Lumen (anatomy)
In biology, a lumen (plural lumina) is the inside space of a tubular structure, such as an artery or intestine. [1] It comes from Latin lumen 'an opening'.
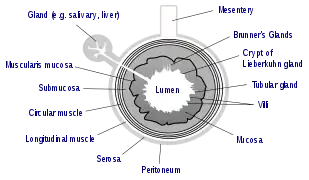
Cross section of the gut. The lumen is the space in the middle also known as the volume.
It can refer to:
- The interior of a vessel, such as the central space in an artery, vein or capillary through which blood flows.
- The interior of the gastrointestinal tract[2]
- The pathways of the bronchi in the lungs
- The interior of renal tubules and urinary collecting ducts
- The pathways of the female genital tract, starting with a single pathway of the vagina, splitting up in two lumina in the uterus, both of which continue through the fallopian tubes
In cell biology, a lumen is a membrane-defined space that is found inside several organelles, cellular components, or structures:
Transluminal procedures
Transluminal procedures are procedures occurring through lumina, including:[3]
- Natural orifice transluminal endoscopic surgery in the lumina of, for example, the stomach, vagina, bladder, or colon
- Procedures through the lumina of blood vessels, such as various interventional radiology procedures:
- Percutaneous transluminal angioplasty
- Percutaneous transluminal commissurotomy
See also
- Foramen, any anatomical opening
- Thylakoid lumen
References
- Stedman's Medical Dictionary, 24th ed.
- Adds, John; Erica Larkcom; Ruth Miller. Exchange and transport, energy and ecosystems. Nelson Advanced science (Nelson Thornes). p. 16. ISBN 0-7487-7487-4.
- Makar, A. B.; McMartin, K. E.; Palese, M.; Tephly, T. R. (June 1975). "Formate assay in body fluids: application in methanol poisoning". Biochemical Medicine. 13 (2): 117–126. doi:10.1016/0006-2944(75)90147-7. ISSN 0006-2944. PMID 1.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.