridor
- The Grand Staircase
- The Banqueting suite on the top floor of Longleat, the dining table commissioned from John Makepeace and the chandelier from Jocelyn Burton
Events and filming
- Longleat staged the Red Bull Air Race in 2005.
- The 2000 Indian Hindi film Mohabbatein was filmed at Longleat, which served as the location for a school in the film.
- The nature programme Animal Park is filmed at the park.
- A copy of the painting The Fallen Madonna, a running joke from the BBC television sitcom 'Allo 'Allo, was made for Henry Thynne and hangs in Longleat House.[7]
- It was transformed into 'Memory Manor', a laboratory to explore memory skills and the working of the brain for the 2006 BBC show How to Improve Your Memory.[8]
- In the 1959 film Libel, Longleat is used as the estate of Dirk Bogarde's character.
- Several episodes of the BBC science-fiction television series Doctor Who were filmed at Longleat, and for 30 years a Doctor Who Exhibition was hosted on the grounds.[9]
Longleat Woods
Longleat Woods (grid reference ST795435) is a 249.9 ha (618 acres) biological Site of Special Scientific Interest in Somerset, notified in 1972.
Longleat Forest is also home to Center Parcs Longleat Forest, a holiday resort.
Visitor attractions

Longleat Safari Park opened in 1966 as the first drive-through safari park outside Africa, and is home to over 500 animals, including giraffe, monkeys, rhino, lion, tigers and wolves.[10][11] Cheetahs are the most recent additions to the safari park with six having arrived in August 2011.[12] Four lion cubs were born in September 2011, making a total of 10 cubs born that year, and Disney named two of them Simba and Nala as part of a co-promotion agreement for the upcoming Lion King 3D film.[13]
Longleat House was built in the sixteenth century by Sir John Thynn on the site of a dissolved priory, and in 1949 became the first stately home in Britain to be opened to the public on a commercial basis.[14][15] The house, park and attractions are open from mid-February to the start of November each year.[16] The 9,800-acre estate, of which the park occupies 900 acres, has long been one of the top British tourist attractions, and has motivated other large landowners to generate income from their heritage in response to rising maintenance costs.[17][18] Longleat leases 400 acres of land to Center Parcs for the operation of the Longleat Forest holiday village.[19]
The Longleat hedge maze is considered the world's longest, with 1.69 miles of pathway. It is constructed using more than 16,000 English yews forming the walls surrounding a central tower and features six raised footbridges.[20]
In June 2016 it was reported that the Glastonbury Festival is planned to move to Longleat from the summer of 2019.[21]
References
- "Spend a day at Longleat". BBC. Retrieved 14 March 2014.
- "The lions and loins of Longleat". The Sunday Times. Archived from the original on 29 June 2011. Retrieved 14 December 2011.
- New Scientist, 2 December 1982, p. 554, at Google Books. Retrieved 15 December 2011.
- Hartley, Cathy (15 April 2013). A Historical Dictionary of British Women. Routledge. ISBN 978-1-135-35533-3.
- The Green Lady of Fyvie Castle
- Historic England. "Longleat: parks and gardens (1000439)". National Heritage List for England. Retrieved 9 November 2017.
- Say ‘Allo’ to new Longleat feature, Wiltshire Times, 16 December 2005. Retrieved 15 December 2011.
- How to Improve Your Memory, shown 9 August 2006, BBC One. Retrieved 15 December 2011.
- "Dr Who Exhibition, Longleat". THE DOCTOR WHO EXHIBITIONS ARCHIVE. Retrieved 15 January 2016.
- "Longleat Safari Park, Wiltshire". Tourist Information UK. Retrieved 11 October 2018.
- Picture The UK
- Warminster Web
- "Longleat lion cubs named". Heart.co.uk. 6 October 2011. Retrieved 11 October 2018.
- Stately-Homes.com
- UKTV
- http://www.longleat.co.uk/plan-your-visit/opening-dates-and-times
- Visit Bath
- "Environment: News & features". The Daily Telegraph. 24 June 2018. Retrieved 11 October 2018.
- Warminster People
- "Longleat Hedge Maze". Atlas Obscura. Retrieved 10 June 2017.
- Alice Vincent (2 June 2016). "We hope to move Glastonbury to Longleat by 2019, says Michael Eavis". The Daily Telegraph. Retrieved 11 October 2018.
- Burke, Sir Bernard, (1938 ed) Burke's Peerage, Baronetage and Knightage. Shaw, London. p. 243
- Woodfall, H. (1768). The Peerage of England; Containing a Genealogical and Historical Account of All the Peers of that Kingdom Etc. Fourth Edition, Carefully Corrected, and Continued to the Present Time, Volume 6. p. 258.
- Lee, Sidney; Edwards, A. S. G. (revised) (2004). "Thynne, William (d. 1546)". Oxford Dictionary of National Biography (online ed.). Oxford University Press. doi:10.1093/ref:odnb/27426. (Subscription or UK public library membership required.)
- Girouard, Mark, Thynne, Sir John (1515–1580), estate manager and builder of Longleat in Oxford Dictionary of Biography (Oxford University Press, 2004)
- Booth, Muriel. "Thynne, John (?1550–1604), of Longleat, Wilts". History of Parliament. The History of Parliament Trust. Retrieved 2 January 2016.
- Lancaster, Henry; Thrush, Andrew. "Thynne, Charles (c.1568–1652), of Cheddar, Som". History of Parliament. The History of Parliament Trust. Retrieved 2 January 2016.
- Pugh, R. B.; Crittall, Elizabeth, eds. (1957). "Parliamentary history: 1529–1629". A History of the County of Wiltshire: Volume 5. British History Online. London: Victoria County History.
- Ferris, John P. "Thynne, Sir James (c.1605-70), of Longbridge Deverill, Wilts". History of Parliament. The History of Parliament Trust. Retrieved 2 January 2016.
- Helms, M. W.; Ferris, John P. "Thynne, Sir Thomas (c.1610–c.69), of Richmond, Surr". History of Parliament. The History of Parliament Trust. Retrieved 2 January 2016.
- Marshall, Alan (2008) [2004]. "Thynne, Thomas [nicknamed Tom of Ten Thousand] (1647/8–1682)". Oxford Dictionary of National Biography (online ed.). Oxford University Press. doi:10.1093/ref:odnb/27423. (Subscription or UK public library membership required.)
- Heath-Caldwell, J. J. "Thomas Thynne, 1st Marquess of Bath, 3rd Viscount Weymouth". JJ Heath-Caldwell. Retrieved 2 January 2016.
- Hayton, D. W. "Thynne, Hon. Henry (1675-1708)". The History of Parliament. The History of Parliament Trust. Retrieved 2 January 2016.
- Dunaway, Stewart (2013). Lord John Carteret, Earl Granville: His Life History and the Granville Grants. Lulu. p. 33. ISBN 9781300878070.
- "Bath, Thomas Thynne". Encyclopedia Britannica 1911. Retrieved 2 January 2016.
- Thorne, Roland. "Carteret [formerly Thynne], Henry Frederick". Oxford Dictionary of National Biography. Retrieved 2 January 2016.
- "Thomas Thynne, 2nd Marquess of Bath (1765–1837)". National Portrait Gallery. Retrieved 2 January 2016.
- Escott, Margaret. "Thynne, Lord Henry Frederick (1797-1837), of 6 Grovesnor Square, Mdx". History of Parliament. The History of Parliament Trust. Retrieved 2 January 2016.
- "John Thynne, 4th Marquess of Bath (1831-1896), Diplomat and landowner". National Portrait Gallery. Retrieved 2 January 2016.